Credit: Kanazawa University
[Background]
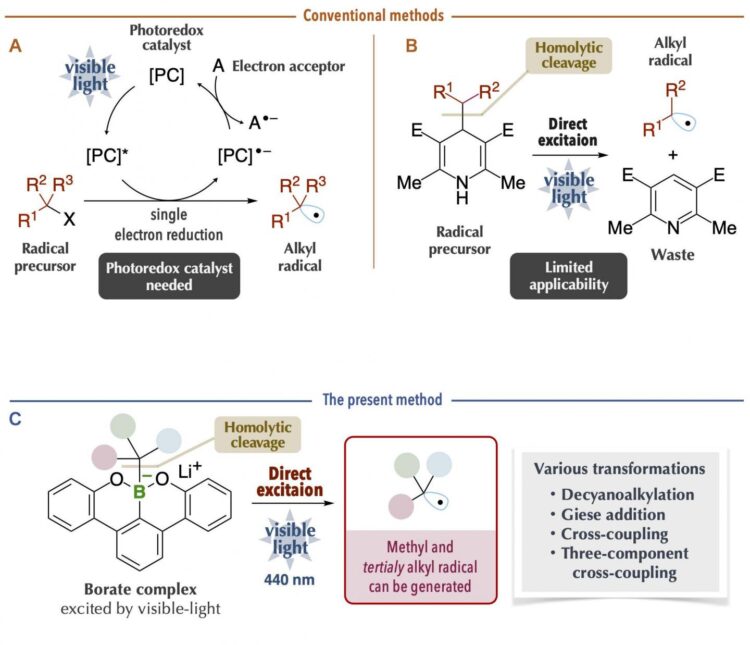
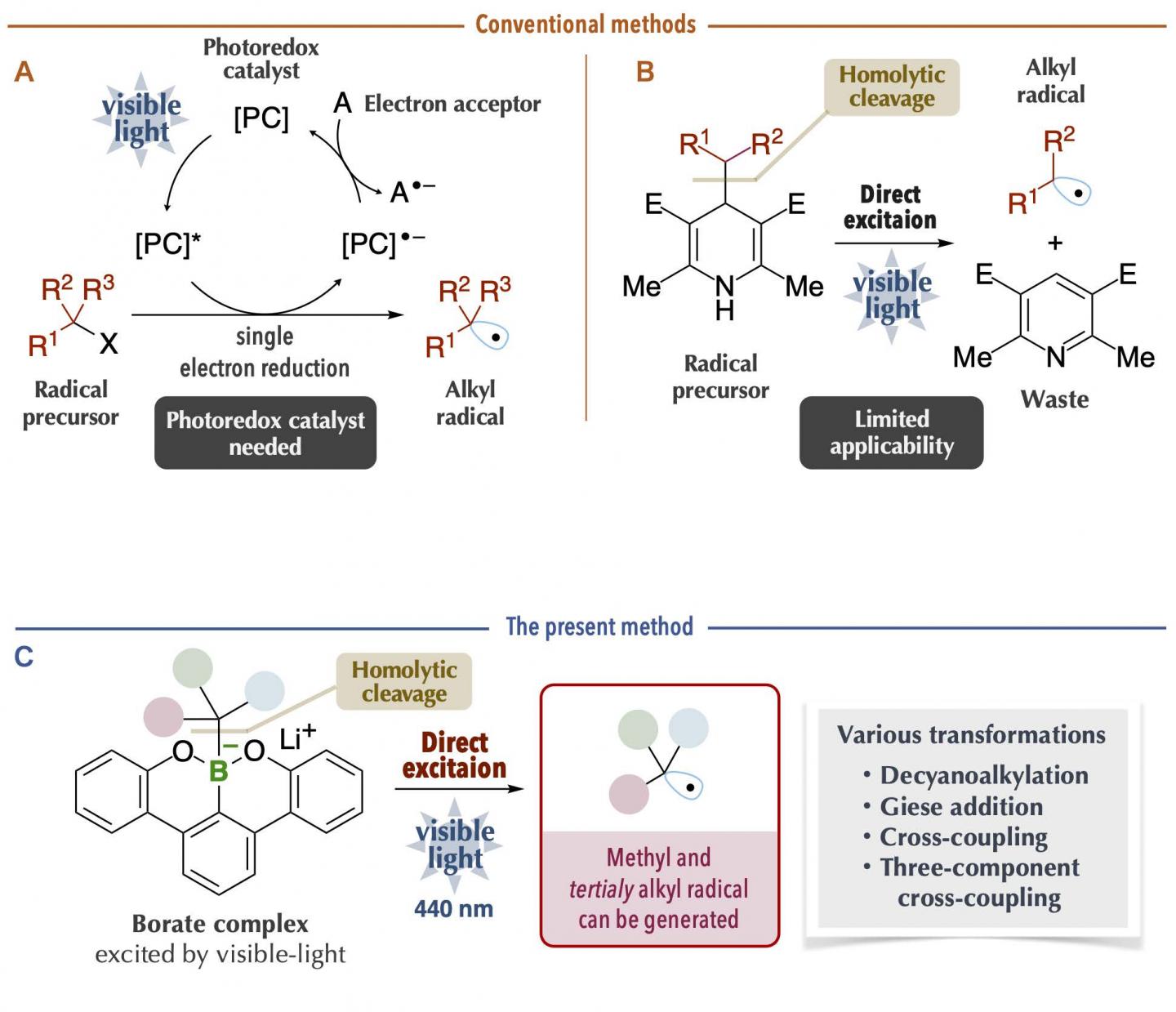
Alkyl radicals are carbon radicals of normal chain and branched chain alkanes, available as reaction intermediates even at late stages of synthesis. Recently, it has become possible to generate alkyl radicals under mild conditions by using a photoredox catalyst with organic chemicals (radical precursors) under visible-light irradiation (Figure 1A). However, since many photoredox catalysts are expensive and since it is necessary to consider the redox process of the catalysts themselves, chemical transformations may become complicated. Thus, a new method was reported on the generation of alkyl radicals by direct visible-light excitation, taking into account the photophysical properties of the organic chemicals themselves (Figure 1B). This is an excellent method in which the use of photoredox catalysts is unnecessary. Nonetheless, there are limitations in terms of the carbon radical species that can be generated. For example, it was difficult to generate bulky tertiary alkyl radicals and unstable methyl radicals, which are useful carbon sources for chemical reactions. In addition, it is problematic that the generation of carbon radicals is accompanied by the generation of waste chemicals of large molecular mass.
[Research results]
The research group at Kanazawa University led by Prof. Ohmiya including graduate students, in collaboration with scientists from RIKEN/Tokyo Medical and Dental University, has succeeded in generating carbon radicals with high chemical reactivity. By using the latest measurement technologies, they made a rational and precise design of an organoborate complex*1) prepared from “boracene,” which has a boron atom in the tetracene-like skeleton, through making full use of various latest measurement technologies. The organoborate complex thus designed and synthesized was able to absorb visible-light, giving rise to alkyl radicals under blue LED irradiation in the absence of photoredox catalysts (Figure 2).
