Credit: Osaka University
Osaka – Cytokines are proteins secreted by several types of immune cells in response to infection, inflammation, or injury. Interleukin-17 (IL-17) is one such cytokine that causes inflammation, by controlling the production of other cytokines and mobilizing a type of white blood cell (neutrophil) that fights infections. During some parasitic infections, host protection is achieved by an IL-17 response, but too much IL-17 causes chronic tissue damage. This response is therefore tightly regulated by other cytokines, but the precise mechanisms were unclear.
Now, Japanese research coordinated by Osaka University has unraveled the complex network of cytokine control that prevents multi-organ damage during infection by the protozoan parasite that causes Chagas disease.
Trypanosoma cruzi is an intracellular parasite that infects and destroys heart and digestive muscle, causing Chagas disease, which affects 6-7 million people worldwide mainly in endemic areas of Central and South America.
Previous work showed that T. cruzi infection in mice led to production of the cytokine IL-23 by host immune cells. This promoted the generation of CD4+ T cells that produce IL-17. Researchers built on these findings by focusing on the protein BATF2, which they found in an earlier study to be switched on by cytokine signaling in innate immune cells derived from bone marrow during T. cruzi infection.
To study the role of BATF2 in this process, the team generated mice lacking the gene encoding this protein. These Batf2 knockout mice produced much more IL-17 in response to the parasite than did control mice. They also produced more IL-23, suggesting that BATF2 normally suppresses expression of the Il23a gene. However, it was not shown to be required for the killing of T. cruzi.
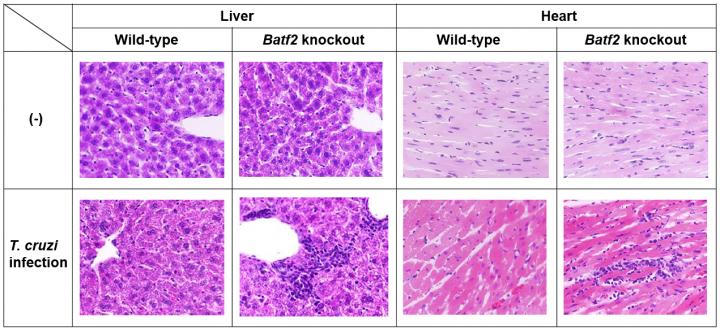
"When we infected both Batf2 knockout and control mice with the same amount of T. cruzi, the knockout mice had a lower number of parasites and improved survival, probably because of increased IL-17 levels," say Hisako Kayama co-author of the report on the study. "Yet, despite this, the extent of immune activation and tissue damage was more severe (Figure 1)."
Further analysis of protein-protein interactions revealed that BATF2 interacts directly with a transcription factor to inhibit Il23a expression (Figure 2).
"This novel function of BATF2 prevents the excessive IL-17 response that would otherwise cause immunopathology during parasitic infection," corresponding author Kiyoshi Takeda explains. "We also think that this negative regulation is not unique to T. cruzi infection, but that it likely occurs in other models of infection because BATF2 is expressed in several different cell types."
###
Media Contact
Saori Obayashi
[email protected]
81-661-055-886
@osaka_univ_e
http://www.osaka-u.ac.jp/en
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag