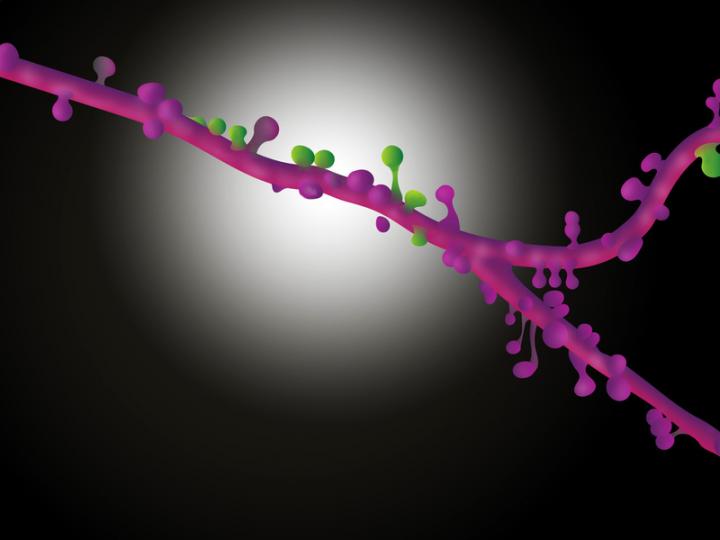
The cerebral cortex resembles a vast switchboard. Countless lines carrying information about the environment, for example from the sensory organs, converge in the cerebral cortex. In order to direct the flow of data into meaningful pathways, the individual pyramidal cells of the cerebral cortex act like miniature switchboard operators. Each cell receives information from several thousand lines. If the signals make sense, the line is opened, and the information is relayed onward. Scientists at the Max Planck Institute of Neurobiology in Martinsried have now shown for the first time that contact points between specific neuron types are clustered in groups on the target neuron. It is probable that signals are coordinated with each other in this way to make them more “convincing”.
The cells of the cerebral cortex have a lot to do. They process various types of information depending on the area in which they are located. For example, signals from the retina arrive in the visual cortex, where, among other things, the motion of objects is detected. The pyramidal cells of the cerebral cortex receive information from other cells through thousands of contact points called synapses. Depending on where, how many and how often synapses are activated, the cell relays the signal onward – or not.
Information is passed on in the form of electrical signals. The neurobiologists were able to measure these signals at various contact points of the neuron. “The exciting thing is that the signals that a cell receives from, say, ten simultaneously active synapses can be greater than the sum of the signals from the ten individual synapses,” says Volker Scheuss, summarizing the basis of his recently published study. “However, until now it was unclear whether this phenomenon can be explained by a specific arrangement of synapses on pyramidal cells.”
By combining modern methods, the neurobiologists in Tobias Bonhoeffer’s Department have analysed the arrangement of synapses. They were able to selectively activate a specific type of pyramid cell in brain slices from mice using optogenetics. Thanks to simultaneous “calcium imaging”, they were then able to observe and record the activity of individual synapses under a two-photon microscope. In this way, they succeeded in showing for the first time how synapses are arranged with respect to each other.
The result of such synapse mapping analysed with a newly developed algorithm was clear: The synapses of pyramidal cells form clusters consisting of 4 to 14 synapses arranged within an area of less than 30 micrometres along the dendrite. “The existence of these clusters suggests that the synapses interact with each other to control the strength of the combined signal,” explains Onur Gökçe, author of the study. This is the first anatomical explanation for the disproportionate strength of clustered synapse signals in comparison to the individual signals – a finding known from activity measurements. The observation in layer 5 pyramidal cells was of particular interest, as the activity of these cells oscillates synchronously. “This rhythmic activity, which probably influences the processing of visual information, could synchronously activate synapse clusters, thus boosting the overall signal received,” says Scheuss.
###
Original publication:
Onur Gökçe, Tobias Bonhoeffer, Volker Scheuss
Clusters of synaptic inputs on dendrites of layer 5 pyramidal cells in mouse visual cortex.
eLife; 19 July, 2016
Media Contact
Prof. Dr. Tobias Bonhoeffer
[email protected]
49-898-578-3751
@maxplanckpress
http://www.mpg.de