Climate, tectonics and time combine to create powerful forces that craft the face of our planet. Add the gradual sculpting of the Earth’s surface by rivers and what to us seems solid as rock is constantly changing.
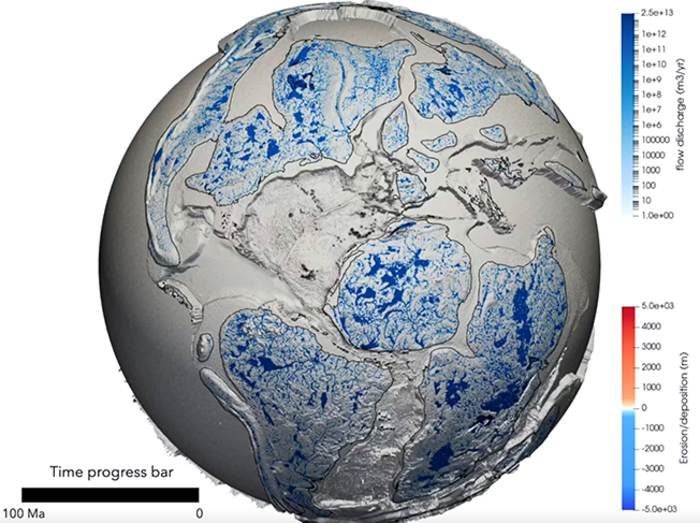
Credit: Dr Tristan Salles, The University of Sydney
Climate, tectonics and time combine to create powerful forces that craft the face of our planet. Add the gradual sculpting of the Earth’s surface by rivers and what to us seems solid as rock is constantly changing.
However, our understanding of this dynamic process has at best been patchy.
Scientists today have published new research revealing a detailed and dynamic model of the Earth’s surface over the past 100 million years.
Working with scientists in France, University of Sydney geoscientists have published this new model in the prestigious journal Science.
For the first time, it provides a high-resolution understanding of how today’s geophysical landscapes were created and how millions of tonnes of sediment have flowed to the oceans.
Lead author Dr Tristan Salles from the University of Sydney School of Geosciences, said: “To predict the future, we must understand the past. But our geological models have only provided a fragmented understanding of how our planet’s recent physical features formed.
“If you look for a continuous model of the interplay between river basins, global-scale erosion and sediment deposition at high resolution for the past 100 million years, it just doesn’t exist.
“So, this is a big advance. It’s not only a tool to help us investigate the past but will help scientists understand and predict the future, as well.”
Using a framework incorporating geodynamics, tectonic and climatic forces with surface processes, the scientific team has presented a new dynamic model of the past 100 million years at high resolution (down to 10 kilometres), broken into frames of a million years.
Second author Dr Laurent Husson from Institut des Sciences de la Terre in Grenoble, France, said: “This unprecedented high-resolution model of Earth’s recent past will equip geoscientists with a more complete and dynamic understanding of the Earth’s surface.
“Critically, it captures the dynamics of sediment transfer from the land to oceans in a way we have not previously been able to.”
Dr Salles said that understanding the flow of terrestrial sediment to marine environments is vital to comprehend present-day ocean chemistry.
“Given that ocean chemistry is changing rapidly due to human-induced climate change, having a more complete picture can assist our understanding of marine environments,” he said.
The model will allow scientists to test different theories as to how the Earth’s surface will respond to changing climate and tectonic forces.
Further, the research provides an improved model to understand how the transportation of Earth sediment regulates the planet’s carbon cycle over millions of years.
“Our findings will provide a dynamic and detailed background for scientists in other fields to prepare and test hypotheses, such as in biochemical cycles or in biological evolution.”
Authors Dr Salles, Dr Claire Mallard and PhD student Beatriz Hadler Boggiani are members of the EarthColab Group and Associate Professor Patrice Rey and Dr Sabin Zahirovic are part of the EarthByte Group. Both groups are in the School of Geosciences at the University of Sydney.
The research was undertaken in collaboration with French geoscientists from CNRS, France, Université Lyon and ENS Paris.
DOWNLOAD animated models of landscape dynamics and photos at this link.
AVAILABLE FOR INTERVIEW
Dr Tristan Salles | School of Geosciences | [email protected] | +61 451 462 502
(Speaks English and French)
Journal
Science
DOI
10.1126/science.add2541
Method of Research
Computational simulation/modeling
Article Title
Hundred million years of landscape dynamics from catchment to global scale
Article Publication Date
2-Mar-2023
COI Statement
This research was supported by National Computational Infrastructure of the Australian Government and the Artemis Computer at the University of Sydney. Researchers received funding from the Australian Research Council through the DARE Centre. There are no conflicts of interest.




