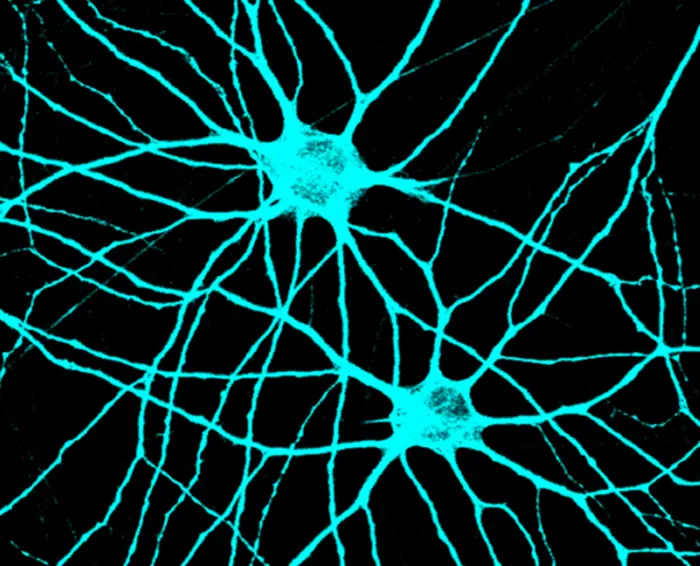
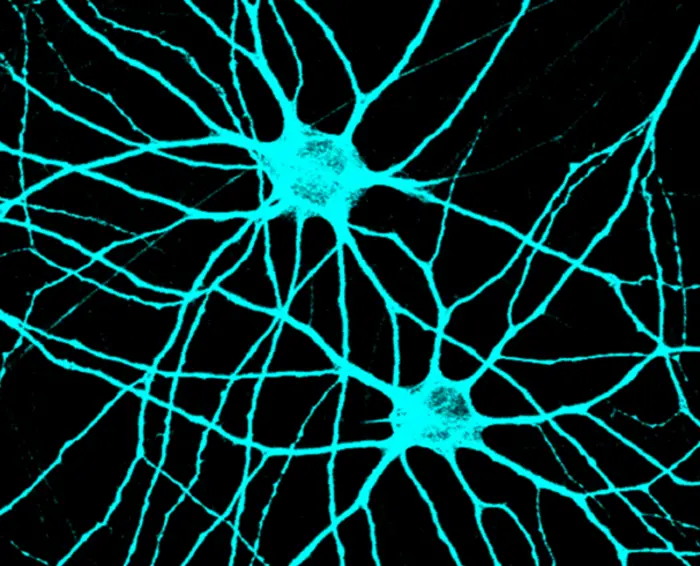
Newly published research from Colorado State University answers fundamental questions about cellular connectivity in the brain that could be useful in the development of treatments for neurological diseases like autism, epilepsy or schizophrenia.
Credit: Please credit Colorado State University
Newly published research from Colorado State University answers fundamental questions about cellular connectivity in the brain that could be useful in the development of treatments for neurological diseases like autism, epilepsy or schizophrenia.
The work, highlighted in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, focuses on how neurons in the brain transmit information between each other through highly specialized subcellular structures called synapses. These delicate structures are key to controlling many processes across the nervous system via electrochemical signaling, and pathogenic mutations in the genes that impair their development can cause severe mental disorders. Despite their important role in linking neurons across different brain regions, the way synapses form and function is still not well understood, said Assistant Professor Soham Chanda.
To answer that fundamental question, Chanda and his team in the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology focused on a specific and important type of synapse called GABAergic. He said neuroscience researchers have long hypothesized that these synapses might form because of a release of GABA and the corresponding sensing activity between two neurons in proximity. However, research in the paper now shows that these synapses can begin to develop autonomously and apart from that neuronal communication, mainly due to the scaffolding action of a protein called Gephyrin. These findings clarify the key mechanisms of synaptic formation, which might allow researchers to further focus on synapse dysfunction and health treatment options.
Chanda’s team used human neurons derived from stem cells to develop a model of the brain that could rigorously test these relationships. Using a gene-editing tool called CRISPR-Cas9, they were able to genetically manipulate the system and confirm the role of Gephyrin in the synapse formation process.
“Our study shows that even if a pre-synaptic neuron is not releasing GABA, the post-synaptic neuron can still put together the necessary molecular machineries prepared to sense GABA,” Chanda said. “We used a gene-editing tool to remove the Gephyrin protein from neurons, which largely reduced this autonomous assembly of synapses – confirming its important role irrespective of neuronal communication.”
Using stem cells to advance understanding of neuron and synapse formation
Neuroscientists have traditionally used rodent systems to study these synaptic connections in the brain. While that provides a suitable model, Chanda and his team were interested in testing synapse properties in a human cellular environment that could eventually be more easily translated into treatments.
To achieve this, his team cultivated human stem cells to form brain cells that could mimic the properties of human neurons and synapses. They then conducted extensive high-resolution imaging of these neurons and tracked their electrical activities to understand synaptic mechanisms.
Chanda said that several mutations in the Gephyrin protein have been associated with neurological disorders like epilepsy, which alters neuronal excitability in the human brain. That makes understanding its basic cellular function an important first step towards treatment and prevention.
“Now that we better understand how these synaptic structures interact and organize, the next question will be to elucidate how defects in their relationships can lead to disease and identify the ways one can predict or intervene in that process,” he said.
Journal
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
DOI
10.1073/pnas.2315100121
Article Title
Gephyrin promotes autonomous assembly and synaptic localization of GABAergic postsynaptic components without presynaptic GABA release
Article Publication Date
18-Jun-2024