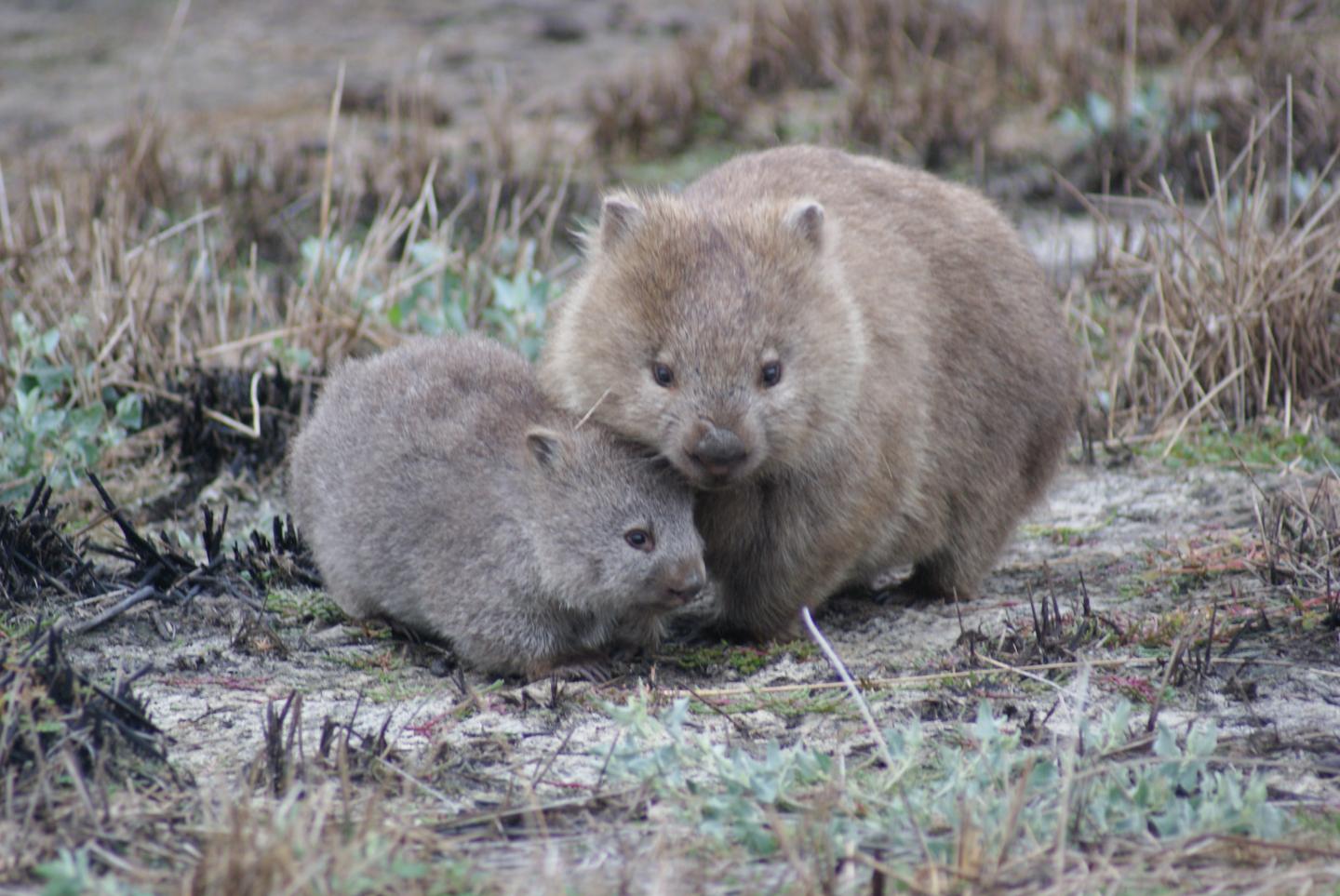
Credit: Scott Carver
New research from the University of Tasmania is offering hope that the deadly mange disease affecting Tasmanian wombats could eventually be brought under control for wild individuals and populations.
Long-term disease control or eradication in wildlife is rare and represents a major challenge to wildlife conservation across the globe.
Control is particularly difficult for pathogens that can be transmitted through the environment, which includes the mite that causes sarcoptic mange in bare-nosed wombats.
In a paper published today in the Journal of Applied Ecology, researchers present a treatment program and lessons learned from it to guide the development of more effective and feasible control of sarcoptic mange disease in wombat populations.
Disease control was attempted during the mange outbreak at Narawntapu National Park in northern Tasmania, where PhD student Alynn Martin showed the disease could be controlled temporarily using a Cydectin treatment, remotely delivered to wombats using flaps over their burrows.
“The logistics of this treatment made long-term disease control extremely challenging,” she said. “After three months of trying to treat each wombat in the population every week, the disease returned, and wombats continued to die. It was very disappointing to see after going to so much effort to save these wombats.”
Rather than giving up, the researchers used their study to identify practical solutions to the problem.
With the help of University of Tasmania ecological modeller Dr Shane Richards, they discovered that a combination of a longer-lasting treatment and improved delivery of the treatment to the wombats would improve capacity to control mange in wombat populations.
“Slight improvements in multiple aspects of disease control can have dramatic impacts on our capacity to control this disease in wombats,” Dr Richards said.
Lead researcher Dr Scott Carver says that they are now researching a longer-lasting treatment for wombats, called Bravecto.
“We have researched the safety and dose, and are currently determining the effectiveness of the new treatment. Our overarching aim is to make the management of this pathogen much more feasible for individual wild wombats and local at-risk populations,” Dr Carver said.
Dr Richards said that field results suggest that the frequency in which wombats change the burrow in which they sleep was an important factor in disease persistence in populations.
The Sarcoptes scabiei mite was introduced to Australia by European settlers and their domestic animals.
###
Media Contact
Duncan Abey
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.