A new study published on October 17th in the journal PNAS, led by a CNRS researcher, has for the first time used zinc isotope analysis to determine the position of Neanderthals in the food chain. Their findings suggest that they were in fact carnivores.
Credit: © Lourdes Montes
A new study published on October 17th in the journal PNAS, led by a CNRS researcher, has for the first time used zinc isotope analysis to determine the position of Neanderthals in the food chain. Their findings suggest that they were in fact carnivores.
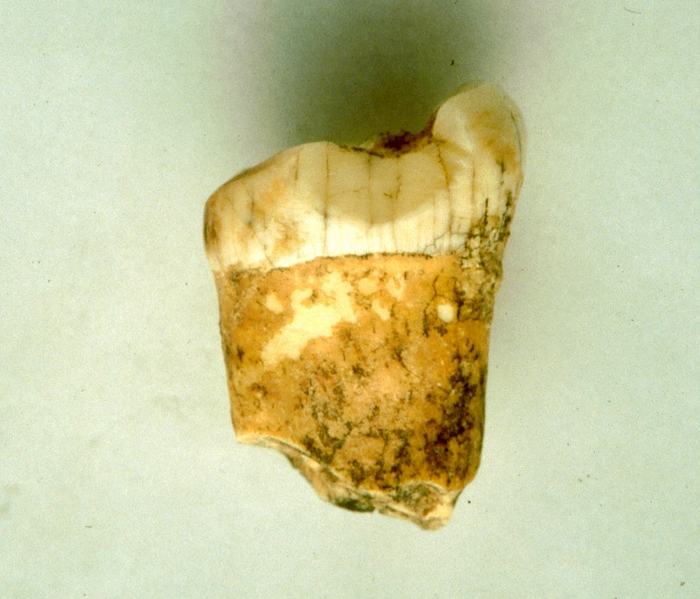
Were Neanderthals carnivores? Scientists have not yet settled the question. While some studies of the dental tartar of individuals from the Iberian Peninsula appear to show that they were major consumers of plants, other research carried out at sites outside Iberia seem to suggest that they consumed almost nothing but meat. Using new analytical techniques on a molar belonging to an individual of this species, researchers1 have shown that the Neanderthals at the Gabasa site in Spain appear to have been carnivores.
To determine an individual’s position in the food chain, scientists have until now generally had to extract proteins and analyse the nitrogen isotopes present in the bone collagen. However, this method can often only be used in temperate environments, and only rarely on samples over 50,000 years old. When these conditions are not met, nitrogen isotope analysis is very complex, or even impossible. This was the case for the molar from the Gabasa site analysed in this study.
Given these constraints, Klevia Jaouen, a CNRS researcher, and her colleagues decided to analyse the zinc isotope ratios present in the tooth enamel, a mineral that is resistant to all forms of degradation. This is the first time this method has been used to attempt to identify a Neanderthal’s diet. The lower the proportions of zinc isotopes in the bones, the more likely they are to belong to a carnivore. The analysis was also carried out on the bones of animals from the same time period and geographical area, including carnivores such as lynxes and wolves, and herbivores like rabbits and chamois. The results showed that the Neanderthal to whom this tooth from the Gabasa site belonged was probably a carnivore who did not consume the blood of their prey.
Broken bones found at the site, together with isotopic data, indicate that this individual also ate the bone marrow of their prey, without consuming the bones, while other chemical tracers show that they were weaned before the age of two. Analyses also show that this Neanderthal probably died in the same place they had lived in as a child.
Compared to previous techniques, this new zinc isotope analysis method makes it easier to distinguish between omnivores and carnivores. To confirm their conclusions, the scientists hope to repeat the experiment on individuals from other sites, especially from the Payre site in south-east France, where new research is under way.
1 In France, the work involved scientists from the Geosciences Environment Toulouse Laboratory (CNRS/CNES/IRD/UT3 Paul Sabatier), and the Geology Laboratory of Lyon: Earth, Planets, Environment (CNRS/UCBL1), together with teams from the University of Zaragoza, the Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology, Leipzig, the Max
Planck Institute for Chemistry, Mainz, and the Johannes Gutenberg University, Mainz.
Journal
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Article Title
A Neandertal dietary conundrum: new insights provided by tooth enamel Zn isotopes from Gabasa
Article Publication Date
17-Oct-2022




