The gut microbiota, a complex ecosystem within the human intestinal tract, is increasingly recognized for its vital role in human health and disease. Notably, its relationship with intestinal damage due to burns has been underexplored. New study has unveiled the pivotal role of gut microbiota in the synthesis and degradation of intestinal mucus following burn injuries in mice. Utilizing advanced 16S rRNA and metagenomic sequencing techniques, researchers have identified significant changes in gut microbiota composition and its impact on the intestinal mucus barrier.
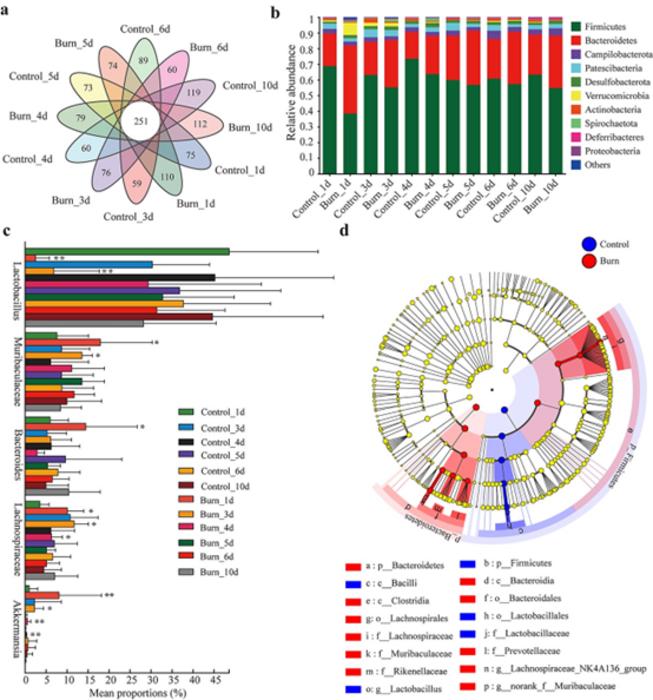
On a study (doi:10.1093/burnst/tkad056) published in the journal Burns & Trauma, researchers employed a combination of techniques to analyze the effects of burn injury on the gut microbiota and mucus barrier in mice. A modified histopathological grading system assessed colon tissue and mucus barrier integrity. 16S rRNA sequencing revealed changes in gut microbial composition over 10 days post-burn. Metagenomic sequencing provided deeper insights into mucus-related bacteria and potential underlying mechanisms.
This study provides compelling evidence that burn injury disrupts the intestinal mucus barrier and alters the gut microbiota composition. Mucus-degrading bacteria appear to play a role in mucus breakdown, while probiotics may promote repair through short-chain fatty acids production.
Professor Xi Peng, the leading researcher of this study, emphasizes, “This study is a breakthrough in understanding the intricate relationship between gut microbiota and intestinal health post-burn injuries. It highlights the dual role of microbiota in both exacerbating and healing intestinal damage, offering a new perspective for targeted therapeutic strategies.”
This research holds significant promise for improving burn treatment outcomes. By targeting specific gut bacteria or their metabolites, it may be possible to protect the intestinal mucus barrier, prevent bacterial translocation, and ultimately improve patient survival and recovery. Further research is warranted to translate these findings into clinical applications.
Credit: Burns & Trauma
The gut microbiota, a complex ecosystem within the human intestinal tract, is increasingly recognized for its vital role in human health and disease. Notably, its relationship with intestinal damage due to burns has been underexplored. New study has unveiled the pivotal role of gut microbiota in the synthesis and degradation of intestinal mucus following burn injuries in mice. Utilizing advanced 16S rRNA and metagenomic sequencing techniques, researchers have identified significant changes in gut microbiota composition and its impact on the intestinal mucus barrier.
On a study (doi:10.1093/burnst/tkad056) published in the journal Burns & Trauma, researchers employed a combination of techniques to analyze the effects of burn injury on the gut microbiota and mucus barrier in mice. A modified histopathological grading system assessed colon tissue and mucus barrier integrity. 16S rRNA sequencing revealed changes in gut microbial composition over 10 days post-burn. Metagenomic sequencing provided deeper insights into mucus-related bacteria and potential underlying mechanisms.
This study provides compelling evidence that burn injury disrupts the intestinal mucus barrier and alters the gut microbiota composition. Mucus-degrading bacteria appear to play a role in mucus breakdown, while probiotics may promote repair through short-chain fatty acids production.
Professor Xi Peng, the leading researcher of this study, emphasizes, “This study is a breakthrough in understanding the intricate relationship between gut microbiota and intestinal health post-burn injuries. It highlights the dual role of microbiota in both exacerbating and healing intestinal damage, offering a new perspective for targeted therapeutic strategies.”
This research holds significant promise for improving burn treatment outcomes. By targeting specific gut bacteria or their metabolites, it may be possible to protect the intestinal mucus barrier, prevent bacterial translocation, and ultimately improve patient survival and recovery. Further research is warranted to translate these findings into clinical applications.
###
References
DOI
10.1093/burnst/tkad056
Original Source URL
https://doi.org/10.1093/burnst/tkad056
Funding information
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82172202) and the Innovative Leading Talents Project of Chongqing, China (No. cstc2022ycjh-bgzxm0148).
About Burns & Trauma
Burns & Trauma is an open access, peer-reviewed journal publishing the latest developments in basic, clinical, and translational research related to burns and traumatic injuries, with a special focus on various aspects of biomaterials, tissue engineering, stem cells, critical care, immunobiology, skin transplantation, prevention, and regeneration of burns and trauma injury.
Journal
Burns & Trauma
DOI
10.1093/burnst/tkad056
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
The impact of gut microbiota changes on the intestinal mucus barrier in burned mice: a study using 16S rRNA and metagenomic sequencing
Article Publication Date
19-Dec-2023
COI Statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests