Credit: Tokyo Institute of Technology
Traditional computer memory, known as DRAM, uses electric fields to store information. In DRAM, the presence or absence of an electric charge is indicated either by number 1 or number 0. Unfortunately, this type of information storage is transient and information is lost when the computer is turned off. Newer types of memory, MRAM and FRAM, use long-lasting ferromagnetism and ferroelectricity to store information. However, no technology thus far combines the two.
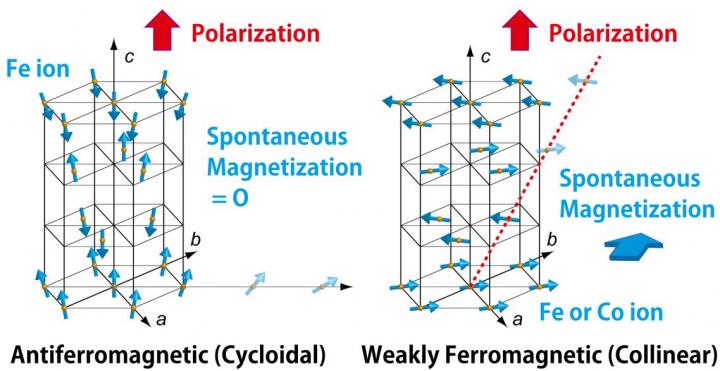
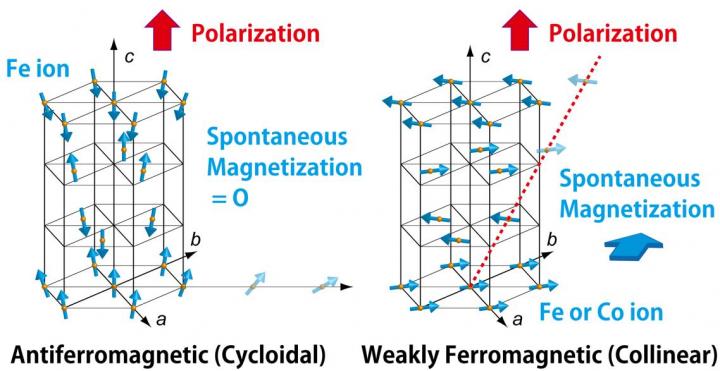
To address this challenge, a group of scientists led by Prof. Masaki Azuma from the Laboratory for Materials and Structures at Tokyo Institute of Technology, along with associate Prof. Hajime Hojo at Kyushu University previously at Tokyo Tech, Prof. Ko Mibu at Nagoya Institute of Technology and five other researchers demonstrated the multiferroic nature of a thin film of BiFe1?xCoxO3 (BFCO). Multiferroic materials exhibit both ferromagnetism and ferroelectricity. These are expected to be used as multiple-state memory devices. Furthermore, if the two orders are strongly coupled and the magnetization can be reversed by applying an external electric field, the material should work as a form of low power consumption magnetic memory.
Previous scientists had speculated that ferroelectric BFO thin film, a close relative of BFCO, might be ferromagnetic as well, but they were thwarted by the presence of magnetic impurity. Prof. M. Azuma's team successfully synthesized pure, thin films of BFCO by using pulsed laser deposition to perform epitaxial growth on a SrTiO3 (STO) substrate. They then conducted a series of tests to show that BFCO is both ferroelectric and ferromagnetic at room temperature. They manipulated the direction of ferroelectric polarization by applying an electric field, and showed that the low-temperature cychloidal spin structure, essentially the same as that of BiFeO3, changes to a collinear one with ferromagnetism at room temperature.
In the future, the scientists hope to realize electrical control of ferromagnetism, which could be applied in low power consumption, non-volatile memory devices.
###
Media Contact
Emiko Kawaguchi
[email protected]
81-357-342-975
http://www.titech.ac.jp/english/index.html
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag