Credit: Mark Garlick/University of Warwick
- University of Warwick researchers identify a white dwarf pulsar — a star type which has eluded astronomers for half a century
- Star lashes its neighbour with intense radiation beam every two minutes
- Research published in Nature Astronomy
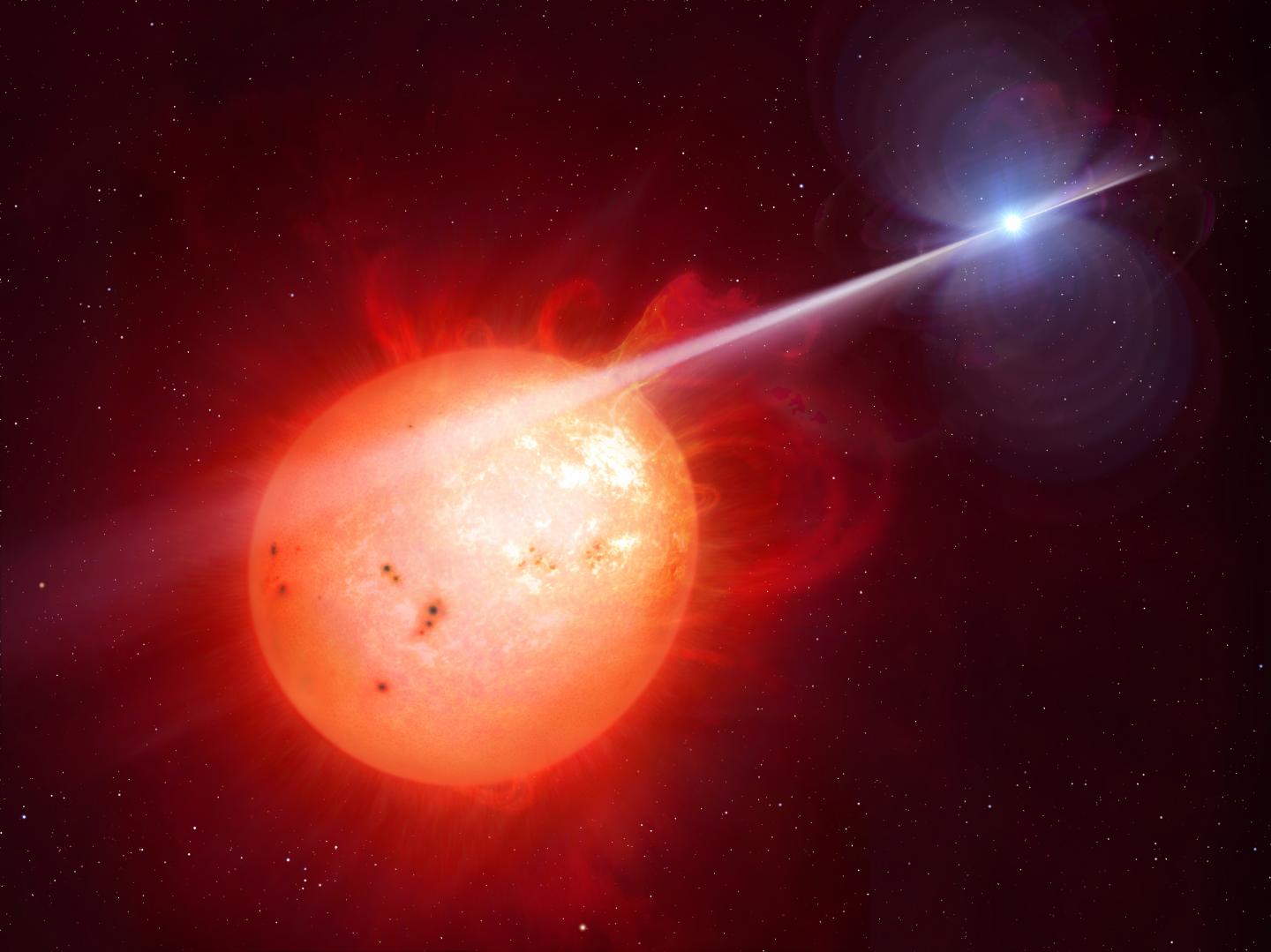
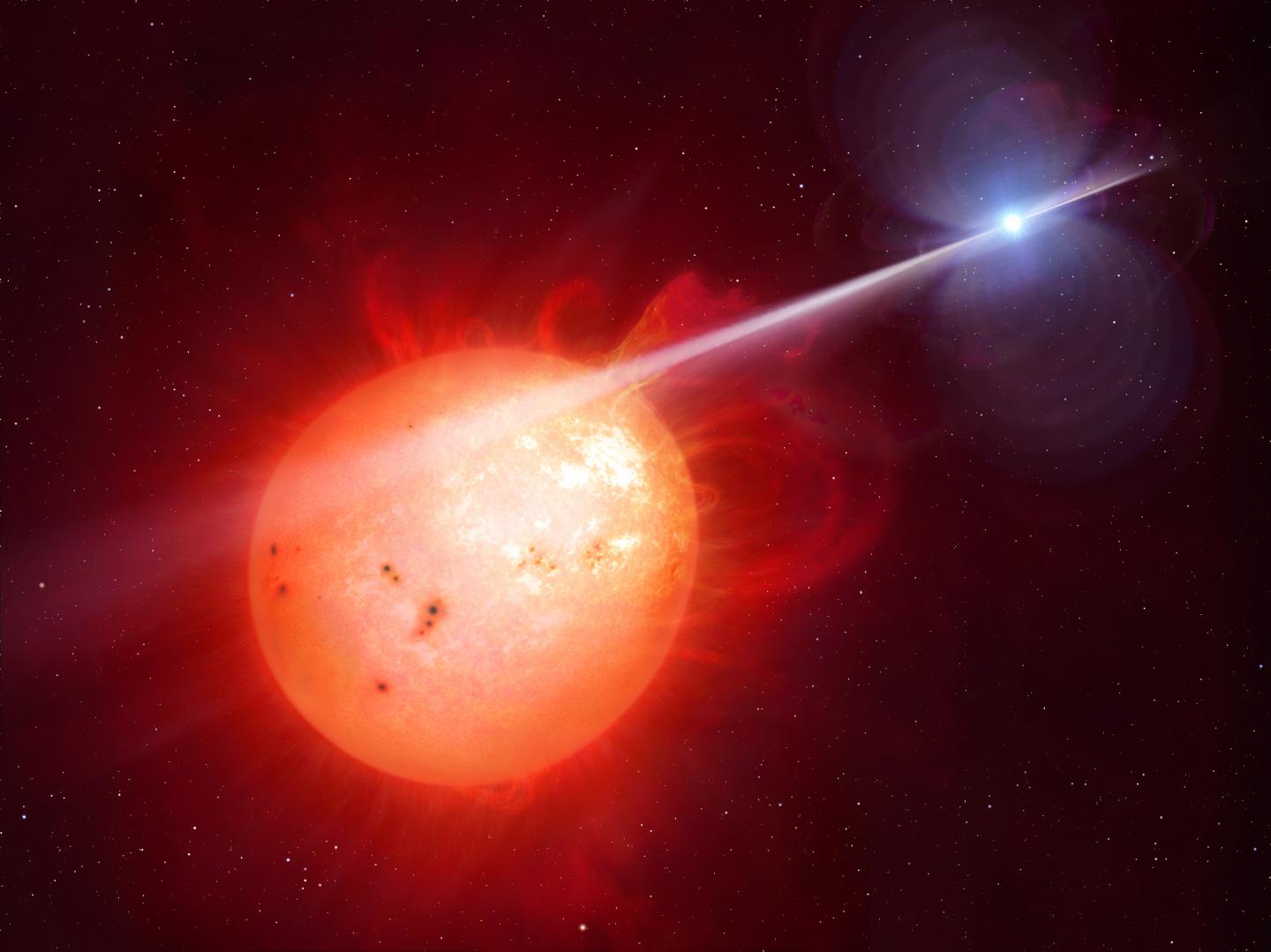
An exotic binary star system 380 light-years away has been identified as an elusive white dwarf pulsar — the first of its kind ever to be discovered in the universe – thanks to research by the University of Warwick.
Professors Tom Marsh and Boris Gänsicke of the University of Warwick's Astrophysics Group, with Dr David Buckley from the South African Astronomical Observatory, have identified the star AR Scorpii (AR Sco) as the first white dwarf version of a pulsar — objects found in the 1960s and associated with very different objects called neutron stars.
The white dwarf pulsar has eluded astronomers for over half a century.
AR Sco contains a rapidly spinning, burnt-out stellar remnant called a white dwarf, which lashes its neighbour – a red dwarf — with powerful beams of electrical particles and radiation, causing the entire system to brighten and fade dramatically twice every two minutes.
The latest research establishes that the lash of energy from AR Sco is a focused 'beam', emitting concentrated radiation in a single direction — much like a particle accelerator — something which is totally unique in the known universe.
AR Sco lies in the constellation Scorpius, 380 light-years from Earth, a close neighbour in astronomical terms. The white dwarf in AR Sco is the size of Earth but 200,000 times more massive, and is in a 3.6 hour orbit with a cool star one third the mass of the Sun.
