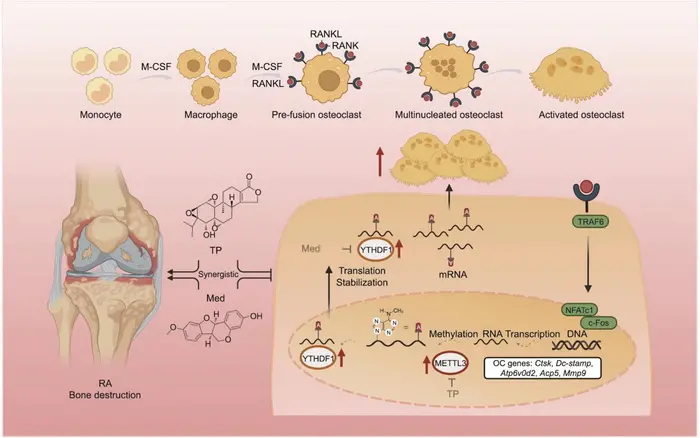
A novel combination therapy has emerged as a beacon of hope for individuals battling rheumatoid arthritis (RA), a debilitating autoimmune disease that causes chronic inflammation and debilitating bone destruction. Recent research published in the esteemed journal Engineering showcases the synergistic potential of triptolide (TP), a potent anti-inflammatory natural compound, and medicarpin (Med), a flavonoid with promising anti-bone resorption properties. Through targeting the m6A methylation pathway, this study underscores a significant advancement in therapeutic strategies against RA, specifically focusing on inhibiting osteoclastogenesis—the process that leads to bone loss.
The devastation caused by rheumatoid arthritis extends beyond mere joint inflammation; it is a progressive disease characterized by the relentless attack on bone tissue. Osteoclasts, the cells responsible for bone resorption, are overactivated in RA, leading to the destruction of bone structures and permanent disability. Currently available treatments, while effective at controlling symptoms, often fall short of preventing or reversing pre-existing joint damage and come with considerable side effects. This gap in effective treatment has propelled researchers to explore combination therapies that can enhance therapeutic efficacy while mitigating toxicity.
.adsslot_hYtD0WQLp1{ width:728px !important; height:90px !important; }
@media (max-width:1199px) { .adsslot_hYtD0WQLp1{ width:468px !important; height:60px !important; } }
@media (max-width:767px) { .adsslot_hYtD0WQLp1{ width:320px !important; height:50px !important; } }
ADVERTISEMENT
Detailed analyses through micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) and histological examinations revealed compelling evidence of the treatment’s efficacy. The combination treatment significantly diminished bone surface-to-volume ratios while increasing overall bone volume in critically impacted joints, such as the ankle and knee. Furthermore, secondary assays, including tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) staining and F-actin ring assays, illustrated a profound reduction in both the number and function of osteoclasts. This finding is crucial as it highlights not only the potential of this combination therapy to inhibit bone resorption but also its applicability to clinical scenarios where RA-induced bone destruction is prevalent.
At the molecular level, the study intricately elucidates the mechanisms by which TP and Med exert their therapeutic effects. The researchers identified that both compounds engage with critical components of the m6A methylation pathway, a cellular mechanism that regulates RNA metabolism and has emerged as an essential player in various biological processes, including osteoclastogenesis. TP targets methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3), which catalyzes the methylation of osteoclast-related mRNAs. Conversely, Med interacts with the YTHDF1 protein, which is responsible for reading and facilitating the translation of these methylated mRNAs. This dual-targeting approach significantly impairs the signaling pathways leading to osteoclast differentiation and activity, marking a pioneering direction in RA treatment.
The validity of these molecular findings was further strengthened through in vitro experiments where primary bone marrow mononuclear cells (BMMs) from mice were utilized. These experiments confirmed that TP and Med inhibited receptor activator of nuclear factor κB ligand (RANKL)-induced osteoclastogenesis in a dose-dependent manner. Moreover, RNA immunoprecipitation assays demonstrated the direct interaction between METTL3 and YTHDF1 with osteoclast-related mRNAs, establishing a clear rationale behind their effectiveness in modulating osteoclast activity.
The overall findings of this groundbreaking study provide a compelling case for the combination of TP and Med as a transformative treatment strategy in rheumatoid arthritis. By effectively targeting the m6A methylation pathway, this therapeutic duo could represent a paradigm shift in the way RA is managed, aiming not only to control symptoms but also to provide long-lasting protection against bone erosion. Furthermore, the potential implications of these findings extend beyond RA, opening up possibilities for similar approaches in other inflammatory and autoimmune diseases characterized by aberrant osteoclast activity.
Future research will undoubtedly need to refine dosing regimens and assess the long-term effects of such combination therapies in larger clinical settings. There is also a critical need to explore the underlying mechanisms in more depth to better understand how these compounds can be optimized for human application. Given the intricate nature of autoimmune diseases, the pursuit of tailored combination therapies offers hope for improved patient outcomes in diseases like RA that have long been challenging to treat satisfactorily.
In conclusion, the integration of triptolide and medicarpin in rheumatoid arthritis therapy illuminates a promising avenue for restoring the delicate balance between inflammation and bone integrity. As the scientific community continues to unravel the complexities of autoimmune diseases, such innovative approaches will undoubtedly usher in new horizons for effective treatment modalities aimed at improving quality of life for those affected.
Subject of Research: Combination Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis
Article Title: Increased Alleviation of Bone Destruction in Individuals with Rheumatoid Arthritis via the Coinhibition of the METTL3 and YTHDF1 Axis by the Combination of Triptolide and Medicarpin
News Publication Date: 13-May-2025
Web References: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2025.03.014
References: Not available
Image Credits: Yi Jiao, Zhaoran Wang, Wenya Diao, Qishun Geng, Xing Wang, Xiaoxue Cao, Tong Shi, Jiahe Xu, Lu Zhao, Zihan Wang, Tiantian Deng, Lei Yang, Tingting Deng, Cheng Xiao
Keywords
Health and medicine
Tags: autoimmune disease research advancementschronic inflammation in rheumatoid arthritiscollagen-induced arthritis modelcombination therapy for RAinnovative approaches to arthritis managementM6A methylation pathwaysmedicarpin bone resorption preventionnatural compounds in RA treatmentosteoclastogenesis inhibition strategiesrheumatoid arthritis treatmenttherapeutic efficacy in arthritistriptolide anti-inflammatory effects