Credit: Tokyo Tech
Diabetes seldom occurs in newborns–a condition known as neonatal diabetes. But when it does, it’s mostly due to a mutation in a single gene such as the KCNJ11 or insulin (INS). This early-onset type of diabetes differs from type-1 diabetes in that it occurs within the first six months of life and can be either transient or permanent. Most of the mutations that underly this disease prevent the pancreas from producing sufficient insulin, which leads to high blood glucose levels or hyperglycemia.
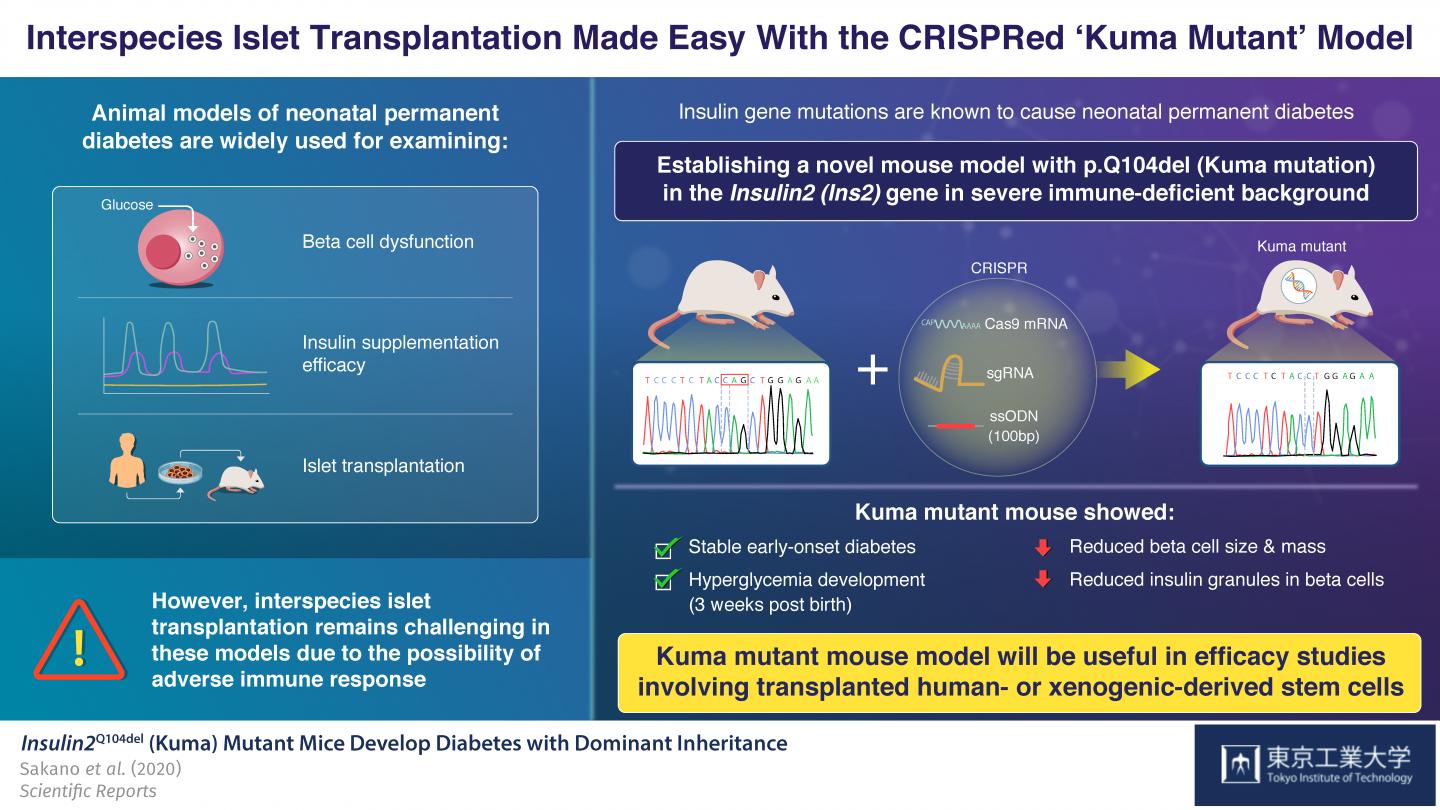
To understand what causes permanent neonatal diabetes and to find a cure, scientists often use mouse and pig models having Insulin2 (Ins2)C96Y gene mutations. These models develop permanent early-onset diabetes resembling neonatal diabetes. However, a major limitation of these models is that by using them, inter-species transplantation of pancreatic insulin-producing cells (pancreatic beta cells), called islet transplantation, cannot be evaluated, due to adverse immune system reactions characterizing such interspecies transplantation.
Now, in a paper published in Scientific Reports, scientists from Tokyo Tech describe how they established a new mouse model of permanent neonatal diabetes, which exhibits severe insulin-deficiency and beta-cell dysfunction in an immune deficient background. As Professor Shoen Kume, who led the study explains, “We wanted to create a mouse model that would allow us to evaluate the efficacy of transplanting human stem cell-derived or xenogeneic pancreatic beta cells into these mice without having to consider immune responses”
To achieve this goal, the scientists used the CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing technique to introduce a three base pair deletion in the Ins2 gene of a severely-immunodeficient BRJ mouse, that lacked mature T and B lymphocytes and natural killer (NK) cells. This mutation causes a Gln (Q) deletion (p.Q104del), hampering insulin production. The scientists named the mutation ‘Kuma mutation’.
Upon examining the Kuma mice as they aged, the scientists discovered that both male and female Kuma mutants developed hyperglycemia three weeks after their birth. They conjectured that this may be due to the low stability of the mutant insulin protein. The scientists also noted that these mice had markedly reduced beta-cell area, size, and mass, as well as a significantly decreased number and size of insulin granules within the beta cells. This meant that the mice could serve as a permanent neonatal diabetes model for islet transplantation.
To corroborate this, their treatment with insulin implants over four weeks successfully reversed their hyperglycemia.
Based on these findings, Prof Kume and his team believe that “the Kuma mutant can not only be used for molecular studies of the Insulin gene and beta cell dysfunction, but its immune-deficient background allows it to be an attractive model for studies examining the functionality of transplanted beta-cells generated from human- or xenogeneic-derived stem cells”.
Moreover, as the Kuma mutation is well conserved across different species, the same gene-editing approach can be applied to creating permanent neonatal diabetic models in other animal species, making advancement in the research on this disease condition a little bit easier.
###
Media Contact
Kazuhide Hasegawa
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.