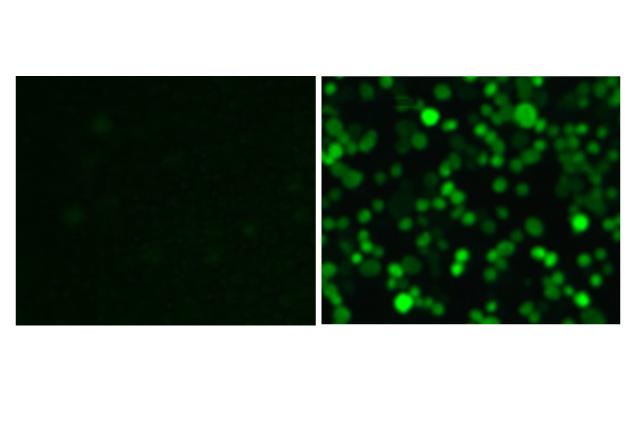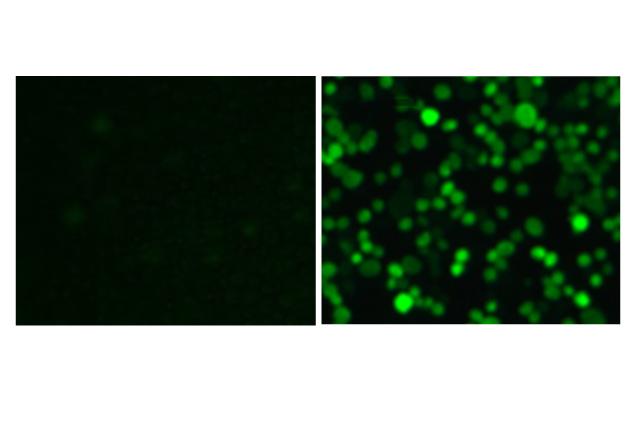
Credit: Source: Marina Freudenberg, Mareike Maler
Adenoviral infections have a mild disease progression in healthy people, but it can be dangerous for immunocompromised people. If a patient is infected with the virus and gets a bacterial infection on top of it, it can lead to an excessive inflammatory response known as a cytokine storm, an overreaction by the immune system leading to high concentrations of proteins that promote inflammation. Many patients do not survive this crisis. Mareike Maler from the University Hospital Freiburg, Prof. Dr. Marina Freudenberg from the Department of Pneumology at the University Hospital Freiburg and the BIOSS Centre for Biological Signalling Studies, Dr. György Fejer from the University of Plymouth, England along with Prof. Dr. Wolfgang Schamel from the Department of Biology and the BIOSS Centre for Biological Signalling Studies have now identified an important adenovirus receptor in macrophages of mice. The receptor "MARCO" enables the adenoviruses to invade macrophages, important immune cells responsible for detecting and destroying pathogens. The findings of this study, in which immunologists from the MPI of Immunobiology and Epigenetics Freiburg, RWTH Aachen and the University of Zurich, Switzerland were also involved, have recently been published in the scientific journal mBio.
Previous studies with epithelial cells from skin and gland tissue showed that the viruses bind to the cell-surface proteins called integrins and to CAR, the receptor for coxsackievirus and adenovirus. Biologists have been searching for the adenovirus receptor in immune cells since the 1990s. The research in Freiburg sought to clarify how adenoviruses attack cells of the immune system; that is, on which receptors the viruses on the cellular surface land, in order to invade the cell. The clarification of this question is of particular interest because the pharmaceutical industry has recently shown interest in using adenoviruses in gene therapy to channel genetic information into human cells. During the first clinical trials, however, some patients showed symptoms of a cytokine storm, suggesting that they may have contracted a bacterial infection.
Up to now, the scavenger receptor MARCO was viewed mainly as a so-called pattern recognition receptor with which the macrophage recognizes bacteria. However, the new findings prove that the receptor has an additional function in fighting viral pathogens. MARCO is probably fundamental for activating macrophages, for instance, in order to produce inflammation-promoting cytokines. In addition, the researchers demonstrate that macrophages derived from bone marrow precursor cells are far less infected with the virus than the macrophages in the lung. The reason for this is partly because the bone marrow macrophages usually lack MARCO and therefore cannot effectively be attacked by the virus.
After the discovery of these scientific findings, it is now time to conduct testing on humans. Although the receptor MARCO is also found in humans, it is still not clear if the virus interacts with the same receptor in humans. Nonetheless, the study has provided information on how macrophages fight viruses and that they have the potential to activate a cytokine storm in humans. In the future, medication could be used to block the receptor MARCO, thereby avoiding the cytokine storm.
Marina Freudenberg has been researching the activation of macrophages since 1972. Since 2013, she has been working in Wolfgang Schamel's department in the Department of Biology at the BIOSS Centre for Biological Signalling Studies and at the Department of Pneumology, University of Freiburg. Mareike Maler, the study's first author, was a graduate student and György Fejer research scientist under Marina Freudenberg. Maler is currently pursuing her doctoral degree in the working group under Prof. Dr. Stefan Martin at the Department of Dermatology at the University Hospital Freiburg.
###
Original publication: Mareike D. Maler, Peter J. Nielsen, Nicole Stichling, Idan Cohen,?Zsolt Ruzsics, Connor Wood, Peggy Engelhard, Maarit Suomalainen,?Ildiko Gyory, Michael Huber, Joachim Müller-Quernheim, Wolfgang W. A. Schamel, Siamon Gordon, Thilo Jakob, Stefan F. Martin,?Willi Jahnen-Dechent, Urs F. Greber, Marina A. Freudenberg, György Fejer. 2017, Key Role of the Scavenger Receptor MARCO in Mediating Adenovirus Infection and Subsequent Innate Responses of Macrophages. mBio, 8 (4): e00670-17.
For more information about BIOSS: http://www.bioss.uni-freiburg.de
Kontakt:
Prof. Dr. Marina Freudenberg
Department of Pneumology
University Hospital Freiburg
BIOSS Centre for Biological Signalling Studies
Tel.: 0761/203-67510
E-Mail: [email protected]
Media Contact
Dr. Marina Freudenberg
[email protected]
49-761-203-67510
Original Source
https://www.pr.uni-freiburg.de/pm-en/2017/new-receptor-found-on-scavenger-cells http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/mBio.00670-17