Credit: LIU Yajun
A research group from the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT), Chinese Academy of Sciences, has developed a novel strategy for cost-efficient lignocellulose conversion. Known as consolidated bio-saccharification (CBS), it combines cellulase production and hydrolysis, while separating fermentation from the integrated process by taking fermentable sugar as the target product to couple various downstream fermentation processes.
The industrial conversion of biomass to high-value biofuels and biochemicals is mainly restricted by lignocellulose solubilization. Previously, three strategies had been reported for lignocellulose bioconversion, i.e., separate enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation (SHF), simultaneous saccharification and fermentation (SSF), and consolidated bioprocessing (CBP).
For SHF and SSF, cellulases are usually produced by fungi aerobically in a different reactor and the enzyme cost is an essential issue to consider. In contrast, CBP integrates enzyme production, cellulose hydrolysis, and fermentation in one step to reduce cellulase and investment costs, but involves relatively low saccharification efficiency and simple products.
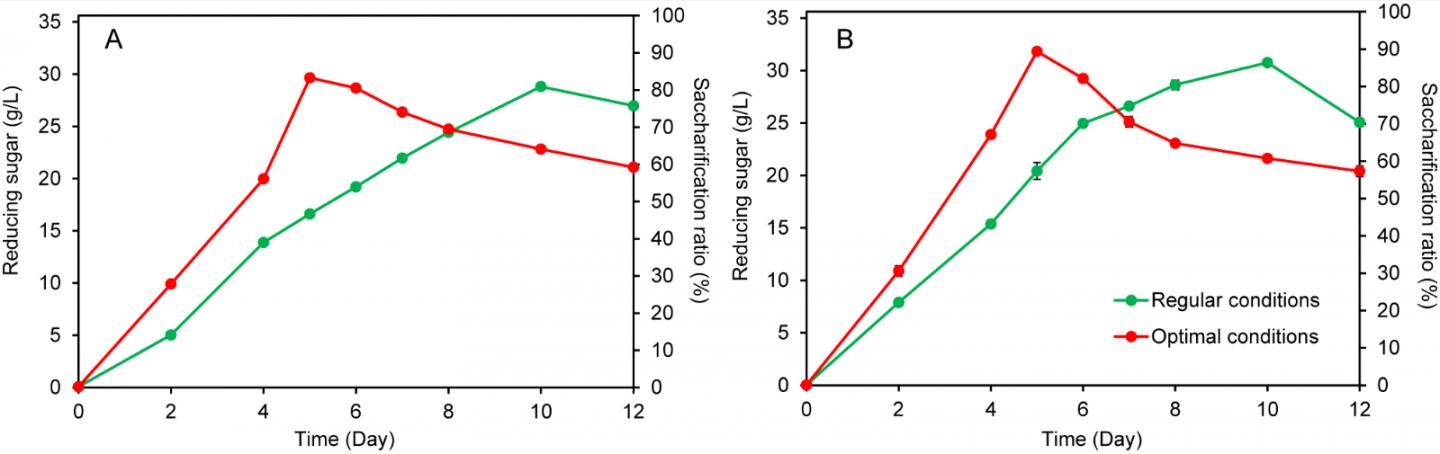
The QIBEBT researchers had previously developed a CBS biocatalyst by genetically engineering Clostridium thermocellum, but it took a long time to reach a high saccharification level. Later, a second-generation CBS biocatalyst was developed and key process factors, including the medium, inoculum and substrate load, etc., were optimized to promote saccharification efficiency and further reduce cost.
Using the newly developed biocatalyst and optimal conditions, the CBS process was shortened by 50% using pretreated wheat straw as the substrate. Under such conditions, the sugar yield reached 0.795 g/g and the saccharification level was 89.3% (Fig. 1).
“CBS is expected to be widely used in producing various lignocellulose-derived chemicals, functional foods and pharmaceuticals. The construction of a pilot-scale CBS demonstration is underway,” said Prof. CUI Qiu, corresponding author of the study.
The study was published in Biotechnology for Biofuels on Feb 18th and was supported by the Transformational Technologies for Clean Energy and Demonstration program of the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Key Technology Research and Development Program of Shandong, and the Major Program of the Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation.
###
Media Contact
CHENG Jing
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




