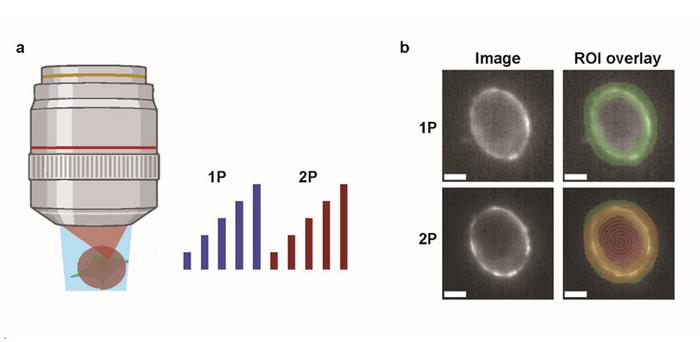
In the quest to unravel the complexities of neural circuits, scientists are beginning to use genetically encoded voltage indicators (GEVIs) to visualize electrical activity in the brain. These indicators are crucial for understanding how neurons communicate and process information. However, the effectiveness of one-photon (1P) versus two-photon (2P) voltage imaging has remained a topic of debate. A recent study by researchers at Harvard University sheds light on the relative merits and limitations of these two imaging techniques, providing valuable insights for the scientific community.
In the quest to unravel the complexities of neural circuits, scientists are beginning to use genetically encoded voltage indicators (GEVIs) to visualize electrical activity in the brain. These indicators are crucial for understanding how neurons communicate and process information. However, the effectiveness of one-photon (1P) versus two-photon (2P) voltage imaging has remained a topic of debate. A recent study by researchers at Harvard University sheds light on the relative merits and limitations of these two imaging techniques, providing valuable insights for the scientific community.
As reported in Neurophotonics, the research team engaged in a comprehensive comparison of 1P and 2P voltage imaging, focusing on the optical and biophysical constraints unique to each method. They evaluated the brightness and voltage sensitivity of commonly used GEVIs under both 1P and 2P illumination. Additionally, they measured how fluorescence decreases with depth in the mouse brain, a critical factor for in vivo imaging.
To quantify their findings, the researchers developed a model that predicts the number of measurable cells based on reporter properties, imaging parameters, and the desired signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). They also explored how advancements in sensor technology and imaging modalities could impact the performance of voltage imaging.
One of the key findings of the study is that 2P excitation requires approximately 10,000 times more illumination power per cell compared to 1P excitation to achieve similar photon count rates. This significant power requirement poses challenges for 2P voltage imaging, particularly in terms of tissue photodamage and shot noise. For instance, using the JEDI-2P indicator in the mouse cortex with a target SNR of 10, a measurement bandwidth of 1 kHz, a laser power limit of 200 mW, and a repetition rate of 80MHz, 2P imaging can record from no more than about 12 neurons simultaneously at depths greater than 300 micrometers.
The researchers concluded that the stringent photon-count requirements and modest voltage sensitivity of current GEVIs make 2P voltage imaging in vivo a challenging endeavor. Achieving high SNR for hundreds of neurons at significant depths will necessitate either substantial improvements in 2P GEVIs or the development of entirely new imaging approaches.
This study highlights the trade-offs between 1P and 2P voltage imaging and underscores the need for continued innovation in imaging technologies to advance our understanding of neural circuits. As researchers strive to overcome these challenges, the insights gained from this study will undoubtedly guide future developments in the field.
For details, see the original Gold Open Access article by F. P. Brooks III, H. C. Davis, et al., “Optical constraints on two-photon voltage imaging,” Neurophotonics 11(3) 035007 (2024), doi 10.1117/1.NPh.11.3. 035007.
Journal
Neurophotonics
DOI
10.1117/1.NPh.11.3.035007
Article Title
Optical constraints on two-photon voltage imaging
Article Publication Date
13-Aug-2024