By upgrading direct international connections of SINET to the United States, Europe and Asia subsequently to upgrading domestic connections towards Society 5.0
Credit: © National Institute of Informatics
Background: Increase of transmission data volume over SINET international links due to the advancement of cutting-edge large-scale academic research projects and other undertakings
SINET is a communications network utilized as academic information infrastructure by universities and research organizations across Japan, and is built and operated by NII. At the launch of SINET5 in 2016, 100 Gbps ultra-high-speed lines were laid through every prefecture of Japan. Today, more than 900 universities and research organizations are connected to the network, and total volume of data transmission has increased far beyond the initial predictions made at the beginning of SINET5 operation. These increases are from higher volumes of transferred data due to the advancement of cutting-edge large-scale academic research.
SINET supports a variety of international joint research projects through interconnection with research networks in other countries/regions, and the jump in communications volume has been seen not only across domestic connections but through overseas connections as well. In particular, the direct connection between Japan and Europe established with two 10 Gbps lines three years ago is now strained due to a sharp rise in communications volume, raising concerns over the impact on research being conducted through international collaboration. Additionally, the research networks in other countries/regions have made progress with the development of 100 Gbps international connections, and NII realized the need to develop a network with an equivalent or higher speed to maintain parity between the Japanese research environment and the rest of the world. Lastly, to achieve stable operation of international connections, backup routing functions were also needed.
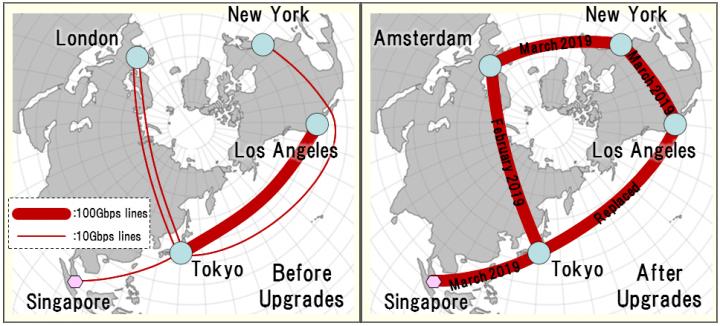
Upgrading SINET International Connections to Ultra-high-speed 100 Gbps and Forming a Globe-spanning Ring Topology
To address these circumstances, NII built a 100 Gbps ring connection that goes around the globe from Japan (Tokyo) to the U.S. West Coast (Los Angeles), U.S. East Coast (New York), Europe (Amsterdam) and back to Japan (Tokyo). At the same time, the Japan-Asia (Singapore) connection was also upgraded to 100 Gbps (see figure1 and table). By adopting a ring topology that extends around the globe, the European line can be accessed via the United States and vice versa, providing a mutual backup and boosting the stability of communications. This configuration also makes it possible to distribute load and absorb fluctuations in network demand for U.S. and Europe-bound traffic. The interconnection upgrade with the pan-European GÉANT network to 100 Gbps now provides SINET’s users with high capacity connectivity across Europe.
Future Outlook: Contribution to International Cooperative Research and Society 5.0
This latest upgrade to SINET’s international connection lines will better facilitate the international distribution of research and educational information cooperating with overseas research networks such as Internet2 in the U.S., GÉANT in Europe, SURFnet in Netherlands, NORDUnet in Nordic counties and so on (see figure2). Collaborative research between Japan and the United States such as the Belle II project through the 100 Gbps connection with the U.S., between Japan and Europe such as the LHC project through the 100 Gbps connection with Europe, and between Japan and Asia through the 100 Gbps Asia connection will all be undertaken in greater depth, offering the promise of greater international cooperation and competitiveness of Japan. In addition, building mutual backup system that cooperates between international lines has been advanced, and it is expected that as global academic community, future cooperation of 100 Gbps lines will make further growth of academic network environment, which is referred to as the GREN (Global Research & Education Network). Upgrading both the domestic and international segments of the network to ultra-high-speed 100 Gbps is also expected to help accelerate the advanced fusion of cyber-space (virtual space) and physical space (real space), bringing Japan a step closer to its vision for a future society in the form of Society 5.0.
###
Media Contact
Takao Fujiyoshi
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/



