Credit: Juha Lahnakoski
The brain works most efficiently when it can focus on a single task for a longer period of time.
Previous research shows that multitasking, which means performing several tasks at the same time, reduces productivity by as much as 40%. Now a group of researchers specialising in brain imaging has found that changing tasks too frequently interferes with brain activity. This may explain why the end result is worse than when a person focuses on one task at a time.
'We used functional magnetic resonance imaging to measure different brain areas of our research subjects while they watched short segments of the Star Wars, Indiana Jones and James Bond movies,' explains Aalto University Associate Professor Iiro Jääskeläinen.
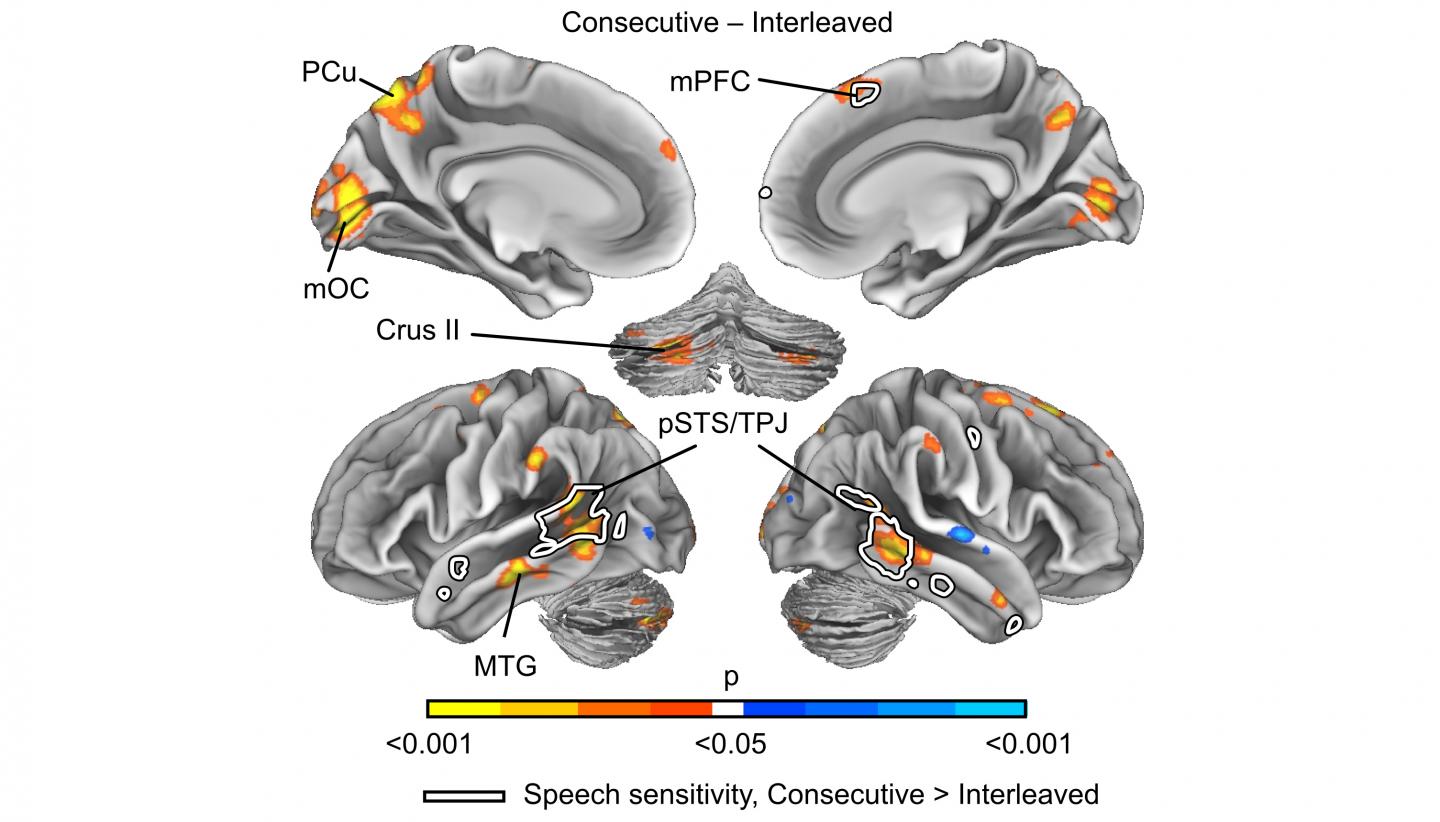
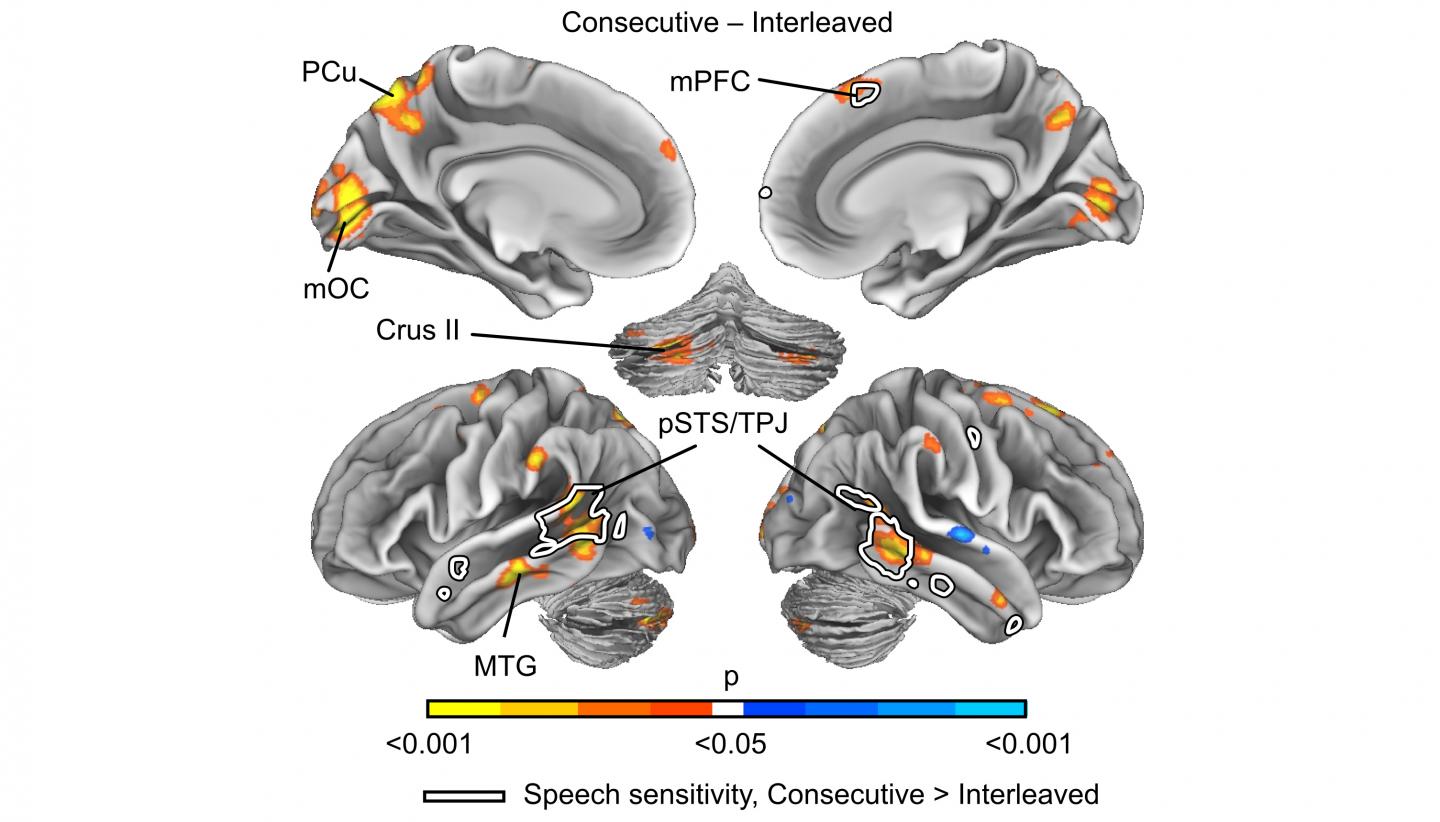
Cutting the films into segments of approximately 50 seconds fragmented their continuity. In the study, the subjects' brain areas functioned more smoothly when they watched the films in segments of 6.5 minutes. The posterior temporal and dorsomedial prefrontal cortices, the cerebellum and dorsal precuneus are the most important areas of the brain in terms of combining individual events into coherent event sequences. These areas of the brain make it possible to turn fragments into complete entities. According to the study, these brain regions work more efficiently when it can deal with one task at a time.
Inadequacy and overloading
Jääskeläinen recommends completing one task each day rather than working on a dozen of different tasks simultaneously.
'It's easy to fall into the trap of multitasking. In that case, it seems like there is little real progress and this leads to a feeling of inadequacy. Concentration decreases, which causes stress. Prolonged stress hinders thinking and memory,' says Jääskeläinen.
The neuroscientist also sees social media as a challenge.
'Social media is really nothing but multitasking, with several parallel plots and issues. You might end up reading the news or playing a game recommended by a friend. From the brain's perspective, social media only increases the load.'
###
In addition to Jääskeläinen, Juha Lahnakoski from Max Planck Institute, Mikko Sams from Aalto University and Lauri Nummenmaa from the University of Turku participated in the research.
More information:
Iiro Jääskeläinen
Aalto University
[email protected]
tel. +358 50 560 9503
Article: Neural mechanisms for integrating consecutive and interleaved natural events http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/hbm.23591/full
Video (intended for research group page only): https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B5pFkSAzmKTTOTlwN0VJXzFHSU0/view
Media Contact
Iiro Jääskeläinen
[email protected]
358-505-609-503
@aaltouniversity
http://www.aalto.fi/en/
############
Story Source: Materials provided by Scienmag