Credit: Darryl Leja, NHGRI
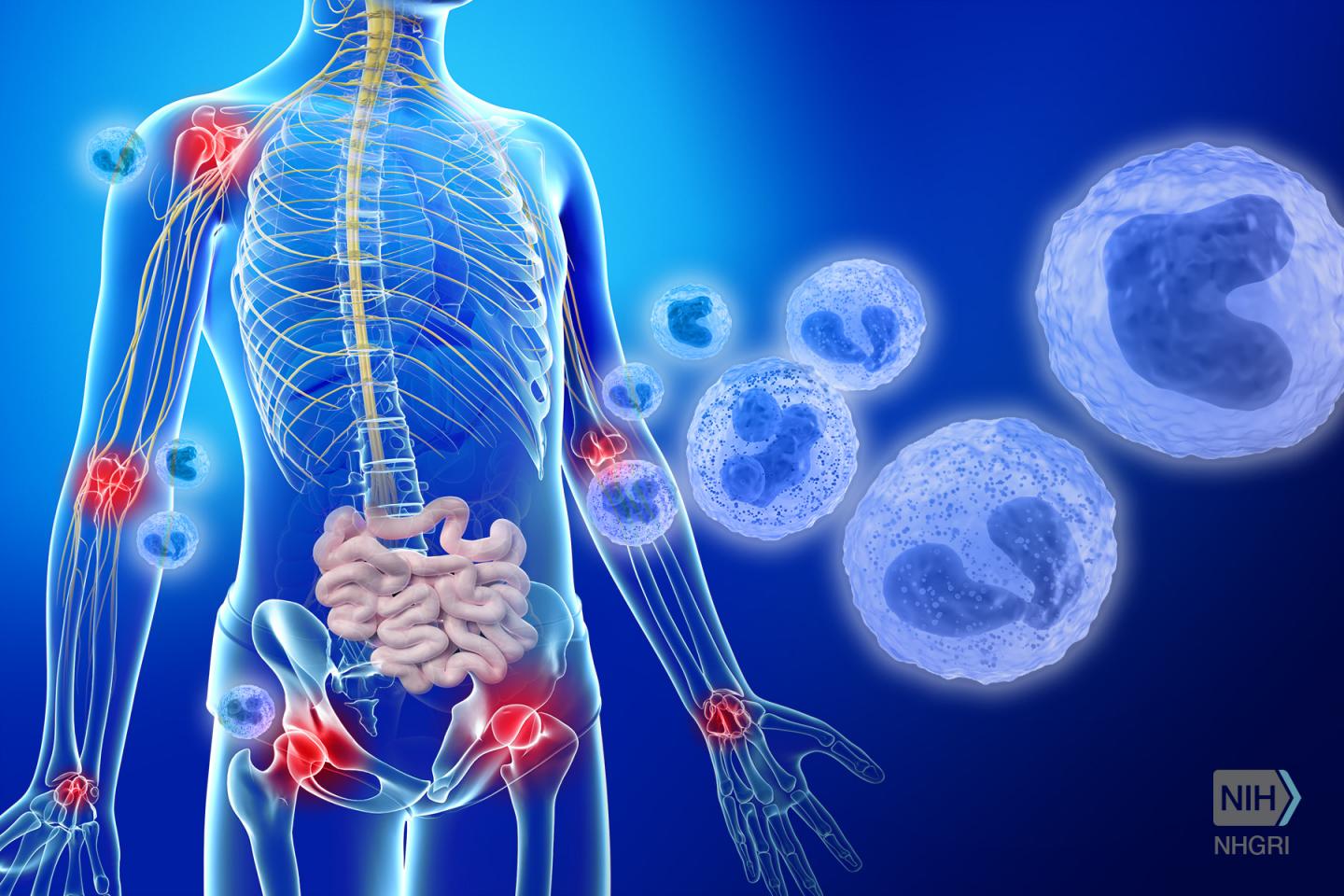
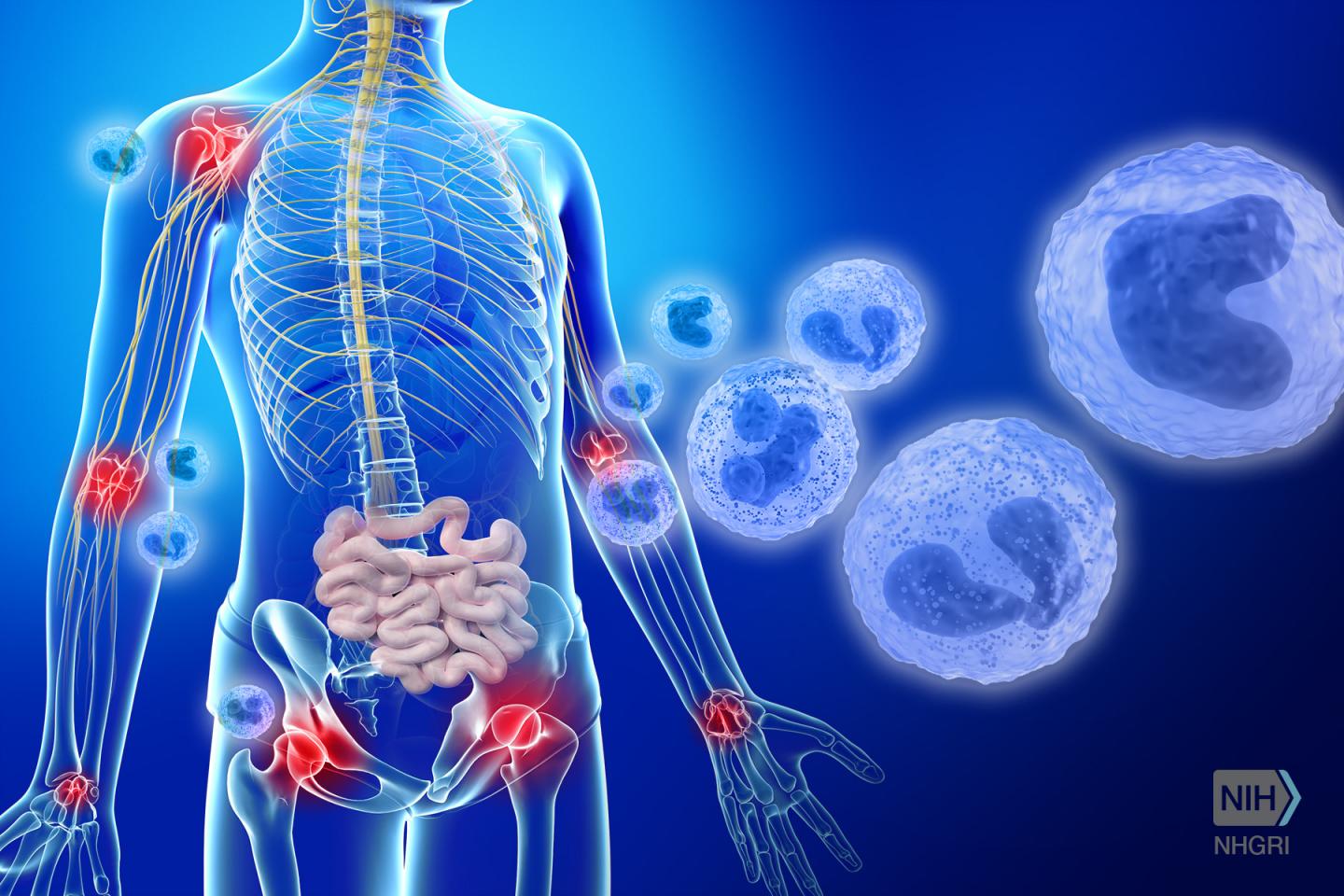
National Institutes of Health researchers have discovered a rare and sometimes lethal inflammatory disease – otulipenia – that primarily affects young children. They have also identified anti-inflammatory treatments that ease some of the patients' symptoms: fever, skin rashes, diarrhea, joint pain and overall failure to grow or thrive.
Otulipenia is caused by the malfunction of OTULIN, a single gene on chromosome 5. When functioning properly, OTULIN regulates the development of new blood vessels and mobilization of cells and proteins to fight infection. NIH researchers published their findings Aug. 22, 2016, in the early edition of the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Contributing to the work were researchers from the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the NIH Clinical Center, all part of NIH, along with their colleagues in Turkey and the United Kingdom.
