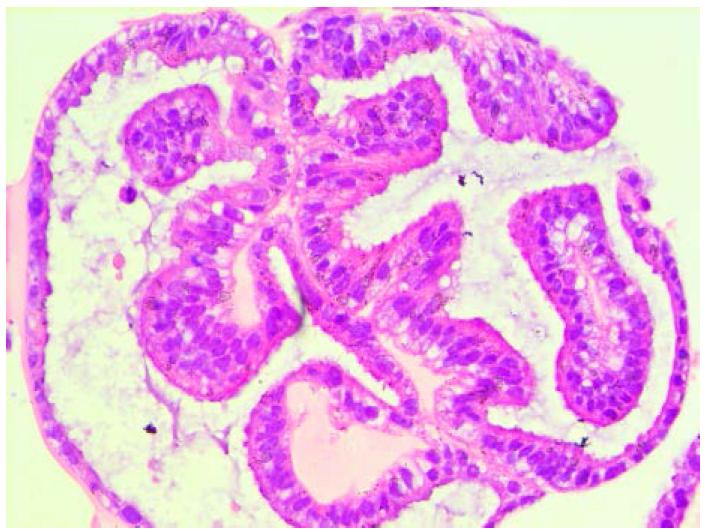
Credit: Matteo Boretto, et al.
Scientists at KU Leuven (University of Leuven), Belgium, have succeeded in growing three-dimensional cultures of the endometrium, the uterus' inner lining, in a dish. These so-called endometrial organoids promise to shed light onto the processes that occur during the monthly menstrual cycle and open up the possibility of studying diseases of the uterus, such as endometrial atrophy (thinning of the lining) or cancer, in a lab culture system.
Every month, the tissue that lines a woman's womb first thickens, then matures and finally – unless the woman becomes pregnant — degenerates in a cycle that is regulated by changing levels of the female hormones oestrogen and progesterone. This process is disrupted in diseases such as endometrial cancer, with serious consequences for the patient's fertility. However, we understand little about how these dynamic changes occur or about what goes wrong in disease, mainly because we lack good culture models for endometrial tissue. In a new study published in the journal Development, the KU Leuven researchers show that individual or small groups of cells from uterus biopsies can be made to grow into three-dimensional structures that show many of the features of the womb lining, including the ability to produce mucus. Importantly, these endometrial organoids respond to the female hormones in a way similar to the endometrium in the body, allowing scientists to mimic the menstrual cycle in a dish.
Matteo Boretto, the first author on this study, commented that "we were very excited to see that we could not only robustly grow and amplify endometrial tissue in a dish, but that the tiny structures were also able to reproduce normal responses of the endometrium to hormones: oestrogen makes the tissue thicken, progesterone then induces maturation including folding (see picture), and subsequent removal of both hormones mimics the cell shedding of the menstrual period".
Although the endometrial organoids produced in the lab only contain a part of the structure that makes up the womb, the researchers hope that it will soon be possible to grow these organoids together with other cells that comprise the uterus, to more accurately model this key reproductive organ.
In the meantime, the new technique will already help scientists to develop a more detailed understanding of how the womb responds to hormones during the menstrual cycle. Importantly, the technique will also make it possible for researchers to grow organoids from diseased endometrium such as in endometrial atrophy or cancer. This approach will allow in-depth study of these diseases and may serve as a valuable system for drug discovery and screening.
Hugo Vankelecom, the lead author on this study, explained that "our new model provides several exciting perspectives. First, it allows the reliable and robust expansion of endometrial biopsies which usually are very small in size, thereby enabling extensive examination which was not possible before. Second, patient organoids will help us to understand malfunctions of the endometrium, which may lead to new and better treatments for uterine diseases and accompanying fertility problems. Simultaneously, the organoids will provide a platform to test the efficiency and toxicity of new drugs. For all these reasons, we also believe that companies will eventually be interested in our accomplishment."
###
Media Contact
Hugo Vankelecom
[email protected]
@Co_Biologists
Home
Original Source
http://dev.biologists.org/content/142/4/681 http://dx.doi.org/10.1242/dev.148478