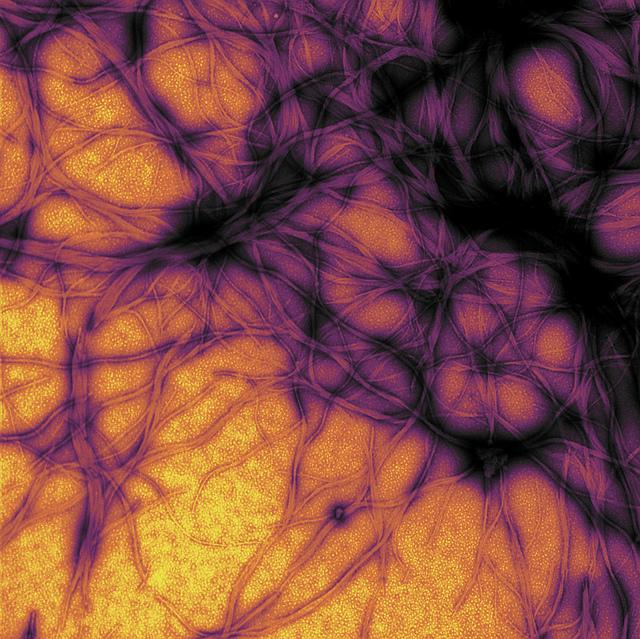
Credit: NIAID
WHAT:
Familial human prion diseases are passed within families and are associated with 34 known prion protein mutations. To determine whether three of the unstudied mutations are transmissible, scientists from the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, part of the National Institutes of Health, exposed research mice to brain samples from three people who died from a familial prion disease. After observing the mice for about two years, they found two of the mutations, Y226X and G131V, are transmissible.
Perhaps more interesting, the Y226X patient sample had previously been preserved in formaldehyde for three days, embedded in wax, and dried on glass specimen slides for several years before being rehydrated for the study. Yet, the sample infected four of eight mice.
The finding illustrates the hardiness of prion infectivity and the potential risks associated with prion transmission, potentially through surgery, blood transfusion or tissue donation. Samples for the other two mutations studied were taken from frozen brain tissue that was thawed.
Prion diseases originate when normally harmless prion protein molecules become abnormal and gather in clusters and filaments in the human body and brain. The reasons for this process are not fully understood. Familial human prion diseases include genetic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker disease, and fatal familial insomnia. All are fatal and thus far untreatable. Of the 34 known prion protein mutations, scientists now have tested 13 for transmissibility, identifying nine as transmissible to monkeys or mice.
###
ARTICLE:
B Race et al. Familial human prion diseases associated with prion protein mutations Y226X and G131V are transmissible to transgenic mice expressing human prion protein. Acta Neuropathologica Communications DOI: 10.1186/s40478-018-0516-2 (2018).
WHO:
Bruce Chesebro, M.D., chief of the NIAID Laboratory of Persistent Viral Diseases, is available to comment on this study.
CONTACT:
To schedule interviews, please contact Ken Pekoc, (301) 402-1663, [email protected].
NIAID conducts and supports research–at NIH, throughout the United States, and worldwide–to study the causes of infectious and immune-mediated diseases, and to develop better means of preventing, diagnosing and treating these illnesses. News releases, fact sheets and other NIAID-related materials are available on the NIAID website.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation's medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit http://www.nih.gov/.
Media Contact
Ken Pekoc
[email protected]
301-402-1663
@NIAIDNews
http://www.niaid.nih.gov
Original Source
https://www.niaid.nih.gov/news-events/niaid-scientists-assess-transmission-risk-familial-human-prion-diseases-mice http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s40478-018-0516-2