Credit: Vasilijevic J, et al (2017)
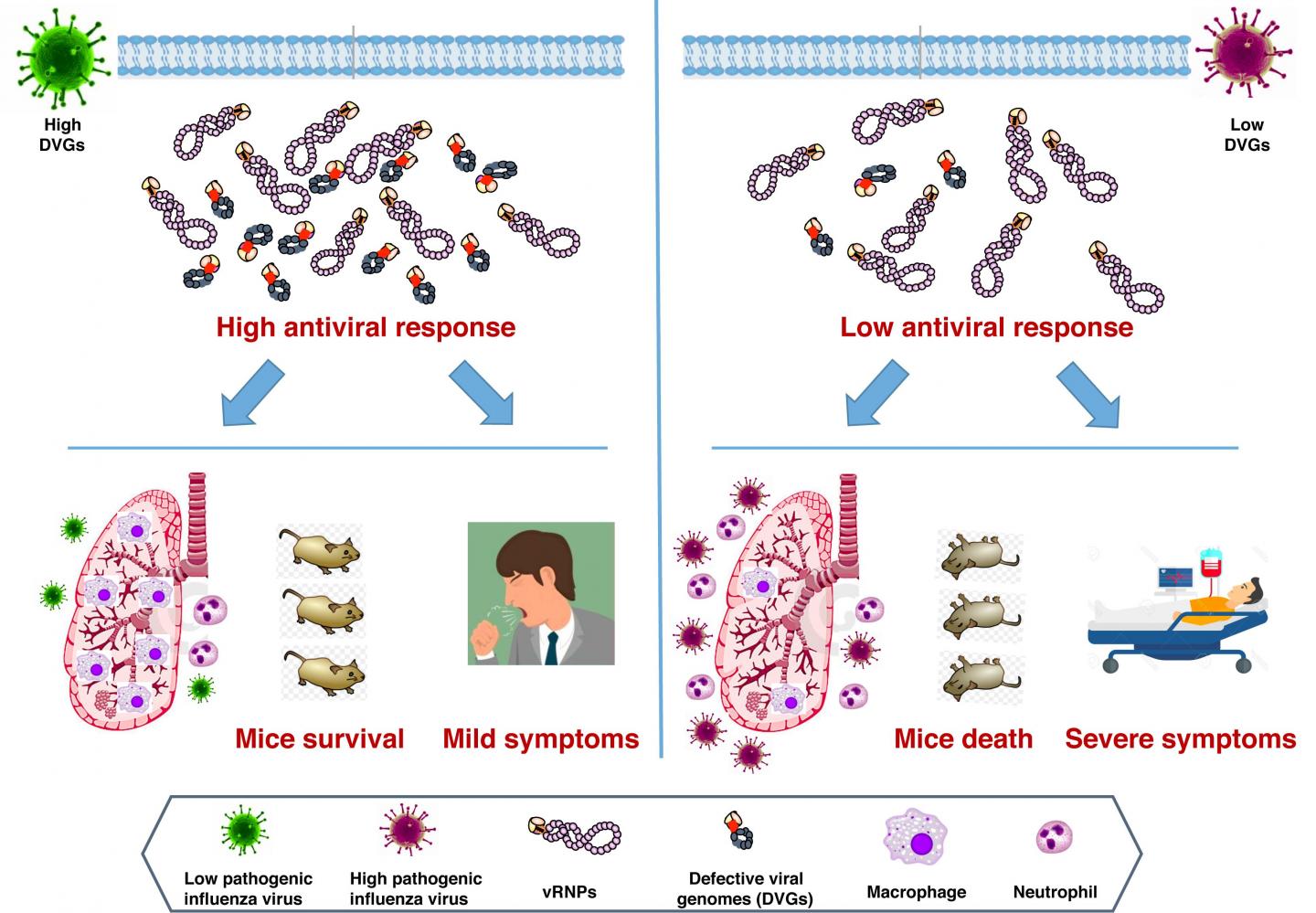
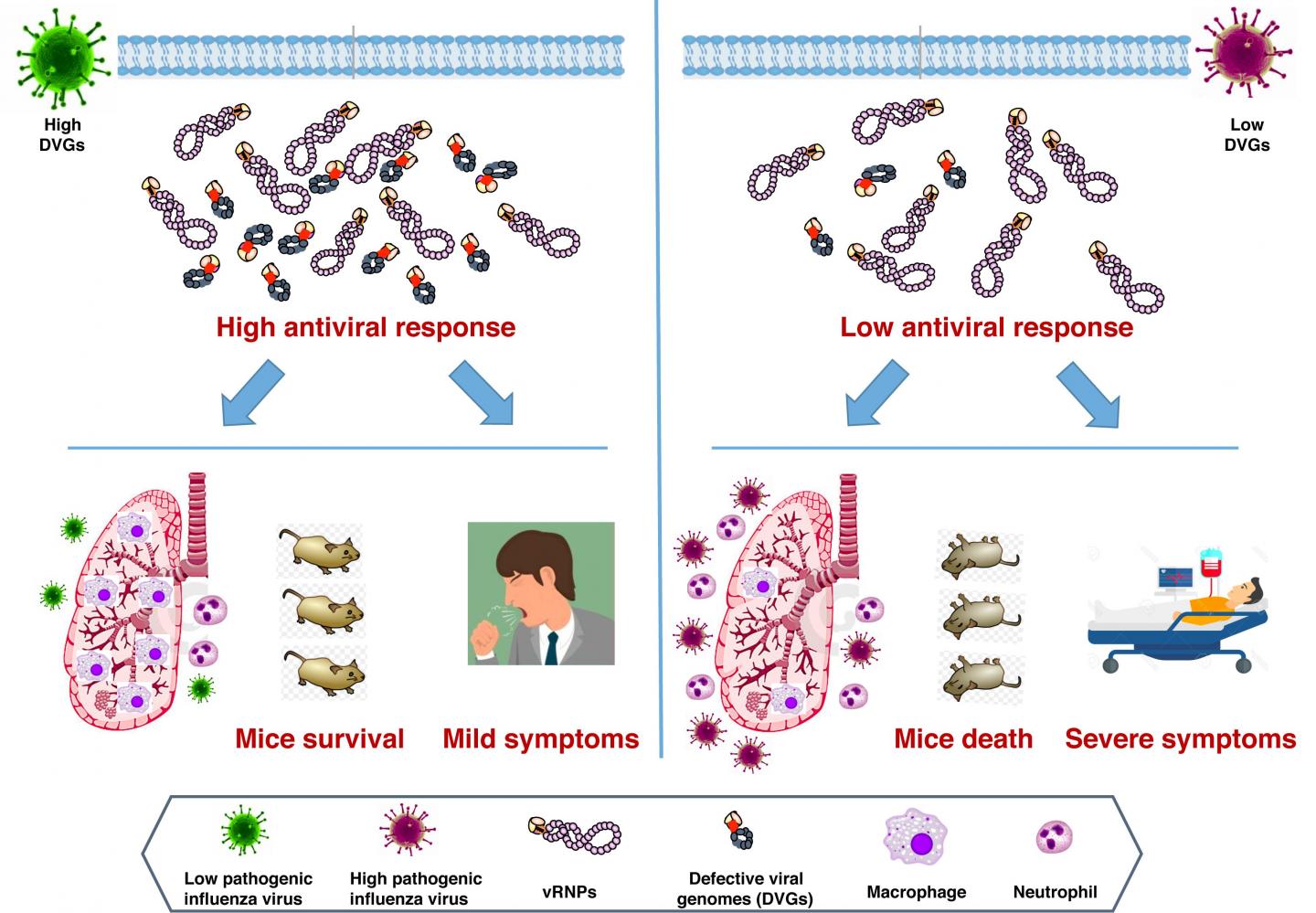
Flu viruses contain defective genetic material that may activate the immune system in infected patients, and new research published in PLOS Pathogens suggests that lower levels of these molecules could increase flu severity.
Influenza is particularly dangerous for infants, the elderly, and people with underlying medical issues, but otherwise-healthy people sometimes experience severe infection, too. This suggests that, among the multiple strains that circulate yearly, some are more virulent than others. Markers of severity have been found for specific strains, but a general marker that applies to multiple strains would be more useful to inform treatment and policy.
To identify such a marker, Ana Falcón of the Spanish National Center for Biotechnology, Madrid, and colleagues focused on defective viral genomes (DVGs). These molecules, which consist of pieces of viral RNA with missing genetic information, are found in multiple strains of flu virus. Previous research suggests that DVGs activate the immune system in infected animals, and thus might restrict severity.
To test whether DVGs could serve as a general marker of flu severity, the researchers infected both mice and human tissue cell cultures with different strains of influenza A H1N1 virus–the subtype responsible for flu pandemics. They found that strains resulting in lower levels of DVG accumulation in the cell cultures also produced more severe infection in the mice.
