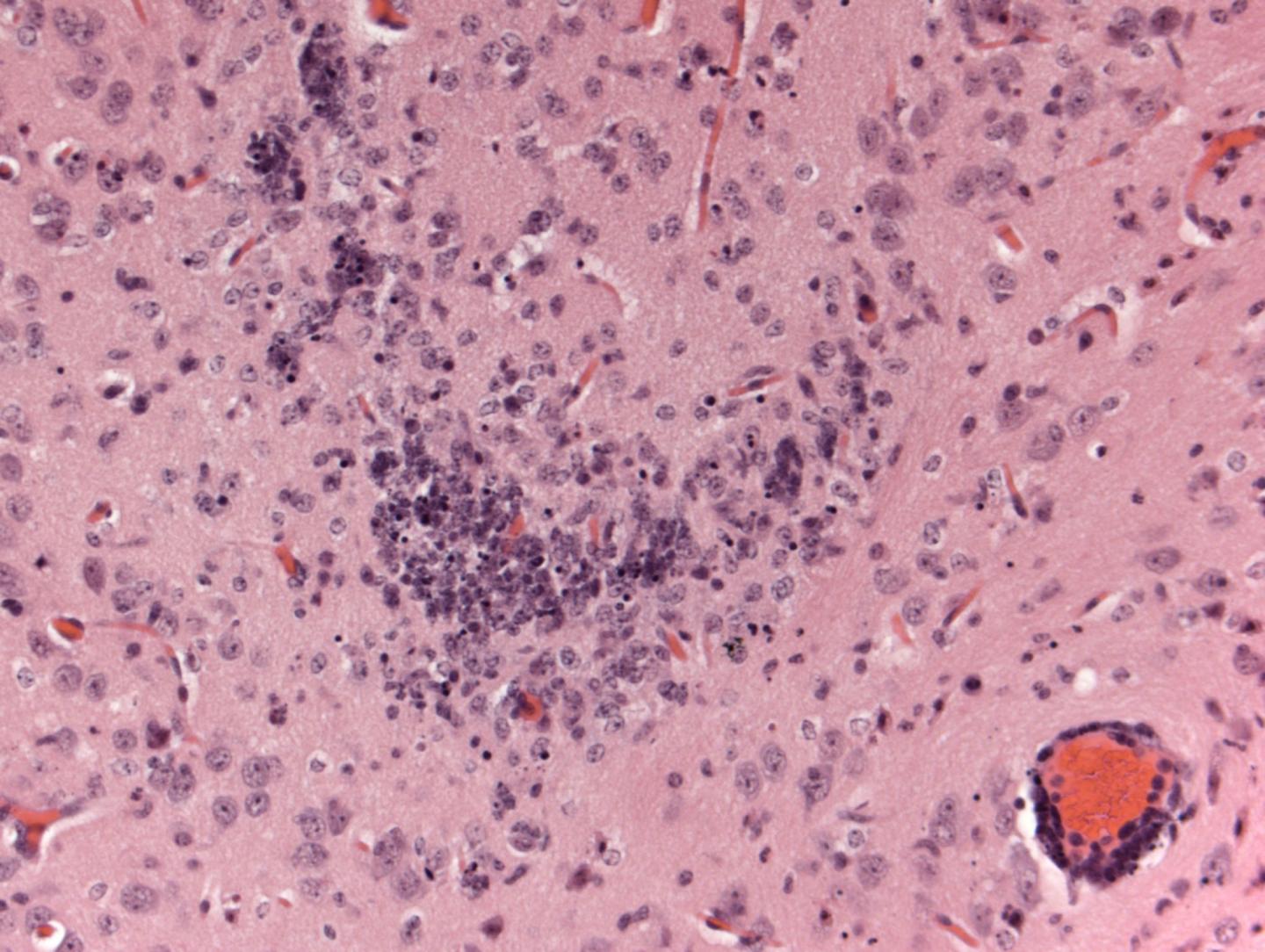
Credit: Dowall et al.
The ongoing Zika virus (ZIKV) epidemic with its link to birth defects and serious immune disease has created an urgent need for a small animal model that can improve our understanding of how the virus causes disease symptoms in humans and speed up the development of vaccines and treatment. A study published in PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases describes one of the first mouse models for ZIKV disease. Following infection via the skin (resembling a mosquito bite), the mice develop disease and accumulate virus in many organs, including the brain. Prior to publication, the results had been uploaded onto the bioRxiv pre-publishing website in response to the Statement on Data Sharing in Public Health Emergencies to which the PLOS journals are a signatory.
Healthy mice are resistant to infection with ZIKV via the skin (the way humans are infected by mosquito bites). Based on experience with viruses related to ZIKV, researchers have therefore turned to mice with mutations in certain immune system genes to test whether they are suitable animal models for ZIKV disease.
The group, led by Professor Roger Hewson from Public Health England in Porton Down, UK, focused on so-called A129 mice that have mutations in the one of the interferon receptors. These mice were injected in their hind legs with a dose of ZIKV similar to the dose known to be transmitted of the related West Nile virus by mosquito bites. The researchers found that the mice exhibited weight loss after 3 days. Their body temperature slightly increased by day 4, and afterwards dropped below normal. All A129 mice died within 6 days of infection, whereas non-mutant mice that were treated the same way did not shown any clinical symptoms.
Viral RNA (which indicates virus invasion of the tissue and subsequent virus multiplication) was detectable on day 3 after infection in all tissues tested, including blood, spleen, liver, ovary, and brain. Viral RNA levels ranged from ~107 in blood and liver to nearly 1011 in brain (where they continued to increase until the death of the animals). These levels are within the range of viral RNA loads detected in human blood serum and breast milk (106), semen (107), and urine (108). The researchers also observed abnormalities in the brain and eyes of the infected A129 mice.
Stating that "although A129 mice are deficient in the innate interferon response, they retain their adaptive immunity and thus have successfully been used as suitable models for the testing of vaccinations and antivirals", the researchers conclude that their study "provides details on a suitable small animal model for the testing of future interventions against ZIKV that can accelerate the testing of novel interventions against this pathogen declared as public health emergency of international concern".
In an accompanying Commentary, M. Javad Aman from Integrated BioTherapeutics, Inc. in Gaithersburg, USA, and Fatah Kashanchi, from the George Mason University in Manassas, USA, discuss the recent advances on mouse models for ZIKV disease and state that collectively, the recent papers mark "an important turning point in Zika virus research and enable in vivo testing and evaluation of candidate vaccines and therapeutics". Referring specifically on the study by Dowall and colleagues, they recommend that future research should examine to what extent the abnormalities in the mouse brain reflect the CNS abnormalities in humans.
###
Please contact [email protected] if you would like more information about our content and specific topics of interest.
All works published in PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases are open access, which means that everything is immediately and freely available. Use this URL in your coverage to provide readers access to the paper upon publication:
http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0004658 (Link goes live upon article publication)
Media Contact
Roger Hewson
[email protected]
44-019-806-12100
The post New Zika mouse model accumulates virus in the brain and other tissues appeared first on Scienmag.