Molecules that act as connected wheels can hold long molecular chains together to modify the properties of soft polymers.
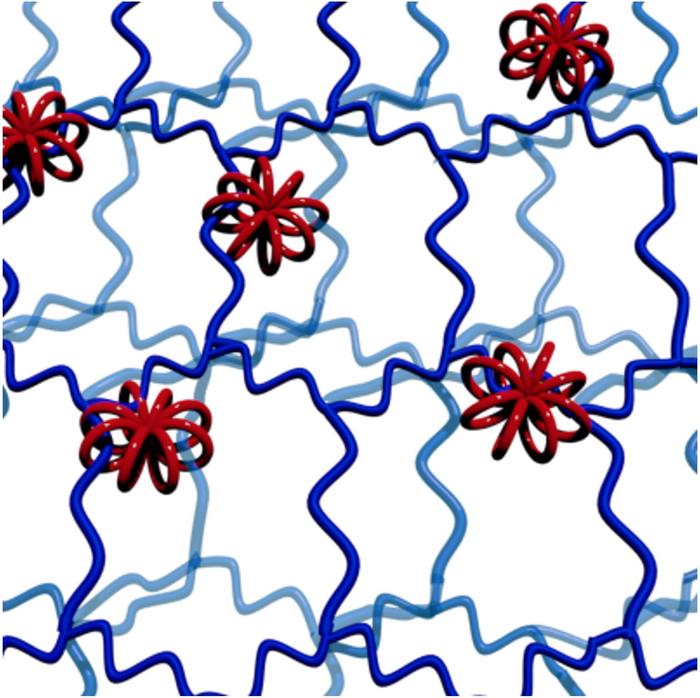
Credit: Minami Ebe, et al. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. July 17, 2023
Molecules that act as connected wheels can hold long molecular chains together to modify the properties of soft polymers.
Rotaxanes are interlocked molecular structures with a linear ‘axle’ molecule penetrating one or more cyclic ‘wheel’ molecules. Bulky groups at the end of the axle prevent the wheels from coming off. Now, researchers at Hokkaido University have taken the previous achievements of this technology a step further, making macro-rotaxanes that have multicyclic wheels interlocked with several high-molecular-weight axles. They report their innovation in the journal Angewandte Chemie International Edition.
Rotaxanes, initially regarded as intriguing chemical curiosities, are now being explored for a wide range of potential applications, ranging from next-generation polymers to ambitious possibilities in molecular computing, sensor technologies and drug delivery.
The Hokkaido University researchers, with collaborators elsewhere in Japan, are focusing their attention on making new network polymers, in which ring structures more complex than simple circles hold together different strands of long polymer chains.
“We think the multicyclic structures in these macro-rotaxanes could be useful as non-leaching additives, permanently retained in a polymer network by the way they hold onto several neighboring polymer chains,” says polymer chemist Professor Toshifumi Satoh of the Hokkaido team.
The 3D wheels act as a unique and highly flexible form of molecular crosslinks, allowing the wheels and the interlocked polymer strands much more freedom of movement than in conventionally cross-linked networks. Structural variations should allow fine control over the properties of soft materials to make them suitable for a variety of industrial and medical applications.
Other research groups have achieved some similar success with smaller molecular arrangements, but the advances at Hokkaido University move the field into the realm of larger molecules.
The researchers explored some of the possibilities of this significant new development in polymer chemistry using chemicals called polydimethylsiloxanes (PDMSs) to make the multicyclic rings. They were able to build different numbers of cyclic units with rings of different sizes. When combined with silicone polymer chains with short crosslinking agents, the multicyclic units became efficiently incorporated into a newly-forming extended, mixed and interlocked network.
“We explored some of the potential for making modified soft materials by measuring the damping performance of the networks, which is essentially the ability of a material to absorb and reduce vibrations,” says Satoh. “This revealed that our macro-rotaxanes achieved significant improvements in damping efficiency relative to conventional polymer networks.”
Satoh and his colleagues now plan to explore further possibilities that can be built on the proof-of-concept foundations laid by their current progress.
Journal
Angewandte Chemie International Edition
DOI
10.1002/anie.202304493
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
Not applicable
Article Title
Rotaxane Formation of Multicyclic Polydimethylsiloxane in a Silicone Network: A Step toward Constructing “Macro-Rotaxanes” from High-Molecular-Weight Axle and Wheel Components
Article Publication Date
17-Jul-2023