"The results have been amazing and life changing for these children and their families," said Daniel Kastner, M.D., Ph.D., co-author, NHGRI scientific director and head of NHGRI's Inflammatory Disease Section. "We have achieved the important goal of helping these young patients and made progress in understanding the biological pathways and proteins that are important for the regulation of the immune system's responses." Cells use biological pathways to send and receive chemical cues in reaction to injury, infection or stress.
Otulipenia is one of several inflammatory diseases that occur when the immune system attacks the host's own tissues. Inflammation is the body's natural response to invading bacteria or viruses. The body releases chemicals that cause blood vessels to leak and tissues to swell in order to isolate a foreign substance from further contact with the body's tissues. Inflammatory diseases affecting the whole body are caused by mutations in genes like OTULIN that are part of a person's innate immunity (the cells and proteins present at birth that fight infections).
An international network of scientists studying inflammatory diseases identified four children from Pakistani and Turkish families with unexplained skin rashes and inflamed joints. NIH scientists then searched for disease-causing genes using next-generation DNA sequencing, technology that allows researchers to sequence DNA quickly and economically.
Once they found that the OTULIN gene was abnormal in the sick children, they studied the immune pathway in order to understand the mechanisms of disease and to improve treatment of these patients. They discovered a problem in the processing of a small protein, ubiquitin, which is critical to the regulation of many other proteins in the body, including immune molecules. In the affected children, the inability to remove the ubiquitin proteins from various molecules resulted in an increased production of chemical messengers that lead to inflammation (inflammatory cytokines).
The researchers determined that the children with otulipenia might respond to drugs that turned off tumor necrosis factor, a chemical messenger involved in systemic inflammation. Inflammation subsided in the children who had been treated with anti-tumor necrosis factor drugs (TNF inhibitors). TNF inhibitors are also used to treat chronic inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis.
"The malfunction in this protein has not been previously linked to clinical disorders of the human immune system," said Ivona Aksentijevich, M.D., staff scientist in NHGRI's Medical Genetics Branch and study co-author. "This discovery suggests a direction that can be explored for development of new therapies for patients with a wide range of inflammatory diseases."
This study together with NIH's 2016 identification of haploinsufficiency of A20 (HA20), suggests a new category of human inflammatory diseases caused by impaired ubiquitination, according to the researchers.
###
NHGRI is one of the 27 institutes and centers at the NIH, an agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The NHGRI Division of Intramural Research develops and implements technology to understand, diagnose and treat genomic and genetic diseases. Additional information about NHGRI can be found at: http://www.genome.gov.
NIAID conducts and supports research at NIH, throughout the United States, and worldwide – to study the causes of infectious and immune-mediated diseases, and to develop better means of preventing, diagnosing and treating these illnesses. News releases, fact sheets and other NIAID-related materials are available on the NIAID website at http://www.niaid.nih.gov.
The mission of the NIAMS, a part of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services' National Institutes of Health (NIH), is to support research into the causes, treatment, and prevention of arthritis and musculoskeletal and skin diseases; the training of basic and clinical scientists to carry out this research; and the dissemination of information on research progress in these diseases. For more information about the NIAMS, call the information clearinghouse at (301) 495-4484 or (877) 22-NIAMS (free call) or visit the NIAMS website at http://www.niams.nih.gov
Part of the National Institutes of Health, the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) plans, conducts, and supports research related to the causes, prevention, diagnosis and treatment of heart, blood vessel, lung and blood diseases; and sleep disorders. The Institute also administers national health education campaigns on women and heart disease, healthy weight for children and other topics. NHLBI press releases and other materials are available online at http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov.
The NIH Clinical Center is the nation's largest hospital devoted entirely to clinical research. Clinician-investigators translate scientific observations and laboratory discoveries into new approaches to diagnosing, treating, and preventing disease. http://clinicalcenter.nih.gov/
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit http://www.nih.gov.
Media Contact
Jeannine Mjoseth
[email protected]
301-402-0911
@genome_gov
http://www.nhgri.nih.gov