With an electromagnetic field 100 million times more powerful than Earth, and spinning on a period just shy of two minutes, AR Sco produces lighthouse-like beams of radiation and particles, which lash across the face of the cool star, a red dwarf.
As the researchers previously discovered, this powerful light house effect accelerates electrons in the atmosphere of the red dwarf to close to the speed of light, an effect never observed before in similar types of binary stars. The red dwarf is thus powered by the kinetic energy of its spinning neighbour.
The distance between the two stars is around 1.4 million kilometres — which is three times the distance between the Moon and the Earth.
Professor Tom Marsh comments:
"The new data show that AR Sco's light is highly polarised, showing that the magnetic field controls the emission of the entire system, and a dead ringer for similar behaviour seen from the more traditional neutron star pulsars."
Professor Boris Gänsicke comments:
"AR Sco is like a gigantic dynamo: a magnet, size of the Earth, with a field that is ~10.000 stronger than any field we can produce in a laboratory, and it is rotating every two minutes. This generates an enormous electric current in the companion star, which then produces the variations in the light we detect."
The latest research, 'Polarimetric evidence of a white dwarf pulsar in the binary system AR Scorpii', is published in Nature Astronomy.
###
Media Contact
Luke Walton
[email protected]
44-782-454-0863
@warwicknewsroom
http://www.warwick.ac.uk
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag