Credit: Nightingale Health
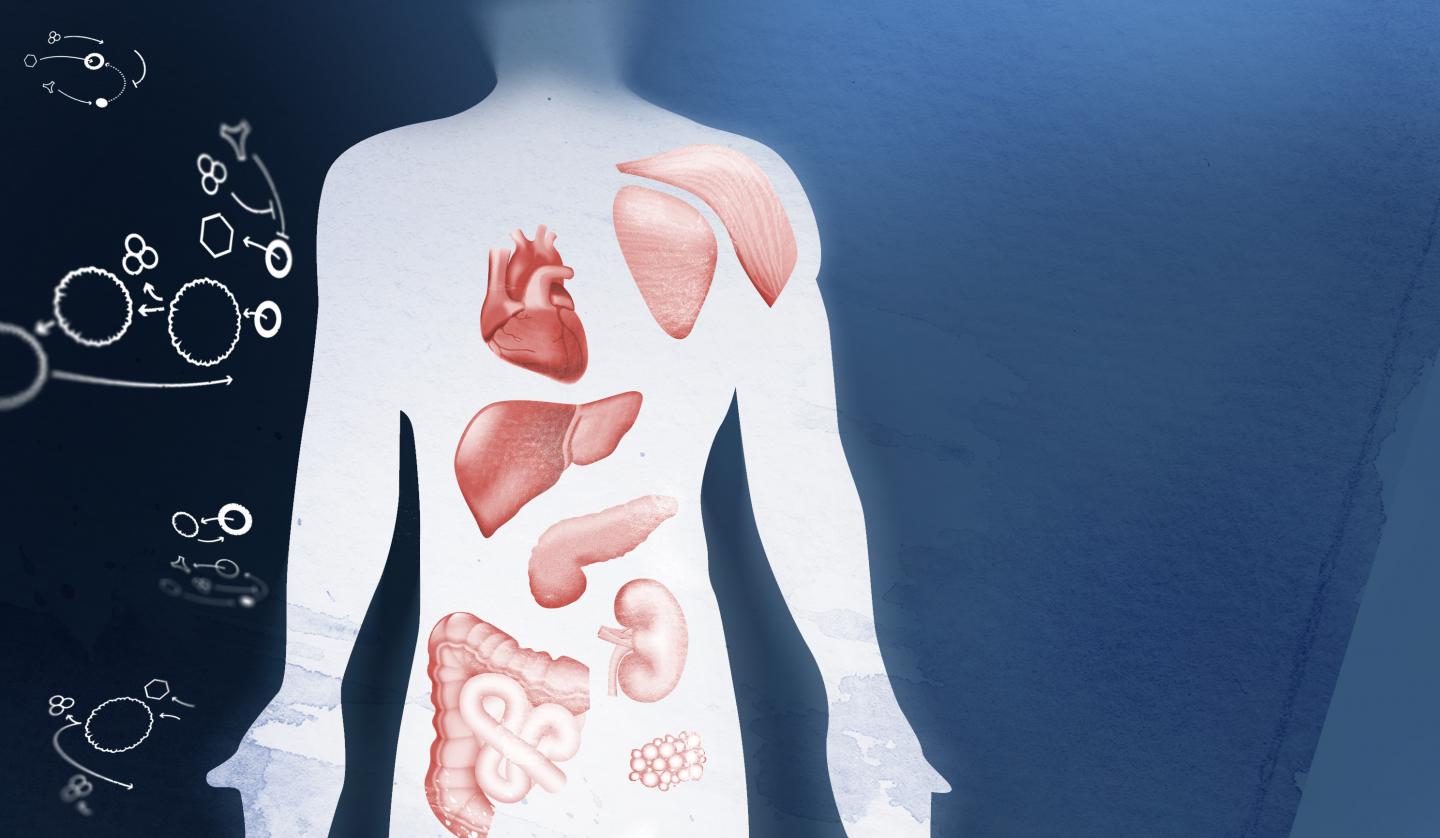
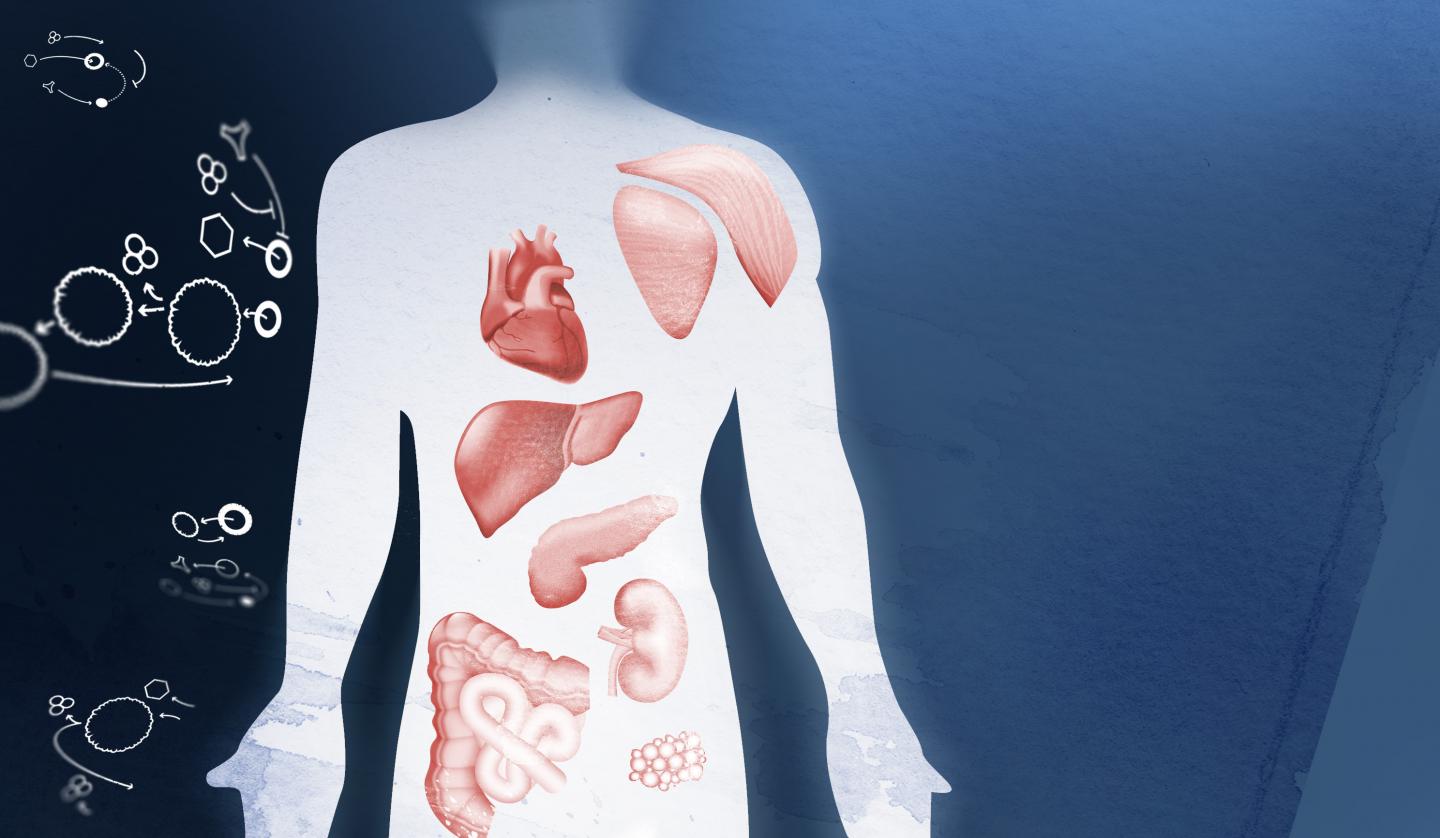
Chronic inflammation is currently a hot topic in health and wellness, being linked to everything from heart disease to clinical depression. In an effort to sort the facts from speculation, researchers have been diving into the links between inflammation and different disease risks. To investigate these connections further, scientists have used Nightingale's blood testing technology to measure GlycA (glycoprotein acetyls), a new marker for chronic inflammation. GlycA is a powerful new way of monitoring a person's current state of chronic inflammation and has been found to be potentially more stable than other markers used in healthcare.
In a recent study, building on prior research linking GlycA to risk for heart disease and shorter lifespan, scientists measured GlycA from blood samples with Nightingale's technology to explore whether it can predict a wide range of diseases in the general population. Analyzing the GlycA levels of 11,861 Finnish volunteers and their electronic health records, researchers found that increased levels of GlycA were linked to many major diseases of internal organs, such as alcoholic liver disease, chronic renal failure, heart failure and heart disease. Several of these disease links were new discoveries. The study also explored how effective GlycA measurements are at predicting and grouping patients into different risk categories for life expectancy. The results found that GlycA levels could successfully identify patients at five-fold risk of cardiovascular disease-related mortality.
"As we have seen in numerous studies with thousands of study volunteers, GlycA has considerable potential as a marker of chronic inflammation that can effectively predict disease onset and prognosis. The findings of this paper add further evidence to support the measurement of GlycA in national biobanks, as well as its utility in future clinical applications," says Dr Peter Würtz, Scientific Director, Nightingale Health. "Looking ahead, I'm excited by the contributions Nightingale's initiative to profile 500,000 samples in the UK Biobank will make towards furthering our understanding GlycA and its relationship with chronic diseases."
Current blood tests (e.g. cholesterol tests) only measure a handful of biomarkers, whereas Nightingale's blood testing technology measures over 220 blood biomarkers from a single sample. The measurements include routinely used markers including cholesterol and glucose, as well as other blood biomarkers that can enhance disease risk prediction, including GlycA and amino acids.
###
Research reference: Kettunen et al. Biomarker Glycoprotein Acetyls Is Associated With the Risk of a Wide Spectrum of Incident Diseases and Stratifies Mortality Risk in Angiography Patients. Circulation: Genomic and Precision Medicine 2018;11:e002234
What is GlycA?
GlycA (glycoprotein acetyls), is a novel Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR)-based biomarker for chronic inflammation. It reflects the amount of N-acetyl groups in circulating glycoproteins. In healthy individuals, higher levels of GlycA have been found to correspond with an overactive immune response or persistent bacterial infection. Chronic low-grade inflammation is thought to increase a person's risk of multiple diseases in internal organs, making it a crucial area of focus for future public health research. GlycA poses a whole host of potential clinical uses, such as informing the treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases. GlycA can also help us to identify high-risk patients, with elevated GlycA levels being previously found in large scientific studies to predict cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes mellitus and all-cause mortality risk.
Nightingale Health
Nightingale Health is a biotech company aiming to solve the global burden of chronic disease. We believe that rather than solely focusing on treatments, health should be about keeping people healthy. We develop pioneering solutions that facilitate active prevention of chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases and diabetes. With our proprietary blood testing technology, we reveal unique molecular insights that are otherwise invisible using standard technologies. This broader visibility allows us to predict the future risk of a person developing a disease, empowering people to make a positive impact on their health through awareness.
http://www.nightingalehealth.com
Media Contact
Teemu Suna
[email protected]
358-401-961-669
@https://twitter.com/NgaleHealth
https://nightingalehealth.com/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1161/CIRCGEN.118.002234