The key to the success of the present study was that the organoborate complex prepared by the reaction of an alkyl nucleophile with “boracene,” in which three carbon atoms of a benzo[fg]tetracene*2) skeleton were replaced with a boron atom and two oxygen atoms, gave rise to homolytic cleavage*3) of a carbon-boron bond upon absorbing visible-light (Figure 2C). The organoborate complex excited by visible-light transfers a single electron to the other reactant or directly induces homolytic cleavage to give an alkyl radical. This process is highly efficient and enables generation of bulky tertiary alkyl radical and unstable methyl radicals, but production of these radicals was difficult to control. The alkyl radical generated by the present method could be used as a carbon source for chemical reactions. It was applied to, for example, decyanoalkylation, radical addition such as Giese addition, and nickel-catalyzed cross-coupling for the synthesis of compounds having complicated structures (Figure 3). It should be especially mentioned that the organoborate complex used in the present method can be reused by reacting an alkyl nucleophile with the boracene recovered after the chemical reaction.
[Future prospects]
The present study has enabled direct visible-light excitation of organoboron compounds*4) prepared from “boracene,” which has successfully generated a variety of alkyl radicals. The alkyl radicals generated by the present method can be used as carbon sources for chemical reactions and employed for the synthesis of complicated and/or bulky organic compounds, which were so far difficult to achieve. The present research outcome represents a novel organic synthesis protocol enabled by the combination of organoboron compounds and light energy and is expected to accelerate synthesis, for example, in drug discovery research. From an academic viewpoint, the reaction process of homolytic cleavage of the carbon-boron bond triggered by visible-light irradiation provides a framework for new molecular transformation technology.
###
[Glossary]
*1) Organoborate complex
An organic boron compound containing a negatively charged boron atom having four chemical bonds.
*2) Benzo[fg]tetracene
Tetracene is a compound with four linearly fused benzene rings. Benzo[fg]tetracene is a derivative of tetracene, having another benzene ring fused to the second and third benzene rings.
*3) Homolytic cleavage
Cleavage of a chemical bond having two electrons, where one electron ends up associated with one product and the other with another product.
*4) Organoboron compound
An organic compound having carbon-boron bond.
Media Contact
Ayako Honda
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.