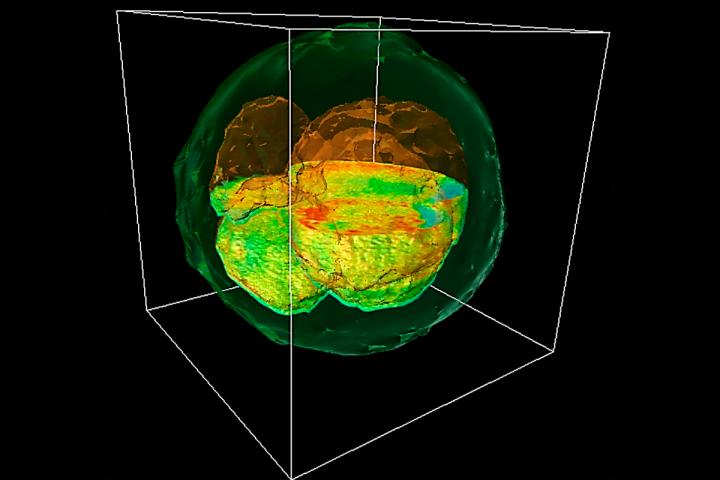
Credit: Image courtesy Gabriel Popescu
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — University of Illinois researchers have developed a way to produce 3-D images of live embryos in cattle that could help determine embryo viability before in vitro fertilization in humans.
Infertility can be devastating for those who want children. Many seek treatment, and the cost of a single IVF cycle can be $20,000, making it desirable to succeed in as few attempts as possible. Advanced knowledge regarding the health of embryos could help physicians select those that are most likely to lead to successful pregnancies.
The new method, published in the journal Nature Communications, brought together electrical and computer engineering professor Gabriel Popescu and animal sciences professor Matthew Wheeler in a collaborative project through the Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology at the U. of I.
Called gradient light interference microscopy, the method solves a challenge that other methods have struggled with — imaging thick, multicellular samples.
In many forms of traditional biomedical microscopy, light is shined through very thin slices of tissue to produce an image. Other methods use chemical or physical markers that allow the operator to find the specific object they are looking for within a thick sample, but those markers can be toxic to living tissue, Popescu said.
"When looking at thick samples with other methods, your image becomes washed out due to the light bouncing off of all surfaces in the sample," said graduate student Mikhail Kandel, the co-lead author of the study. "It is like looking into a cloud."
GLIM can probe deep into thick samples by controlling the path length over which light travels through the specimen. The technique allows the researchers to produce images from multiple depths that are then composited into a single 3-D image.
To demonstrate the new method, Popescu's group joined forces with Wheeler and his team to examine cow embryos.
"One of the holy grails of embryology is finding a way to determine which embryos are most viable," Wheeler said. "Having a noninvasive way to correlate to embryo viability is key; before GLIM, we were taking more of an educated guess."
Those educated guesses are made by examining factors like the color of fluids inside the embryonic cells and the timing of development, among others, but there is no universal marker for determining embryo health, Wheeler said.
"This method lets us see the whole picture, like a three-dimensional model of the entire embryo at one time," said Tan Nguyen, the other co-lead author of the study.
Choosing the healthiest embryo is not the end of the story, though. "The ultimate test will be to prove that we have picked a healthy embryo and that it has gone on to develop a live calf," said Marcello Rubessa, a postdoctoral researcher and co-author of the study.
"Illinois has been performing in vitro studies with cows since the 1950s," Wheeler said. "Having the resources made available through Gabriel's research and the other resources at Beckman Institute have worked out to be a perfect-storm scenario."
The team hopes to apply GLIM technology to human fertility research and treatment, as well as a range of different types of tissue research. Popescu plans to continue collaborating with other biomedical researchers and already has had success looking at thick samples of brain tissue in marine life for neuroscience studies.
###
The National Science Foundation, the U. of I. Computational Science and Engineering fellowship and the U. of I. Yuen T. Lo Outstanding Research Award supported this research.
Editor's notes:
To reach Gabriel Popescu, call 217-333-4840; [email protected]
To reach Matthew Wheeler, call 217-333-2239; [email protected]
The paper "Gradient light interference microscopy for 3D imaging of unlabeled specimens" is available online and from the U. of I. News Bureau.
Media Contact
Lois E Yoksoulian
[email protected]
217-244-2788
@NewsAtIllinois
http://www.illinois.edu