Hydrogen has attracted much attention due to its potential as a clean energy carrier. To date, the majority of hydrogen is produced from fossil fuels, such as natural gas, coal and oil. Such fossil-derived hydrogen must be purified from common contaminants (e.g., CO2, CH4, CO and H2S) for further fuel cell applications.
Credit: HE Guanghu
Hydrogen has attracted much attention due to its potential as a clean energy carrier. To date, the majority of hydrogen is produced from fossil fuels, such as natural gas, coal and oil. Such fossil-derived hydrogen must be purified from common contaminants (e.g., CO2, CH4, CO and H2S) for further fuel cell applications.
Fossil-derived hydrogen-assisted water splitting using a dense oxygen-ion-conduction ceramic membrane is a promising H2-purification technique due to the membrane’s 100% oxygen selectivity for directly obtaining pure hydrogen. However, existing oxygen-conducting membranes suffer from chemical stability issues under the above harsh operating conditions.
Recently, researchers from the Qingdao Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology (QIBEBT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have developed a new “Interface-reaction-induced reassembly” approach to fabricating multilayered ceramic membranes with ceria-based thin-film for stable hydrogen production.
The study was published in Angewandte Chemie International Edition on Nov. 3.
“Multilayered ceramic membranes are typically fabricated using layer-by-layer deposition methods. However, these methods often require a serial procedure, and the thickness of the dense thin layers is commonly between 10 and 1000 μm. In addition, the deposited thin layers often delaminate from the support layers during co-sintering,” said corresponding author Prof. JIANG Heqing from QIBEBT.
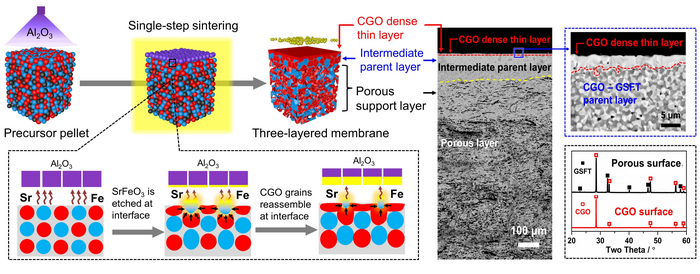
Inspired by the architectural structure of the rooted grasses in soil, the researchers developed an interface-reaction-induced reassembly approach to fabricating a three-layered ceramic membrane with an oxygen-conducting dense thin layer rooted in its parent layer, directly resulting from a single-step sintering of dual-phase ceramic precursors.
“In this new approach, by deliberately applying a proper etchant Al2O3, the surface Fe-containing grains in the pressed pellet were selectively etched via interface reactions at high temperatures, producing reaction enthalpy,” said Associate Professor HE Guanghu from QIBEBT, first author of the study. “The heat is expected to increase the local temperature for driving the reassembly of the surface-isolated fluorite-type grains into a dense thin layer that cut off the interface reactions, avoiding the continuous growth of the thin layer.”
With this interface-reaction-induced reassembly approach, the researchers found that the resulting ceria-based layers were very thin (~1 μm), highly dense and adhered strongly to the parent layers, not only significantly reducing ionic transport resistance, but also ensuring the structural integrity of the multilayered membranes for various applications.
Using the developed multilayered membrane, the researchers demonstrated hydrogen production from water splitting assisted by oxidation of simulated coke oven gas containing H2, CH4, CO2, CO and H2S. They found that the membrane with a CGO dense thin layer showed very long durability (>1000 hours), underscoring the promise of high-performance membrane reactors for hydrogen production in practical conditions.
“These results suggest that this technique paves the way for the development of high-performance multilayered ceramics with functional layers for various applications, for example solid oxide fuel cells and solid oxide electrolysis cells. This is also the focus of our future work,” said Prof. JIANG Heqing from QIBEBT, who led the study.
Journal
Angewandte Chemie International Edition
DOI
10.1002/anie.202210485
Article Title
Multilayered ceramic membrane with ion conducting thin layer induced by interface reaction for stable hydrogen production
Article Publication Date
3-Nov-2022




