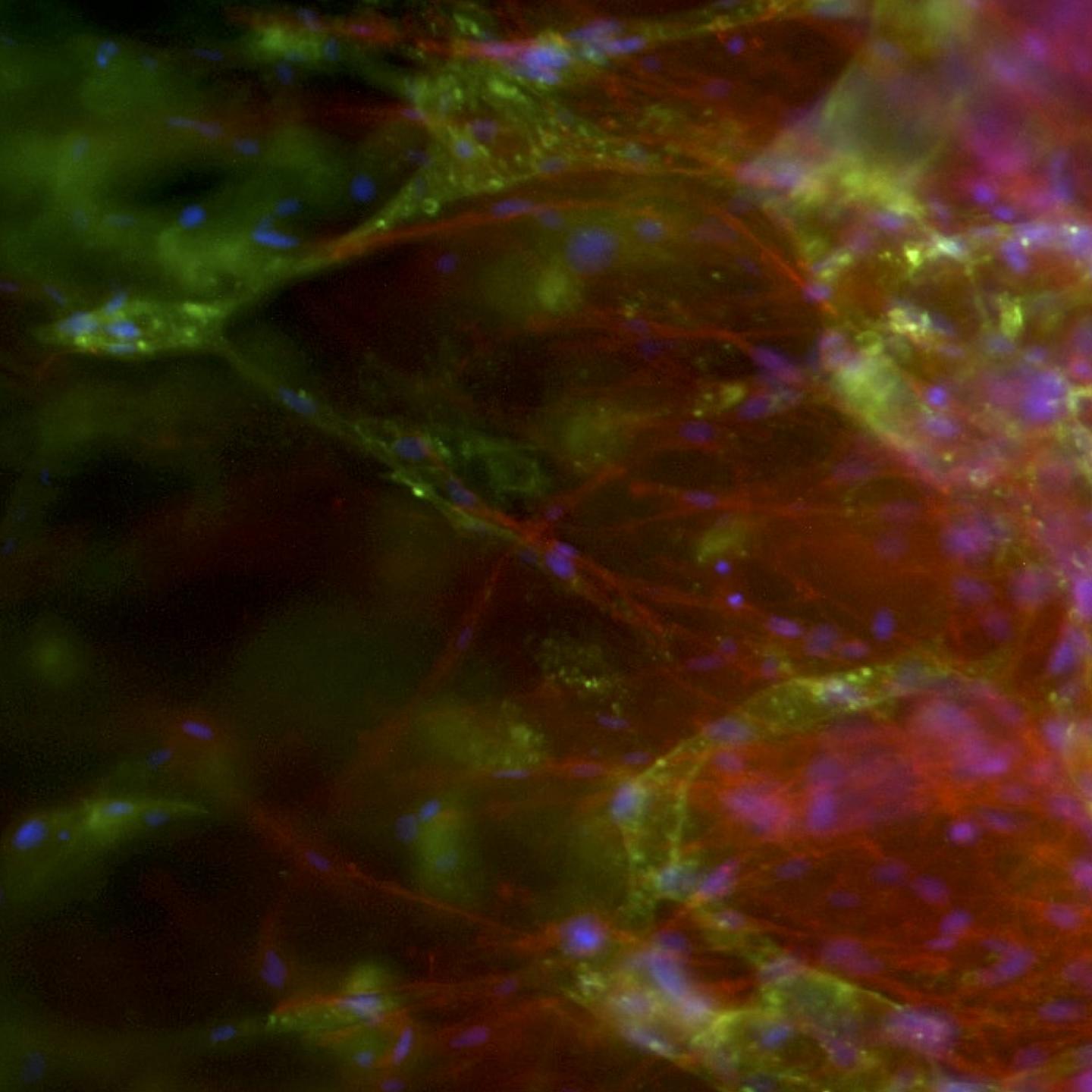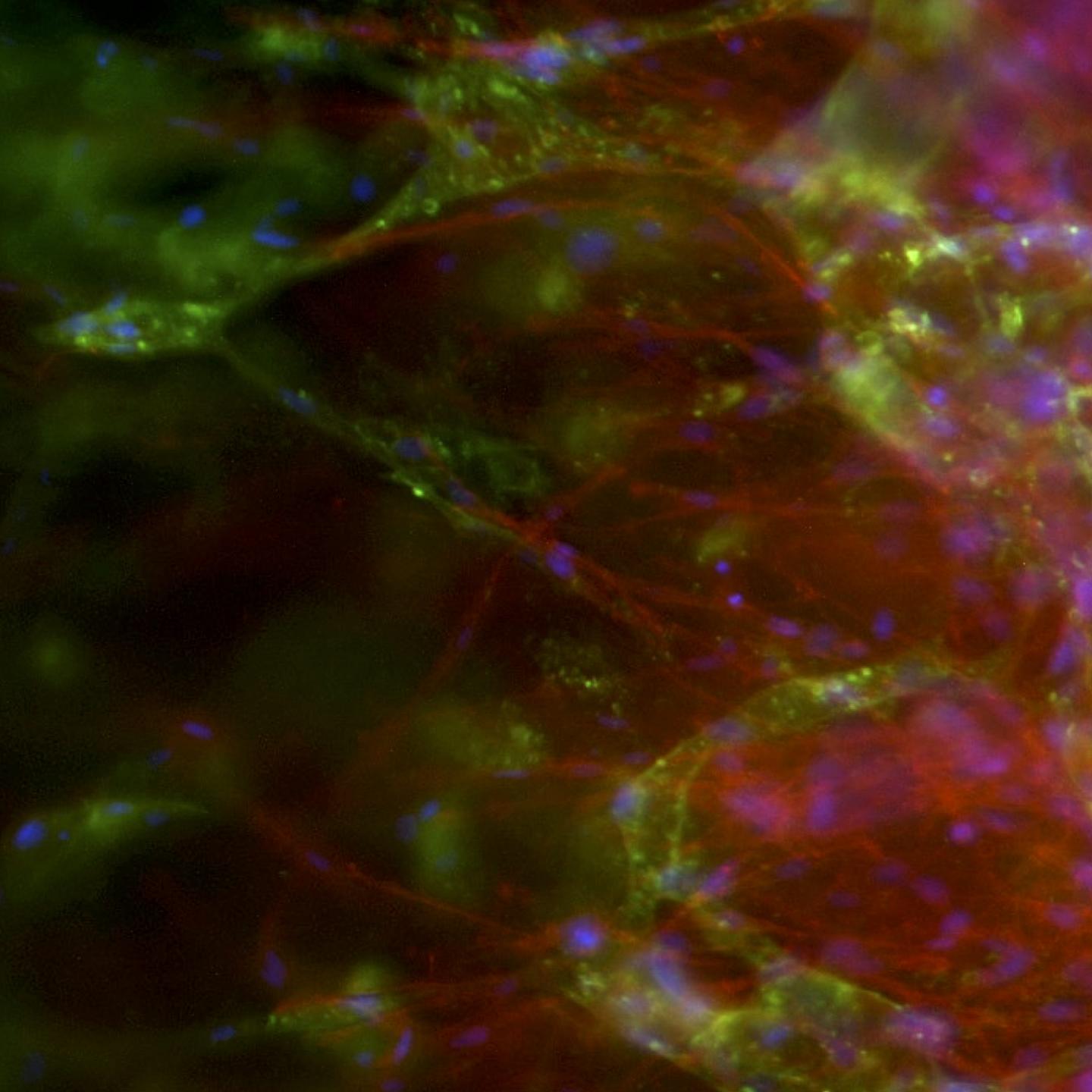
In addition the technique to grow the blood vessels in a 3D scaffold cuts down on the risk of transplant rejection because it uses cells from the patient. It was developed by researchers from the University of Bath's Department of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, working with colleagues at Bristol Heart Institute.
The study is published in Scientific Reports.
So far the shortage of adequate patient-derived scaffolds that can support blood vessel growth has been a major limitation for regenerative medicine and tissue engineering.
Other methods only allow limited formation of small blood vessels such as capillaries, which makes tissue less likely to successfully transplant into a patient. In addition other methods of tissue growth require the use of animal products, unnecessary in this technique which uses human platelet lysate gel (hPLG) and endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) – a type of cell which helps maintain blood vessel walls.
Dr Giordano Pula, Lecturer in Pharmacology at the University of Bath and head of the research team making the discovery, said: "A major challenge in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine is providing the new tissue with a network of blood vessels, and linking this to the patient's existing blood supply; this is vital for the tissue's survival and integration with adjacent tissues."
Dr Paul De Bank, Senior Lecturer in Pharmaceutics at the University of Bath and co-author of the paper, said: "By embedding EPCs in a gel derived from platelets, both of which can be isolated from the patient's blood, we have demonstrated the formation of a network of small vessels.
"What is more, the gel contains a number of different growth factors which can induce existing blood vessels to infiltrate the gel and form connections with the new structures. Combining tissue-specific cells with this EPC-containing gel offers the potential for the formation of fully vascularised, functional tissues or organs, which integrate seamlessly with the patient.
"This discovery has the potential to accelerate the development of regenerative medicine applications."
