Credit: by Linli Shi, Ying Jiang, Fernando R. Fernandez, Guo Chen, Lu Lan, Heng-ye Man, John A. White, Ji-Xin Cheng, Chen Yang
Neuromodulation at high spatial resolution has been an invaluable approach for treating neurological diseases and advancing fundamental knowledge in the field of neuroscience, as firing of a small population or even single neurons can specifically alter animal behavior or brain state. Optogenetics is a powerful method capable of modulating population neural activity in rodents, yet its requirement for viral transfection limits its applications in nonhuman primates and humans. As a rapidly growing modality, focused ultrasound has been harnessed in a myriad of brain neuromodulation applications. However, conventional piezo-based transducers offer a spatial resolution of several millimeters. It is also challenging to directly measure electrophysiological response of cells under ultrasound stimulation using whole-cell patch-clamp electrophysiology, which is the gold standard technique for high-fidelity analysis of the biophysical mechanisms of neuromodulation. New strategies with essential capabilities, including single and subcellular precision and integration of single cell electrophysiology recording, are still sought to enable the understanding of mechanical stimulation at the single cell level and to offer high precision for potential clinical applications.
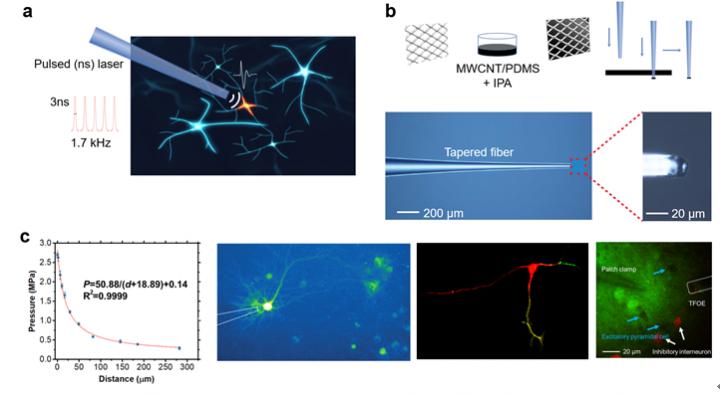
In a new paper published in Light Science & Application, a team of scientists, led by Professors Chen Yang and Ji-xin Cheng from Boston University have developed a tapered fiber optoacoustic emitter (TFOE), which exploits the optoacoustic effect and generates acoustic field localized within 40 μm, for photoacoustic neural stimulation at the single cell and subcellar level. The significant advancement of TFOE in both spatial resolution and optoacoustic conversion efficiency are achieved by fiber engineering, material modification and a new deposition method. Spatially, they demonstrated acoustic stimulation with an unprecedent precision. Temporally, single acoustic pulse with duration of sub-microsecond generated by TFOE successfully activated neurons, which was found as the shortest acoustic stimuli for successful neuromodulation. Importantly, the near field acoustic wave generated by TFOE allowed optoacoustic stimulation with simultaneously monitoring cell response using whole cell patch clamp recording. Their studies revealed cell-type-specific response to acoustic stimulation for excitatory and inhibitory neurons.
These findings show the exciting potential of TFOE as a platform technology for non-genetic stimulation of the neural system with high spatial and temporal precision. Many new research opportunities will be opened up by the new capabilities offered by TFOE. For example, by unveiling the cell-type-specific threshold to acoustic stimulation for excitatory and inhibitory neurons, different acoustic pressure and duration can be applied to achieve certain cell-type selectivity in multiscale brain region. Meanwhile, single acoustic pulse with duration of sub-microsecond can be further fine-tuned to design the temporal profile of stimulus, which will allow controlling the neuron activity patterns to mimic natural neural codes. Furthermore, acoustic stimulation of neurons, with pharmacologically or genetically modifying ion channels integrated with patch clamp, provides new insight to the electrophysiological mechanisms of mechanical neuromodulation. Without any metal components, the TFOE is immune to electromagnetic interference and is compatible with functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), which holds promise for future study toward understanding of behavior and disease in human patients. Given the increasing popularity of ultrasound neuromodulation, the compactness, cost-effectiveness and versatility of TFOE open broad opportunities to utilize the optoacoustic effect in the field of neuroscience, the scientists forecast.
###
Media Contact
Chen Yang
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




