Irvine, CA – May 3, 2022 – New research from the University of California, Irvine, finds that drug withdrawal-induced anxiety and reinstatement of drug seeking behaviors are controlled by a single pathway in the brain and centered around dopamine cells.
Credit: UCI School of Medicine
Irvine, CA – May 3, 2022 – New research from the University of California, Irvine, finds that drug withdrawal-induced anxiety and reinstatement of drug seeking behaviors are controlled by a single pathway in the brain and centered around dopamine cells.
The study, “An extended amygdala-midbrain circuit controlling cocaine withdrawal-induced anxiety and reinstatement,” was published today in Cell Reports.
Addiction occurs in phases: initial drug exposures are rewarding, repeated administration leads to tolerance or sensitization to the drug’s effects, and withdrawal leads to anxiety and a negative affective state, which, in turn, contribute to reinstatement of drug taking/seeking.
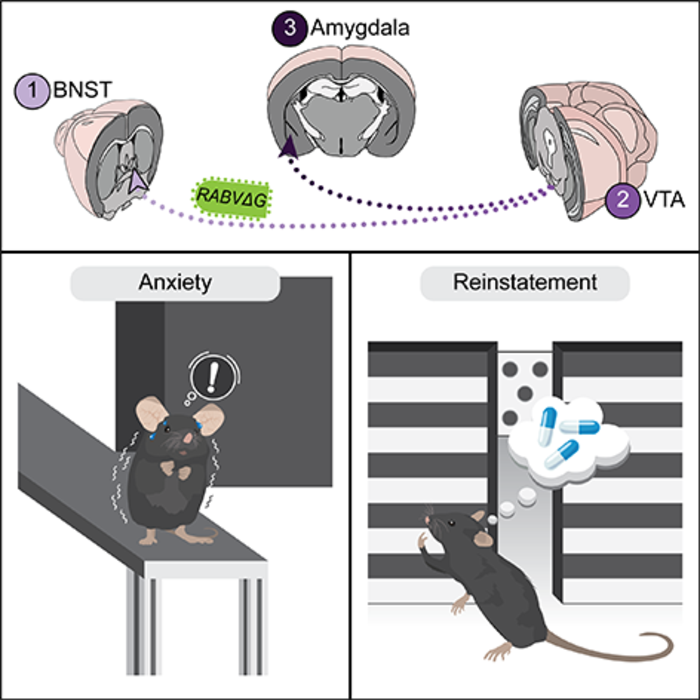
“In order to prevent relapse among drug users, specifically cocaine users, we need to understand the factors in the brain that contribute to drug seeking behaviors and the vulnerability to relapse,” said Kevin Beier, PhD, assistant professor of physiology and biophysics at UCI School of Medicine. “In this study, we identified a brain circuit that is responsible for drug withdrawal-induced anxiety as well as relapse-related behavior, along with the identification of a potential target for therapeutic interventions.”
The negative affective state induced by withdrawal from use of drugs of abuse is a critical factor causing drug users to relapse.
“Both the drug withdrawal-induced anxiety and reinstatement of drug seeking are controlled by a single pathway centered around dopamine cells in the ventral midbrain,” explained Beier. “That a single pathway controls both sets of behavioral changes may help to explain many addiction-related behavioral phenomena. Importantly, it links them both directly to dopamine, which is more typically linked to reward-related behaviors.”
Although midbrain dopamine circuits are central to motivated behaviors, the knowledge of how experience modifies these circuits to facilitate subsequent behavioral adaptations is limited. This study demonstrates the selective role of a ventral tegmental area dopamine projection to the amygdala for cocaine induced anxiety, but not cocaine reward or sensitization. Silencing this projection prevents development of anxiety during protracted withdrawal after cocaine use.
According to the National Center for Drug Abuse Statistics, there are roughly 70,000 drug overdoses each year in the United States. In 2017, nearly one in five drug overdose deaths was cocaine-related, with the highest rate of cocaine-related overdoses and deaths occurring among non-Hispanic black populations. Between 2012 and 2018, the rate of cocaine-related overdose deaths increased from 1.4 to 4.5 percent. The American Addiction Centers state recent drug relapse statistics show that more than 85 percent of individuals relapse and return to drug use within a year following treatment.
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health, Tobacco-Related Disease Research Program, American Parkinson Disease Association, Alzheimer’s Association, New Vision Research, and the Brain and Behavior Research Foundation.
About the UCI School of Medicine: Each year, the UCI School of Medicine educates more than 400 medical students, and nearly 150 doctoral and master’s students. More than 700 residents and fellows are trained at UCI Medical Center and affiliated institutions. The School of Medicine offers an MD; a dual MD/PhD medical scientist training program; and PhDs and master’s degrees in anatomy and neurobiology, biomedical sciences, genetic counseling, epidemiology, environmental health sciences, pathology, pharmacology, physiology and biophysics, and translational sciences. Medical students also may pursue an MD/MBA, an MD/master’s in public health, or an MD/master’s degree through one of three mission-based programs: Health Education to Advance Leaders in Integrative Medicine (HEAL-IM), Leadership Education to Advance Diversity-African, Black and Caribbean (LEAD-ABC), and the Program in Medical Education for the Latino Community (PRIME-LC). The UCI School of Medicine is accredited by the Liaison Committee on Medical Accreditation and ranks among the top 50 nationwide for research. For more information, visit som.uci.edu.
Journal
Cell Reports
DOI
10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110775
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
An extended amygdala-midbrain circuit controlling cocaine withdrawal-induced anxiety and reinstatement
Article Publication Date
3-May-2022
COI Statement
The authors declare no competing interests.




