A soil nematode reanimated from Siberian permafrost had laid dormant for approximately 46,000 years, according to a study publishing July 27, 2023 in the open access journal PLOS Genetics by Anastasia Shatilovich at the Institute of Physicochemical and Biological Problems in Soil Science RAS in Russia, Vamshidhar Gade at the Max Planck Institute for Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics in Germany, and colleagues.
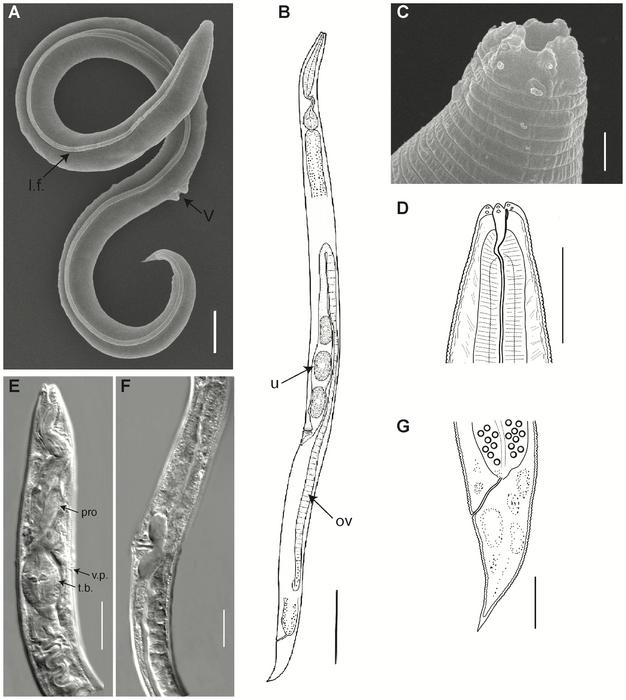
Credit: Shatilovich et al, 2023, PLOS Genetics, CC-BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
A soil nematode reanimated from Siberian permafrost had laid dormant for approximately 46,000 years, according to a study publishing July 27, 2023 in the open access journal PLOS Genetics by Anastasia Shatilovich at the Institute of Physicochemical and Biological Problems in Soil Science RAS in Russia, Vamshidhar Gade at the Max Planck Institute for Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics in Germany, and colleagues.
Some animals, such as tardigrades, rotifers, and nematodes, can survive harsh conditions by entering a dormant state known as “cryptobiosis”. Previously, nematode individuals were reanimated from samples collected from a fossilized burrow in silt deposits in the northeastern Arctic. In this study, radiocarbon analysis of plant material from the burrow revealed that these frozen deposits, 40 meters below the surface, had not thawed since the late Pleistocene, between 45,839 and 47,769 years ago.
Using genome sequencing, assembly, and phylogenetic analysis of the nematode’s relationship to modern species, the researchers determined that it belongs to a previously undescribed species, Panagrolaimus kolymaensis. They compared its genome with the model organism, Caenorhabditis elegans, and identified genes in common that are involved in cryptobiosis. When mildly desiccated in the laboratory, both species increased production of a sugar called trehalose, which may help them to survive harsh desiccation and freezing. They tested the survival capabilities of P. kolymaensis and found that exposure to mild desiccation before freezing helped prepare the worms for cryptobiosis and improved survival at -80°C. This treatment also benefitted C. elegans dauer larvae, which then survived 480 days at -80°C with no reductions in viability or reproduction after thawing.
This study extends the longest reported cryptobiosis in nematodes by tens of thousands of years. By adapting to cope with extreme conditions, such as permafrost, for short periods of time, the nematodes might have gained the potential to remain dormant over geological timescales.
The authors add, “This work also suggests that fluctuations in the environment also determine the time an organism can remain in a cryptobiotic state.”
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS Genetics: http://journals.plos.org/plosgenetics/article?id=10.1371/journal.pgen.1010798
Citation: Shatilovich A, Gade VR, Pippel M, Hoffmeyer TT, Tchesunov AV, Stevens L, et al. (2023) A novel nematode species from the Siberian permafrost shares adaptive mechanisms for cryptobiotic survival with C. elegans dauer larva. PLoS Genet 19(7): e1010798. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1010798
Author Countries: Germany, Ireland, Russia, UK
Funding: This work was supported by the Russian Foundation fr Basic Research (19-29-05003-mk) to AS and ER. VRG and TVK acknowledge the financial support from the Volkswagen Foundation (Life research grant 92847). PHS and TTH are supported by a DFG ENP grant to PHS (DFG project 434028868). GMH is funded by a UCD Ad Astra Fellowship. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Journal
PLoS Genetics
DOI
10.1371/journal.pgen.1010798
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Animals
Article Title
A novel nematode species from the Siberian permafrost shares adaptive mechanisms for cryptobiotic survival with C. elegans dauer larva
COI Statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.




