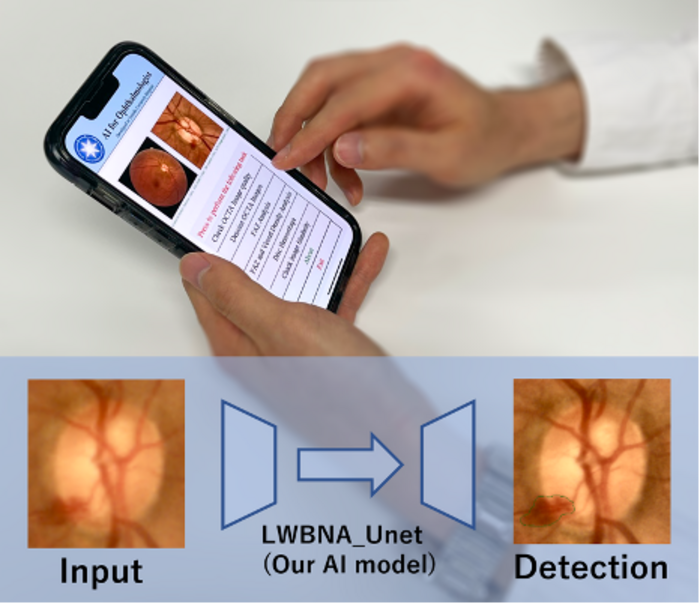
A new deep learning (DL) model that can identify disease-related features from images of eyes has been unveiled by a group of Tohoku University researchers. This ‘lightweight’ DL model can be trained with a small number of images, even ones with a high-degree of noise, and is resource-efficient, meaning it is deployable on mobile devices.
Credit: Sharma et al.
A new deep learning (DL) model that can identify disease-related features from images of eyes has been unveiled by a group of Tohoku University researchers. This ‘lightweight’ DL model can be trained with a small number of images, even ones with a high-degree of noise, and is resource-efficient, meaning it is deployable on mobile devices.
Details were published in the journal Scientific Reports on May 20, 2022.
With many societies aging and limited medical personnel, DL model reliant self-monitory and tele-screening of diseases are becoming more routine. Yet, deep learning algorithms are generally task specific, and identify or detect general objects such as humans, animals, or road signs.
Identifying diseases, on the other hand, demands precise measurement of tumors, tissue volume, or other sorts of abnormalities. To do so requires a model to look at separate images and mark boundaries in a process known as segmentation. But accurate prediction takes greater computational output, rendering them difficult to deploy on mobile devices.
“There is always a trade-off between accuracy, speed and computational resources when it comes to DL models,” says Toru Nakazawa, co-author of the study and professor at Tohoku University’s Department of Ophthalmology. “Our developed model has better segmentation accuracy and enhanced model training reproducibility, even with fewer parameters – making it efficient and more lightweight when compared to other commercial softwares.”
Professor Nakazawa, Associate Professor Parmanand Sharma, Dr Takahiro Ninomiya, and students from the Department of Ophthalmology worked with professor Takayuki Okatani from Tohoku University’s Graduate School of Information Sciences to produce the model.
Using low resource devices, they obtained measurements of the foveal avascular zone, a region with the fovea centralis at the center of the retina, to enhance screening for glaucoma.
“Our model is also capable of detecting/segmenting optic discs and hemorrhages in fundus images with high precision,” added Nakazawa.
In the future, the group is hopeful of deploying the lightweight model to screen for other common eye disorders and other diseases.
Journal
Scientific Reports
DOI
10.1038/s41598-022-12486-w
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
New Deep Learning Model Helps the Automated Screening of Common Eye Disorders
Article Publication Date
20-May-2022




