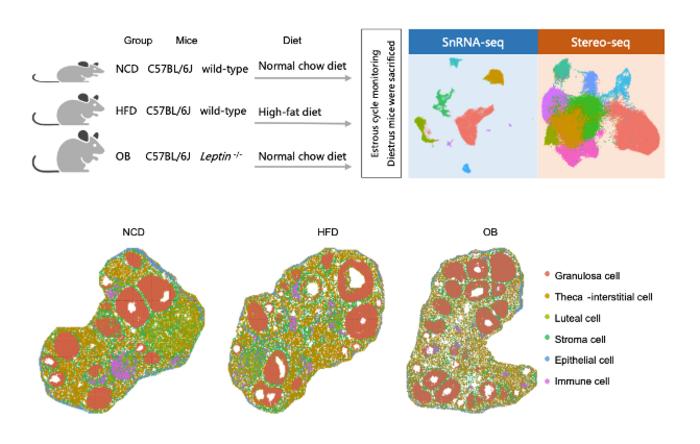
This study was led by Prof. Zi-Jiang Chen’ team from the Center for Reproductive Medicine of Shandong University, in collaboration with Prof. Fei Gao from the Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The researchers employed two types of obese mice induced by environmental and genetic factors as their experimental subjects. They utilized single-cell transcriptome technology(snRNA-seq) and nanoscale spatial transcriptome sequencing technology (Stereo-seq) to describe the panoramic cell map of the ovary (as shown in the figure). This mapping revealed both the similarities and differences in follicle development between the two types of obese mice, as well as the key regulatory molecular mechanisms involved.
Credit: ©Science China Press
This study was led by Prof. Zi-Jiang Chen’ team from the Center for Reproductive Medicine of Shandong University, in collaboration with Prof. Fei Gao from the Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. The researchers employed two types of obese mice induced by environmental and genetic factors as their experimental subjects. They utilized single-cell transcriptome technology(snRNA-seq) and nanoscale spatial transcriptome sequencing technology (Stereo-seq) to describe the panoramic cell map of the ovary (as shown in the figure). This mapping revealed both the similarities and differences in follicle development between the two types of obese mice, as well as the key regulatory molecular mechanisms involved.
The researchers identified six common cell types (see below, the bottom). They subsequently analyzed the cellular composition and functional changes within the follicles and in the extrafollicular region. Specifically, they focused on granulosa cells within the follicles, defining distinct types of granulosa cells at different stages of follicle development and elucidating their specific gene sets.
Through a series of advanced analyses, the researchers pinpointed the key transcription factor FOXO1, which plays a critical role in mediating the differences in granulosa cell development between the different types of obese mice. In the two types of obese model mice, the expression patterns of FOXO1 and its regulatory gene set differed greatly. For instance, Foxo1 and its target gene Cyp11a1 exhibited a negative correlation expression pattern in ovarian granulosa cells and displayed opposite expression patterns in the two types of obese model mice. These findings suggest that maintaining a dynamic balance of FOXO1 during follicular development is crucial, as excessive or insufficient expression can impair normal follicle development.
Additionally, the study discovered alterations in the composition and function of extrafollicular cells in obese mice. Notably, a small population of tumor-like cells was observed in the ovaries of obese mice. Given that obesity is associated with an increased risk of various tumors, including ovarian cancer, these findings warrant attention.
By providing a detailed panoramic view of the ovary under diet and genetically induced obesity conditions, this study enhances our understanding of the impact of obesity on the ovarian microenvironment. It holds significant implications for further research on obesity-related reproductive health issues in women.
See the article:
Cellular atlases of ovarian microenvironment alterations by diet and genetically-induced obesity
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-023-2360-3
Journal
Science China Life Sciences
DOI
10.1007/s11427-023-2360-3




