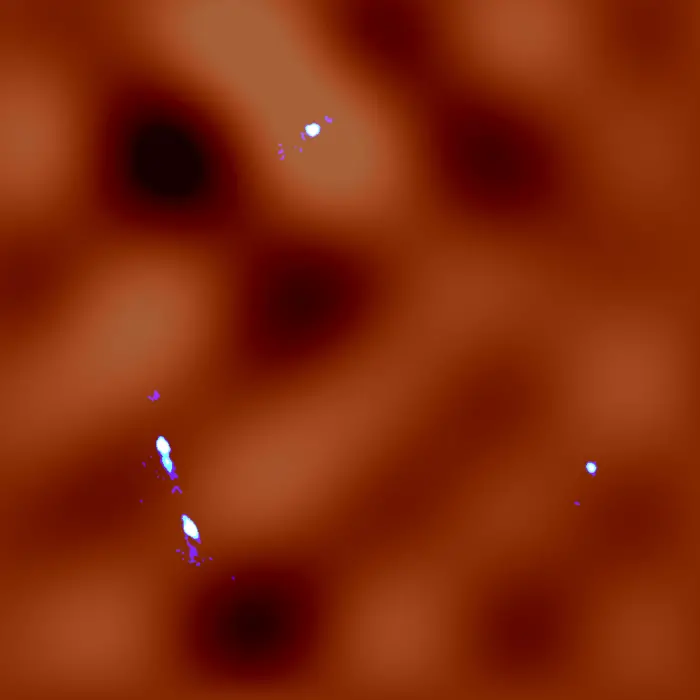
New research has revealed the distribution of dark matter in never before seen detail, down to a scale of 30,000 light-years. The observed distribution fluctuations provide better constraints on the nature of dark matter.
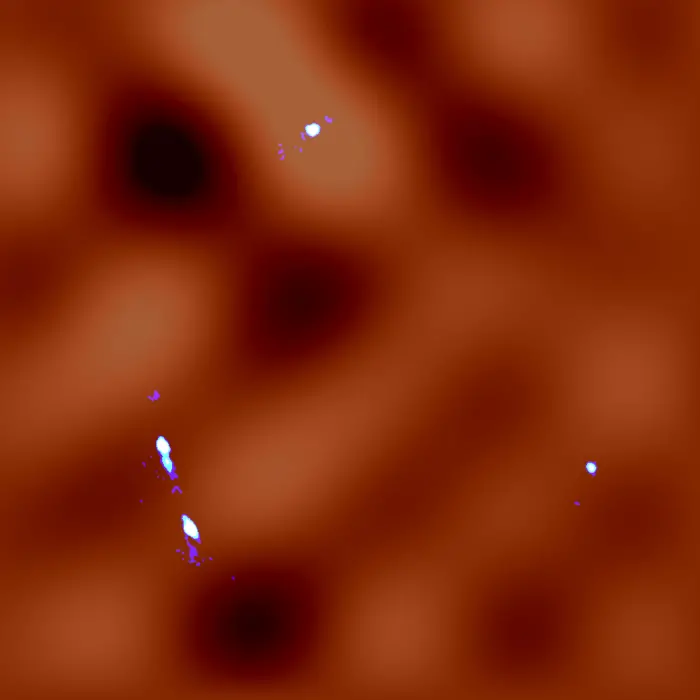
Credit: ALMA(ESO/NAOJ/NRAO), K. T. Inoue et al.
New research has revealed the distribution of dark matter in never before seen detail, down to a scale of 30,000 light-years. The observed distribution fluctuations provide better constraints on the nature of dark matter.
Mysterious dark matter accounts for most of the matter in the Universe. Dark matter is invisible and makes itself know only through its gravitational effects. Dark matter has never been isolated in a laboratory, so researchers must rely on “natural experiments” to study it.
One type of natural experiment is a gravitational lens. Sometimes by random chance, two objects at different distances in the Universe will lie along the same line-of-sight when seen from Earth. When this happens, the spatial curvature caused by the matter around the foreground object acts like a lens, bending the path of light from the background object and making a lensed image. However, it is difficult to achieve the high resolution to detect clumps of dark matter which are less massive than galaxies in natural experiments, so the exact nature of dark matter has been poorly constrained.
A team of Japanese researchers led by Professor Kaiki Taro Inoue at Kindai University used ALMA (Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array) to study the gravitational lens system known as MG J0414+0534 in the direction of the constellation Taurus. In this system, the foreground object forms not one, but four images of the background object due to the gravitational force of a massive galaxy acting on the light. With the help of the bending effect and their new data analysis method, the team was able to detect fluctuations in the dark matter distribution along the line-of-sight in higher resolution than ever before, down to a scale of 30,000 light-years.
The new constraints provided by the observed distribution are consistent with models for slow moving, or “cold,” dark matter particles.
In the future the team plans to further constrain the nature of dark matter with additional observations.
Journal
The Astrophysical Journal
DOI
10.3847/1538-4357/aceb5f
Method of Research
Observational study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
ALMA Measurement of 10 kpc-scale Lensing Power Spectra towards the Lensed Quasar MG J0414+0534
Article Publication Date
7-Sep-2023