There are plenty of body parts that don’t grow back when you lose them. Nails are an exception, and a new study published in The Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) reveals some of the reasons why.
A team of USC Stem Cell researchers led by principal investigator Krzysztof Kobielak and co-first authors Yvonne Leung and Eve Kandyba has identified a new population of nail stem cells, which have the ability to either self-renew or undergo specialization or differentiation into multiple tissues.
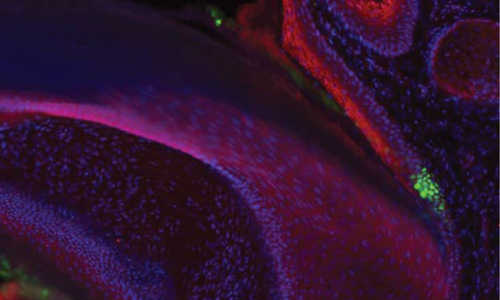
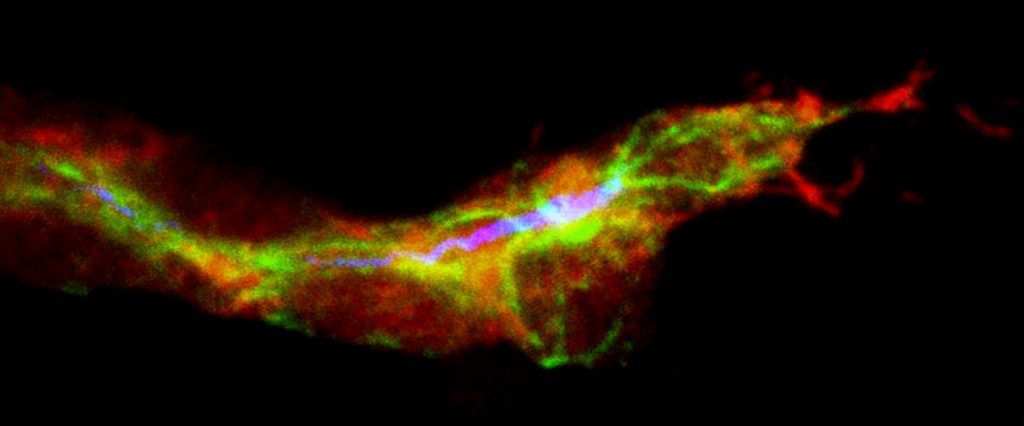
To find these elusive stem cells, the team used a sophisticated system to attach fluorescent proteins and other visible “labels” to mouse nail cells. Many of these cells repeatedly divided, diluting the fluorescence and labels among their increasingly dim progeny. However, a few cells located in the soft tissue attached to the base of the nail retained strong fluorescence and labels because they either did not divide or divided slowly — a known property of many stem cells.
The researchers then discovered that these slow-dividing stem cells have the flexibility to perform dual roles. Under normal circumstances, the stem cells contribute to the growth of both the nails and the adjacent skin. However, if the nail is injured or lost, a protein called “Bone Morphogenetic Protein,” or BMP, signals to the stem cells to shift their function exclusively to nail repair.
The researchers are now wondering whether or not the right signals or environmental cues could induce these nail stem cells to generate additional types of tissue — potentially aiding in the repair of everything from nail and finger defects to severe skin injuries and amputations.
“That was very surprising discovery, since the dual characteristic of these nail stem cells to regenerate both the nail and skin under certain physiological conditions is quite unique and different from other skin stem cells, such as those of the hair follicle or sweat gland,” said Kobielak.
Story Source:
The above story is based on materials provided by University of Southern California – Health Sciences.