Research led by the University of Plymouth has shown that a new deep learning AI model can identify what happens and when during embryonic development, from video.
Credit: University of Plymouth
Research led by the University of Plymouth has shown that a new deep learning AI model can identify what happens and when during embryonic development, from video.
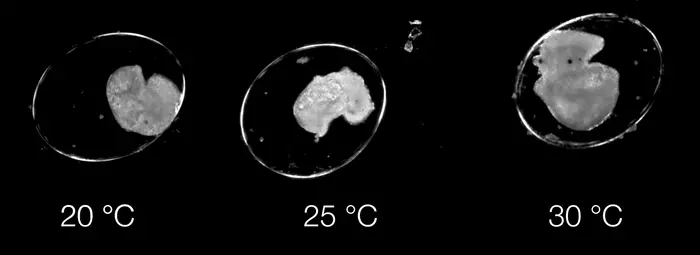
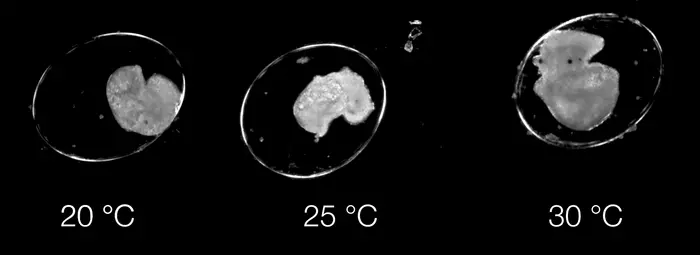
Published today (Wednesday 29 May) in the Journal of Experimental Biology, the study highlights how the model, known as Dev-ResNet, can identify the occurrence of key functional developmental events in pond snails, including heart function, crawling, hatching and even death.
A key innovation in this study is the use of a 3D model that uses changes occurring between frames of the video, and enables the AI to learn from these features, as opposed to the more traditional use of still images.
The use of video means features ranging from the first heartbeat, or crawling behaviour, through to shell formation or hatching are reliably detected by Dev-ResNet, and has revealed sensitivities of different features to temperature not previously known.
While used in pond snail embryos for this study, the authors say the model has broad applicability across all species, and they provide comprehensive scripts and documentation for applying Dev-ResNet in different biological systems.
In future, the technique could be used to help accelerate understanding on how climate change, and other external factors, affect humans and animals.
The work was led by PhD candidate, Ziad Ibbini, who studied BSc Conservation Biology at the University, before taking a year out to upskill himself in software development, then beginning his PhD. He designed, trained and tested Dev-ResNet himself.
He said: “Delineating developmental events – or working out what happens when in an animal’s early development – is so challenging, but incredibly important as it helps us to understand changes in event timing between species and environments.
“Dev-ResNet is a small and efficient 3D convolutional neural network capable of detecting developmental events using videos, and can be trained relatively easily on consumer hardware.
“The only real limitations are in creating the data to train the deep learning model – we know it works, you just need to give it the right training data.
“We want to equip the wider scientific community with the tools that will enable them to better understand how a species’ development is affected by different factors, and thus identifying how we can protect them. We think that Dev-ResNet is a significant step in that direction.”
Dr Oli Tills, the paper’s senior author and a UKRI Future Leaders Research Fellow, added: “This research is important on a technological level, but it is also significant for advancing how we perceive organismal development – something that the University of Plymouth, within the Ecophysiology and Development research Group, has more than 20 years’ history of researching.
“This milestone would not have been possible without deep learning, and it is exciting to think of where this new capability will lead us in the study of animals during their most dynamic period of life.”
The full paper, entitled Dev-ResNet: Automated developmental event detection using deep learning, is now available to view in the Journal of Experimental Biology (doi: 10.1242/jeb.247046).
Journal
Journal of Experimental Biology
DOI
10.1242/jeb.247046
Method of Research
Computational simulation/modeling
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
Dev-ResNet: Automated developmental event detection using deep learning
Article Publication Date
29-May-2024