Credit: Professor Luning Liu
Researchers at the University of Liverpool have unlocked new possibilities for the future development of sustainable, clean bioenergy. The study, published in Nature Communications, shows how bacterial protein ‘cages’ can be reprogrammed as nanoscale bioreactors for hydrogen production.
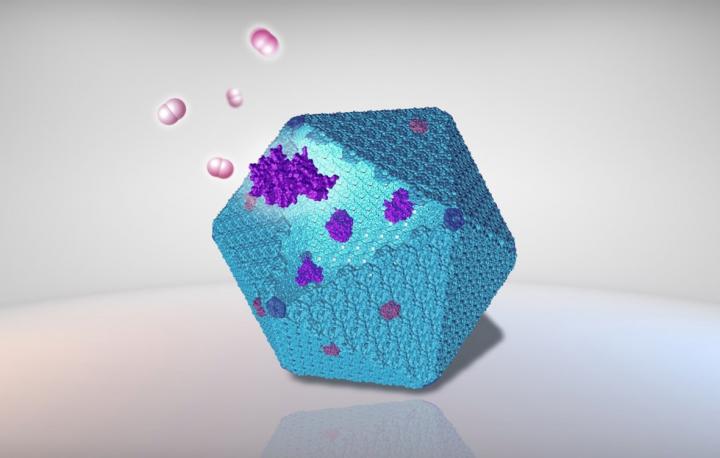
The carboxysome is a specialised bacterial organelle that encapsulates the essential CO2-fixing enzyme Rubisco into a virus-like protein shell. The naturally designed architecture, semi-permeability, and catalytic improvement of carboxysomes have inspired the rational design and engineering of new nanomaterials to incorporate different enzymes into the shell for enhanced catalytic performance.
The first step in the study involved researchers installing specific genetic elements into the industrial bacterium E. coli to produce empty carboxysome shells. They further identified a small ‘linker’ – called an encapsulation peptide – capable of directing external proteins into the shell.
The extreme oxygen sensitive character of hydrogenases (enzymes that catalyse the generation and conversion of hydrogen) is a long-standing issue for hydrogen production in bacteria, so the team developed methods to incorporate catalytically active hydrogenases into the empty shell.
Project lead Professor Luning Liu, Professor of Microbial Bioenergetics and Bioengineering at the Institute of Systems, Molecular and Integrative Biology, said: “Our newly designed bioreactor is ideal for oxygen-sensitive enzymes, and marks an important step towards being able to develop and produce a bio-factory for hydrogen production.”
In collaboration with Professor Andy Cooper in the Materials Innovation Factory (MIF) at the University, the researchers then tested the hydrogen-production activities of the bacterial cells and the biochemically isolated nanobioreactors. The nanobioreactor achieved a ~550% improvement in hydrogen-production efficiency and a greater oxygen tolerance in contrast to the enzymes without shell encapsulation.
“The next step for our research is answering how we can further stabilise the encapsulation system and improve yields,” said Professor Liu. “We are also excited that this technical platform opens the door for us, in future studies, to create a diverse range of synthetic factories to encase various enzymes and molecules for customised functions.”
First author, PhD student Tianpei Li, said: “Due to climate change, there is a pressing need to reduce the emission of carbon dioxide from burning fossil fuels. Our study paves the way for engineering carboxysome shell-based nanoreactors to recruit specific enzymes and opens the door for new possibilities for developing sustainable, clean bioenergy.”
###
The project was funded by Royal Society, Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (BBSRC), British Council Newton Fund and Leverhulme Trust. The project was also carried out in collaboration with the Centre for Cell Imaging, Centre for Proteome Research and Biomedical Electron Microscopy Unit at the University, and researchers from Henan University and Central South University, China.
Media Contact
Nicola Frost
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




