Credit: SIAT
Magnetic resonance thermometry (MRT) is the only imaging technique that noninvasively provides temperature distribution in vivo. The water proton resonance frequency shift (PRFS)-based method is the most popular choice for MR temperature monitoring in aqueous tissues.
A research team led by Prof. ZHENG Hairong from the Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences developed a "dual-step iterative temperature estimation (DITE)" method for fat-referenced PRFS temperature imaging in fat-containing tissues.
In mammals, there are two types of adipose (i.e., fat-containing) tissue: white adipose tissue (WAT) and brown adipose tissue (BAT).
"WAT stores excess energy as triacylglycerol, whereas BAT burns fat to dissipate energy in the form of heat after activation and is now considered to be the next potential therapeutic target for metabolic syndrome" said ZHENG.
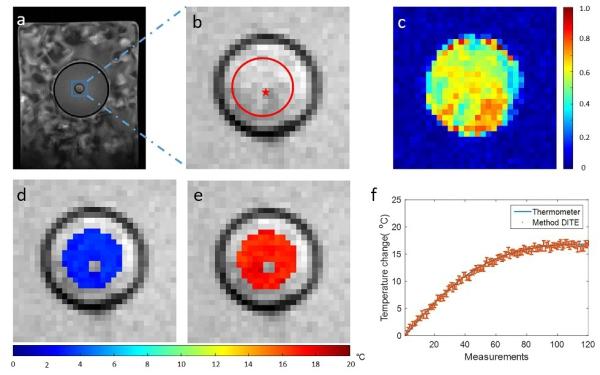
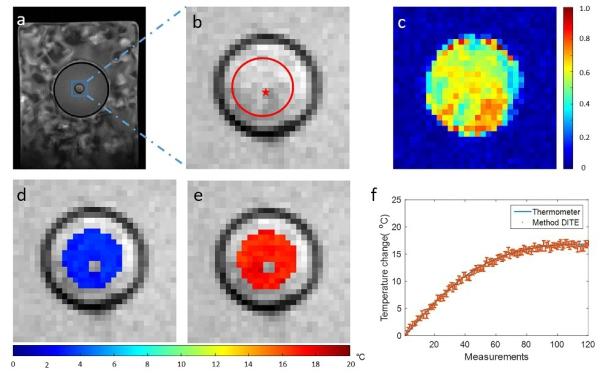
The proposed DITE method achieved accurate and precise temperature estimation compared with the results measured by the fluorescent thermometer, a common method and a golden standard of measuring temperature.
The average mean error, standard deviation, and root mean squared error were -0.08°C, 0.46°C and 0.56°C, respectively, within the region of interest (ROI) around the thermometer in the ex vivo BAT using a water bath experiment. The method can provide a potential imaging tool for the characterization of brown adipose tissue in vivo.
Prof. ZHENG said, "In the future, we will apply this method to monitor the temperature in BAT in vivo and characterize BAT activity using this temperature imaging technique."
By modulating BAT activity, this study provides crucial insight relevant to the treatment of metabolic diseases such as diabetes, obesity, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
###
The study entitled "Dual-step iterative temperature estimation method for accurate and precise fat-referenced PRFS temperature imaging" was published in Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Media Contact
ZHANG Xiaomin
[email protected]
http://english.cas.cn/
Original Source
http://english.cas.cn/ http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/mrm.27396