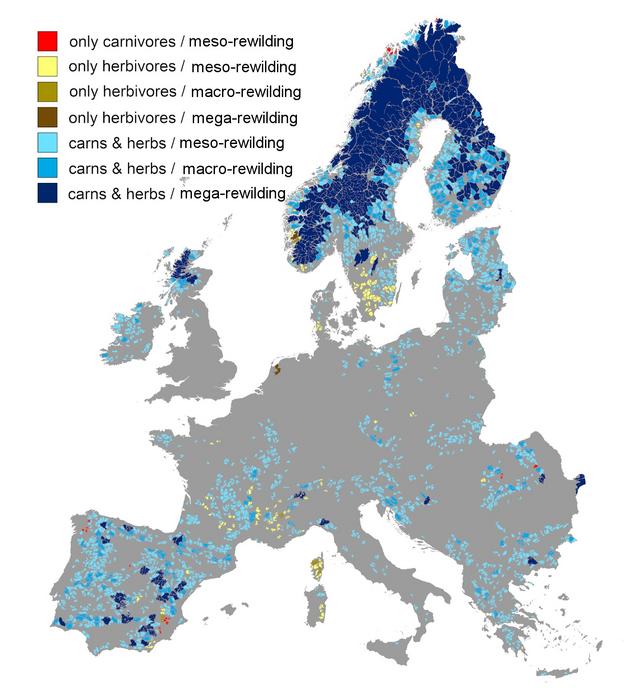
Europe’s abandoned farmlands could find new life through rewilding, a movement to restore ravaged landscapes to their wilderness before human intervention. A quarter of the European continent, 117 million hectares, is primed with rewilding opportunities, researchers report August 15 in the Cell Press journal Current Biology. They provide a roadmap for countries to meet the 2030 European Biodiversity Strategy’s goals to protect 30% of land, with 10% of those areas strictly under conservation.
Europe’s abandoned farmlands could find new life through rewilding, a movement to restore ravaged landscapes to their wilderness before human intervention. A quarter of the European continent, 117 million hectares, is primed with rewilding opportunities, researchers report August 15 in the Cell Press journal Current Biology. They provide a roadmap for countries to meet the 2030 European Biodiversity Strategy’s goals to protect 30% of land, with 10% of those areas strictly under conservation.
“There are many areas in Europe that have a low enough human footprint, as well as the presence of key animal species, to potentially be rewilded,” says first author and biogeographer Miguel B. Araújo (@Araujo_lab) of the National Museum of Natural Sciences, CSIC, Spain, and the University of Évora, Portugal. “We also highlight the need for different strategies depending on the conditions of each region.”
The researchers established criteria to determine areas with rewilding potentials: extensive tracts of land, covering more than 10,000 hectares, with little human disturbance that feature vital species. Based on the size of the land and the types of animals that inhabit the area, they further identified two strategies for rewilding—passive and active.
Passive rewilding relies on natural recolonization, where animals gradually move back into abandoned areas on their own. The approach works best in regions with a healthy population of key herbivores, such as deer, ibex, moose, and rabbits, as well as carnivores, such as wolves, bears, and lynxes. Regions without key herbivore or carnivore species would require active rewilding by reintroducing the missing species to kickstart the ecosystem’s recovery. Both strategies aim to create a self-sustaining, biodiverse landscape.
“I often refer to herbivores as the ecosystem engineers as they graze and shape the vegetation, while predators would be the architects creating ‘fear landscapes’ that herbivores avoid,” says Araújo. “The interaction between herbivores and carnivores creates mosaic patterns in the landscapes, essential for biodiversity.”
“Conservation strategies involving ecological restoration of densely populated areas could help some countries reach conservation goals,” says Araújo. “Countries could reclaim land to turn it into conservation areas or establish networks of small, protected habitats. Traditional multi-use landscapes, like the oak parklands in the Iberian Peninsula and various extensive agricultural and forestry systems across Europe, could also help if managed sustainably.”
As governments and organizations continue to invest in land conservation, the researchers hope their findings and framework will help these efforts to acquire or manage areas with the greatest potential for successful rewilding. However, despite the prospects, the researchers caution that time is of the essence.
“We’re racing against time,” says Araújo. “The areas that look most promising for rewilding today may not be the same in 50 years due to the impacts of climate change.”
###
This work was supported by the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology, the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation, and the European Union’s Horizon Europe Research and Innovation Programme.
Current Biology, Araújo and Alagador: “Expanding European protected areas through rewilding.” https://www.cell.com/current-biology/fulltext/S0960-9822(24)00948-5
Current Biology (@CurrentBiology), published by Cell Press, is a bimonthly journal that features papers across all areas of biology. Current Biology strives to foster communication across fields of biology, both by publishing important findings of general interest and through highly accessible front matter for non-specialists. Visit http://www.cell.com/current-biology. To receive Cell Press media alerts, contact [email protected].
Journal
Current Biology
DOI
10.1016/j.cub.2024.07.045
Method of Research
Observational study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Expanding European protected areas through rewilding
Article Publication Date
15-Aug-2024