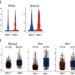
When visualizing data using networks, the type of representation is crucial for extracting hidden information and relationships. The research group of Jörg Menche, Adjunct Principal Investigator at the CeMM Research Center for Molecular Medicine of the Austrian Academy of Sciences, Professor at the University of Vienna, and Group leader at Max Perutz Labs, developed a new method for generating network layouts that allow for visualizing different information of a network in two- and three-dimensional virtual space and exploring different perspectives. The results could also facilitate future research on rare diseases by providing more versatile, comprehensible representations of complex protein interactions.
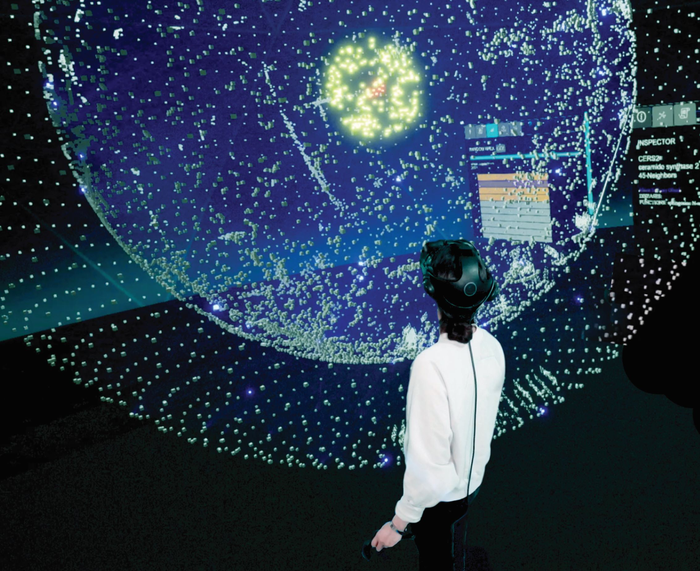

Credit: Christiane V.R. Hütter, published in Nature Computational Science 2022.
When visualizing data using networks, the type of representation is crucial for extracting hidden information and relationships. The research group of Jörg Menche, Adjunct Principal Investigator at the CeMM Research Center for Molecular Medicine of the Austrian Academy of Sciences, Professor at the University of Vienna, and Group leader at Max Perutz Labs, developed a new method for generating network layouts that allow for visualizing different information of a network in two- and three-dimensional virtual space and exploring different perspectives. The results could also facilitate future research on rare diseases by providing more versatile, comprehensible representations of complex protein interactions.
Network visualizations allow for exploring connections between individual data points. However, the more complex and larger the networks, the more difficult it becomes to find the information you are looking for. For lack of suitable layouts, so-called “hairballs” visualizations emerge, that often obscure network structure, rather than elucidate it. Scientists from Jörg Menche’s research group at CeMM and Max Perutz Labs (a joint venture of the University of Vienna and the Medical University of Vienna), developed a method that makes it possible to specify in advance which network properties and information should be visually represented in order to explore them interactively. The results have now been published in Nature Computational Science.
Reducing complexity
For the study, first author Christiane V. R. Hütter, a PhD student in Joerg Menche’s research group, used the latest dimensionality reduction techniques that allow visualizations for networks with thousands of points to be computed within a very short time on a standard laptop. “The key idea behind our research was to develop different views for large networks to capture the complexity and get a more comprehensive view and present it in a visually understandable way – similar to looking at maps of the same region with different information content, detailed views and perspectives.” Menche Lab scientists developed four different network layouts, which they termed cartographs, as well as two- and three-dimensional visualizations, each following different rules to open up new perspectives on a given dataset. Any network information can be encoded and visualized in this fashion, for example, the structural significance of a particular point, but also functional features. Users can switch between different layouts to get a comprehensive picture. Study leader Jörg Menche explains: “Using the new layouts, we can now specify in advance that we want to see, for example, the number of connections of a point within the network represented, or a particular functional characteristic. In a biological network, for instance, I can explore connections between genes that are associated with a particular disease and what they might have in common.”
The interplay of genes
The scientists performed a proof-of-concept on both simple model networks and the complex interactome network, which maps all the proteins of the human body and their interactions. This consists of more than 16,000 points and over 300,000 connections. Christiane V.R. Hütter explains: “Using our new layouts, we are now able to visually represent different features of proteins and their connections, such as the close relationship between the biological importance of a protein and its centrality within the network. We can also visualize connection patterns between a group of proteins associated with the same disease that are difficult to decipher using conventional methods.”
Tailored solutions
The flexibility of the new framework allows users to tailor network visualizations for a specific application. For example, the study authors were able to develop 3D interactome layouts specifically for studying the biological functions of certain genes whose mutations are suspected to cause rare diseases. Jörg Menche adds, “To facilitate the visual representation and also analysis of large networks such as the interactome, our layouts can also be integrated into a virtual reality platform.”
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
The study “Network Cartographs for Interpretable Visualizations” was published in the journal Nature Computational Science on 24 February 2022. DOI: 10.1038/s43588-022-00199-z.
Authors: Christiane V. R. Hütter, Celine Sin, Felix Müller, Jörg Menche;
Jörg Menche studied physics in Leipzig, Recife and Berlin. He did his PhD at the Max-Planck-Institute for Colloids and Interfaces in Potsdam (Germany) and was a postdoctoral fellow at Northeastern University and at the Center for Cancer Systems Biology at Dana Farber Cancer Institute in Boston. He joined CeMM in 2015 as a Principal Investigator. In September 2020, he received a joint professorship at the Max Perutz Labs and the Faculty of Mathematics of the University of Vienna and became CeMM Adjunct PI.
The CeMM Research Center for Molecular Medicine of the Austrian Academy of Sciences is an international, independent and interdisciplinary research institution for molecular medicine under the scientific direction of Giulio Superti-Furga. CeMM is oriented towards medical needs and integrates basic research and clinical expertise to develop innovative diagnostic and therapeutic approaches for precision medicine. Research focuses on cancer, inflammation, metabolic and immune disorders, and rare diseases. The Institute’s research building is located on the campus of the Medical University and the Vienna General Hospital. www.cemm.at
The Max Perutz Labs are a research institute established by the University of Vienna and the Medical University of Vienna to provide an environment for excellent, internationally recognized research and education in the field of Molecular Biology. Dedicated to a mechanistic understanding of fundamental biomedical processes, scientists at the Max Perutz Labs aim to link breakthroughs in basic research to advances in human health. The Max Perutz Labs are located at the Vienna BioCenter, one of Europe’s hotspots for Life Sciences, and host around 45 research groups, involving more than 450 scientists and staff from 40 nations. www.maxperutzlabs.ac.at
Journal
Nature Computational Science
DOI
10.1038/s43588-022-00199-z
Article Title
Network Cartographs for Interpretable Visualizations
Article Publication Date
24-Feb-2022