The research team also analyzed the genomes of viruses isolated from respiratory samples taken from people who experienced severe infection or death during the 2009 "swine flu" pandemic or later "swine flu-like" seasons. They found that the H1N1 strain that caused severe symptoms had significantly less DVG accumulation than influenza A strains sampled from people who experienced only mild symptoms.
Together, these results suggest that low levels of DVGs may indicate greater risk of severe disease in patients infected with influenza A virus. With further research, these findings could help predict flu severity, guide patient treatment, and inform flu prevention strategies.
###
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS Pathogens: http://journals.plos.org/plospathogens/article?id=10.1371/journal.ppat.1006650
Citation: Vasilijevic J, Zamarreño N, Oliveros JC, Rodriguez-Frandsen A, Gómez G, Rodriguez G, et al. (2017) Reduced accumulation of defective viral genomes contributes to severe outcome in influenza virus infected patients. PLoS Pathog13(10): e1006650. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1006650
Funding: JV is a PhD fellow of the La Caixa Foundation International Fellowship Programme (La Caixa/CNB). This work was supported by the Spanish Ministry of Economy and Competitiveness (Plan Nacional de Investigacion Científica, Desarrollo e Innovacion Tecnológica BFU2011-26175 and BFU2014-57797-R to AN) and the network Ciber de Enfermedades Respiratorias (CIBERES). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Media Contact
PLOS Pathogens
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1006650