LA JOLLA, CA—Scientists at Scripps Research have invented a way to image, across different tissues and with higher precision than ever before, where drugs bind to their targets in the body. The new method could become a routine tool in drug development.
Credit: Scripps Research
LA JOLLA, CA—Scientists at Scripps Research have invented a way to image, across different tissues and with higher precision than ever before, where drugs bind to their targets in the body. The new method could become a routine tool in drug development.
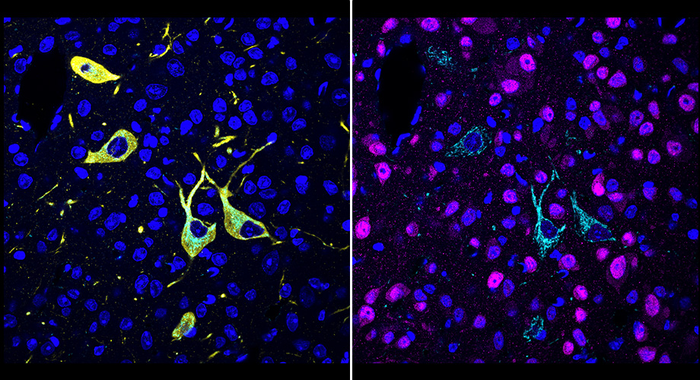
Described in a paper in Cell on April 27, 2022, the new method, called CATCH, attaches fluorescent tags to drug molecules and uses chemical techniques to improve the fluorescent signal. The researchers demonstrated the method with several different experimental drugs, revealing where—even within individual cells—the drug molecules hit their targets.
“This method ultimately should allow us, for the first time, to see relatively easily why one drug is more potent than another, or why one has a particular side effect while another one doesn’t,” says study senior author Li Ye, PhD, assistant professor of neuroscience at Scripps Research and The Abide-Vividion Chair in Chemistry and Chemical Biology.
The study’s first author, Zhengyuan Pang, is a graduate student in the Ye lab. The study also was a close collaboration with the laboratory of Ben Cravatt, PhD, Gilula Chair of Chemical Biology at Scripps Research.
“The unique environment at Scripps Research, where biologists routinely work together with chemists, is what made the development of this technique possible,” Ye says.
Understanding where drug molecules bind their targets to exert their therapeutic effects—and side effects—is a basic part of drug development. However, drug-target interaction studies traditionally have involved relatively imprecise methods, such as bulk analyses of drug-molecule concentration in entire organs.
The CATCH method involves the insertion of tiny chemical handles into drug molecules. These distinct chemical handles don’t react with anything else in the body, but do allow the addition of fluorescent tags after the drug molecules have bound to their targets. In part because human or animal tissue tends to diffuse and block the light from these fluorescent tags, Ye and his team combined the tagging process with a technique that makes tissue relatively transparent.
In this initial study, the researchers optimized and evaluated their method for “covalent drugs,” which bind irreversibly to their targets with stable chemical bonds known as covalent bonds. This irreversibility of binding makes it particularly important to verify that such drugs are hitting their intended targets.
The scientists first evaluated several covalent inhibitors of an enzyme in the brain called fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH). FAAH inhibitors have the effect of boosting levels of cannabinoid molecules, including the “bliss molecule” anandamide, and are being investigated as treatments for pain and mood disorders. The scientists were able to image, at the single-cell level, where these inhibitors hit their targets within large volumes of mouse brain tissue, and could easily distinguish their different patterns of target engagement.
In one experiment, they showed that an experimental FAAH inhibitor called BIA-10-2474, which caused one death and several injuries in a clinical trial in France in 2016, engages unknown targets in the midbrain of mice even when the mice lack the FAAH enzyme—offering a clue to the source of the inhibitor’s toxicity.
In other tests demonstrating the unprecedented precision and versatility of the new method, the scientists showed that they could combine drug-target imaging with separate fluorescent-tagging methods to reveal the cell types to which a drug binds. They also could distinguish drug-target engagement sites in different parts of neurons. Finally, they could see how modestly different doses of a drug often strikingly affect the degree of target engagement in different brain areas.
The proof-of-principle study is just the beginning, Ye emphasizes. He and his team plan to develop CATCH further for use on thicker tissue samples, ultimately perhaps whole mice. Additionally, they plan to extend the basic approach to more common, non-covalently-binding drugs and chemical probes. On the whole, Ye says, he envisions the new method as a basic tool not only for drug discovery but even for basic biology.
“In situ Identification of Cellular Drug Targets in Mammalian Tissue” was co-authored by Zhengyuan Pang, Michael Schafroth, Daisuke Ogasawara, Yu Wang, Victoria Nudell, Neeraj Lal, Dong Yang, Kristina Wang, Dylan Herbst, Jacquelyn Ha, Carlos Guijas, Jacqueline Blankman, Benjamin Cravatt and Li Ye—all of Scripps Research during the study.
The study was funded in part by the National Institutes of Health (DP2DK128800, DK114165, DK124731, DA033760), the Whitehall Foundation, the Baxter Foundation, and the Dana Foundation.
About Scripps Research
Scripps Research is an independent, nonprofit biomedical institute ranked the most influential in the world for its impact on innovation by Nature Index. We are advancing human health through profound discoveries that address pressing medical concerns around the globe. Our drug discovery and development division, Calibr, works hand-in-hand with scientists across disciplines to bring new medicines to patients as quickly and efficiently as possible, while teams at Scripps Research Translational Institute harness genomics, digital medicine and cutting-edge informatics to understand individual health and render more effective healthcare. Scripps Research also trains the next generation of leading scientists at our Skaggs Graduate School, consistently named among the top 10 US programs for chemistry and biological sciences. Learn more at www.scripps.edu.
Journal
Cell