Professor Peter Weissberg, Medical Director of the British Heart Foundation, said: "Over a half a million people in the UK are living with heart failure, a disabling condition which can leave people unable to carry out everyday activities such as climbing the stairs or even walking to the shops. This regenerative research brings the British Heart Foundation's goal to mend a broken heart and beat heart failure one step closer.
"All living tissues, including new heart muscle, need a blood supply. One of the fundamental goals of regenerative medicine is to find ways to grow a new blood supply from scratch. Previous attempts at this using human cells and synthetic scaffolds have met with only limited success.
"The beauty of this new approach is that components of a person's own blood could be manipulated to create a scaffold on which new blood vessels could grow. This increases the likelihood that the new tissue will be integrated into the patient's body which, if proven successful with more research, could improve the lives of people affected by heart failure."
###
The study was supported by funds from the University of Bath, the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC), the Royal Society and the British Heart Foundation.
Platelet lysate gel and endothelial progenitors stimulate microvascular network formation in vitro: tissue engineering implications is published at: http://www.nature.com/articles/srep25326 doi:10.1038/srep25326
For further information, please contact Chris Melvin in the University of Bath Press Office on +44 (0)1225 386 319 or [email protected]
Notes
We are one of the UK's leading universities both in terms of research and our reputation for excellence in teaching, learning and graduate prospects.
In the REF 2014 research assessment 87 per cent of our research was defined as 'world-leading' or 'internationally excellent'. From making aircraft more fuel efficient, to identifying infectious diseases more quickly, or cutting carbon emissions through innovative building solutions, research from Bath is making a difference around the world. Find out more: http://www.bath.ac.uk/research/
Well established as a nurturing environment for enterprising minds, Bath is ranked highly in all national league tables. We were chosen as the UK's top university in the Times Higher Education Student Experience Survey 2015. Internationally, Bath was placed 'first in Europe' according to the latest QS 'Top 50 under 50' ranking.
Media Contact
Chris Melvin
[email protected]
44-012-253-86319
@uniofbath
http://www.bath.ac.uk