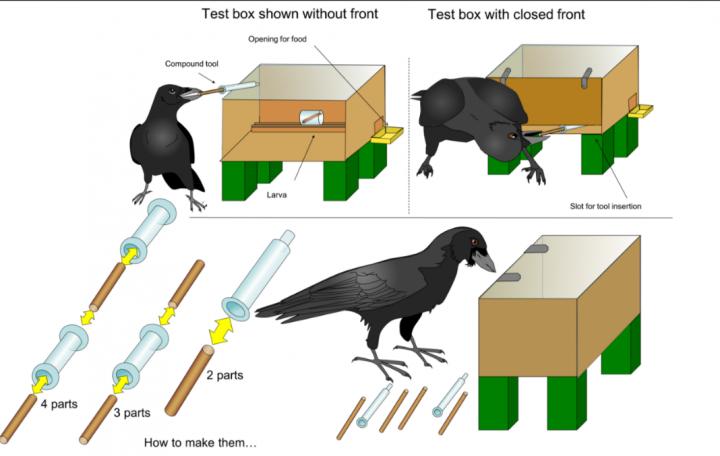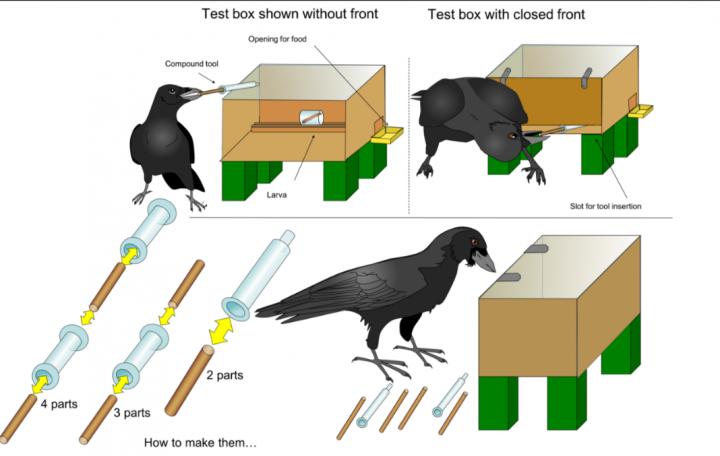
Credit: Alice Auersperg
The new study, published today in Scientific Reports, shows that these birds can create long-reaching tools out of short combinable parts – an astonishing mental feat. Assemblage of different components into novel functional and manoeuvrable tools has, until now, only been observed in apes, and anthropologists regard early human compound tool manufacture as a significant step in brain evolution. Children take several years before creating novel tools, probably because it requires anticipating properties of yet unseen objects. Such anticipation, or planning, is usually interpreted as involving creative mental modelling and executive functions.
The study demonstrates that this species of crow possess highly flexible abilities that allow them to solve complex problems involving anticipation of the properties of objects they have never seen.
'The finding is remarkable because the crows received no assistance or training in making these combinations, they figured it out by themselves,' said Auguste von Bayern, from the Max-Planck-Institute for Ornithology and University of Oxford. The New Caledonia crows (Corvus moneduloides) from the South Pacific are of the same species as Betty, who became famous in 2002 as the first animal shown to be able to create a hooked tool by bending a pliable material.
Researchers had already been able to show how this remarkable species were able to use and make tools in the wild and in captivity, but they had never previously been seen to combine more than one piece to make a tool.
Alex Kacelnik (University of Oxford) said: 'The results corroborate that these crows possess highly flexible abilities that allow them to solve novel problems rapidly, but do not show how they do it. It is possible that they use some form of virtual simulation of the problem, as if different potential actions were played in their brains until they figure out a viable solution, and then do it. Similar processes are being modelled on artificial intelligences and implemented in physical robots, as a way to better understand the animals and to discover ways to build machines able to reach autonomous creative solutions to novel problems.'
The researchers presented eight New Caledonian crows with a puzzle box they had never encountered before, containing a small food container behind a door that left a narrow gap along the bottom. Initially, the scientists left some sufficiently long sticks scattered around, and all the birds rapidly picked one of them, inserted it through the front gap, and pushed the food to an opening on the side of the box. All eight birds did this without any difficulty. In the next steps, the scientists left the food deep inside the box but provided only short pieces, too short to reach the food. These short pieces could potentially be combined with each other, as some were hollow and others could fit inside them. In one example, they gave the birds barrels and plungers of disassembled hypodermic syringes. Without any help or demonstration, four of the crows partially inserted one piece into another and used the resulting longer compound pole to reach and extract the food. At the end of the five-step investigation, the scientists made the task more difficult by supplying even shorter combinable parts, and found that one bird particular bird, 'Mango', was able to make compound tools out of three and even four parts.
Although the authors explain that the mental processes by which the birds achieve their goals have not yet been fully established, the ability to invent a tool is interesting in itself. Few animals are capable of making and using tools, and also in human development the capacity only emerges late. While children start using tools reliably when they are about 18 months old, they only invent novel tools suited to solve a given problem reliably when they are at least five years old. Archaeological findings indicate that such compound tools arose only late in human cultural evolution (probably around 300,000 years ago in the Middle Palaeolithic) and might have coevolved with planning abilities, complex cognition and language. The crows' ability to construct novel compound tools does not imply that their cognitive mechanisms equal those of humans or apes, but helps to understand the cognitive processes that are necessary for physical problem solving.
###
Read the full paper, 'Compound tool construction by New Caledonian crows', Scientific Reports when the embargo lifts here: http://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-018-33458-z
Watch Tumulte, Jungle and Mango create and use compound tools: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EryZPmOxwC0
Media Contact
Ruth Abrahams
[email protected]
186-528-0730
@UniofOxford
http://www.ox.ac.uk/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-33458-z