Credit: Mark Lee
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Polyhedral boranes, or clusters of boron atoms bound to hydrogen atoms, are transforming the biomedical industry. These manmade materials have become the basis for the creation of cancer therapies, enhanced drug delivery and new contrast agents needed for radioimaging and diagnosis. Now, a researcher at the University of Missouri has discovered an entirely new class of materials based on boranes that might have widespread potential applications, including improved diagnostic tools for cancer and other diseases as well as low-cost solar energy cells.
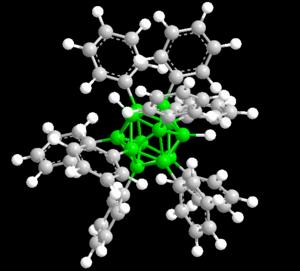
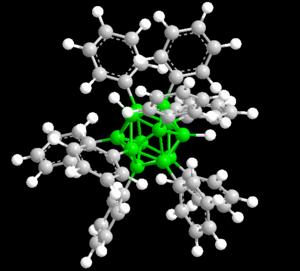
Mark Lee Jr., an assistant professor of chemistry in the MU College of Arts and Science, discovered the new class of hybrid nanomolecules by combining boranes with carbon and hydrogen. Boranes are chemically stable and have been tested at extreme heat of up to 900 degrees Celsius or 1,652 degrees Fahrenheit. It is the thermodynamic stability these molecules exhibit that make them non-toxic and attractive to the biomedical, personal computer and alternative energy industries.
"Despite their stability, we discovered that boranes react with aromatic hydrocarbons at mildly elevated temperatures, replacing many of the hydrogen atoms with rings of carbon," Lee said. "Polyhedral boranes are incredibly inert, and it is their reaction with aromatic hydrocarbons like benzene that will make them more useful."
Lee also showed that the attached hydrocarbons communicate with the borane core.
"The result is that these new materials are highly fluorescent in solution," Lee said. "Fluorescence can be used in applications such as bio-imaging agents and organic light-emitting diodes like those in phones or television screens. Solar cells and other alternative energy sources also use fluorescence, so there are many practical uses for these new materials."
Lee's discovery is based on decades of research. Lee's doctoral advisor, M. Frederick Hawthorne, MU Curators Distinguished Professor of Chemistry and Radiology, discovered several of these boron clusters as early as 1959. In the past, boranes have been used for medical imaging, drug delivery, neutron-based treatments for cancer and rheumatoid arthritis, catalysis and molecular motors. Borane researchers also have created a specific type of nanoparticle that selectively targets cancer cells.
"When these molecules were discovered years ago we never could have imagined that they would lead to so many advancements in biomedicine," Lee said. "Now, my group is expanding on the scope of this new chemistry to examine the possibilities. These new materials, called 'polyarylboranes,' are much broader than we imagined, and now my students are systematically exploring the use of these new clusters."
###
The study, "Catalyst-Free Polyhydroboration of Dodecaborate Yields Highly Photoluminescent Ionic Polyarylated Clusters," recently was published in the international journal Angewandte Chemie with funding from the University of Missouri Research Board.
Editor's Note: For more on the story, please see: https://coas.missouri.edu/news/chemist-discovers-new-class-materials
Media Contact
Jeff Sossamon
[email protected]
573-882-3346
@mizzounews
http://www.missouri.edu
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag