Credit: The Authors.
BELLINGHAM, Washington, USA, and CARDIFF, UK — A new Java-based application for Android tablets that provides neurosurgeons with the ability to manipulate 3D models of pediatric patients' neuroanatomy and accurately tailor radiation doses for imaging has been hailed as "a big step forward" by editors of the Journal of Medical Imaging. The advance is reported in an article published today by SPIE, the international society for optics and photonics.
The Journal of Medical Imaging publishes papers on advances in early detection, diagnostics, and therapy of disease as well as in the understanding of normal. The journal is published in the SPIE Digital Library, at http://www.spiedigitallibrary.org/journals/journal-of-medical-imaging.
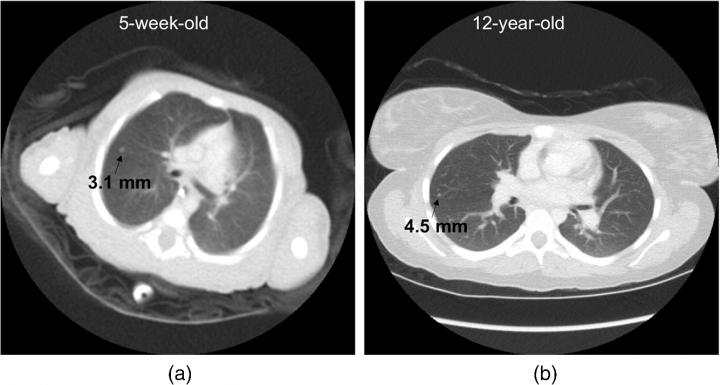
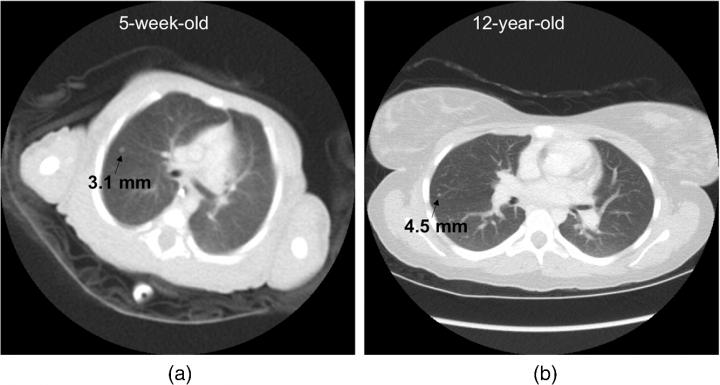
Ideally, a size-specific protocol is defined based on diagnostic accuracy for a particular procedure, and a targeted balance is calculated between image accuracy requirements and patient dose.
With the wide range of size from newborns to teenagers, size is a particularly dominant factor for pediatric patients in computed tomography imaging of tissues and structures inside the body, note the authors.
However, designing an approach tailored to patient size is possible only if the three-way dependency of quality, dose, and size is known, and current technologies have not provided this ability.
The study by Ehsan Samei and Donald Frush of Duke University Medical Center and Xiang Li of the Cleveland Clinic offers a new methodology to determine the interdependency of these data across the range of pediatric sizes. The work is reported in "Size-based quality-informed framework for quantitative optimization of pediatric CT."
"This is really a big step forward in imaging brain tumors and other issues in young patients," said Journal of Medical Imaging associate editor Christoph Hoeschen of Otto-von-Guericke Universität. "This methodology can serve as an advanced strategy to analyze the accuracy-dose tradeoff for other imaging systems, imaging technologies, or clinical tasks."
Based on two prior foundational studies by the authors, radiation dosage was assessed for organ doses, effective dose, and risk index within nine pediatric age-size groups. The cases, supplemented with added noise and simulated lesions, were assessed in terms of nodule detection accuracy. The resulting continuous accuracy-dose relationships were used to optimize individual scan parameters for each patient category.
The resulting model can be used to optimize individual scan parameters and provide for consistent diagnostic performance across the broad range of body sizes in children, the authors reported.
###
Maryellen Giger, A.N. Pritzker Professor of Radiology and Medical Physics at the University of Chicago, is editor-in-chief of the Journal of Medical Imaging, published in print and digitally. The SPIE Digital Library contains more than 460,000 articles from SPIE journals, proceedings, and books, with approximately 18,000 new research papers added each year. Abstracts are freely searchable, and a number of journal articles are published with open access.
About SPIE
SPIE is the international society for optics and photonics, an educational not-for-profit organization founded in 1955 to advance light-based science, engineering, and technology. The Society serves nearly 264,000 constituents from approximately 166 countries, offering conferences and their published proceedings, continuing education, books, journals, and the SPIE Digital Library. In 2016, SPIE provided more than $4 million in support of education and outreach programs. http://www.spie.org
Media Contact
Amy Nelson
[email protected]
360-685-5478
@SPIEtweets
http://spie.org/
Original Source
http://www.spie.org/x127279.xml http://dx.doi.org/10.1117/1.JMI.4.3.031209