An analysis of 5.8 million authors across all scientific disciplines shows that the gender gap is closing, but there is still a long distance to go. The new research by John Ioannidis of the Meta-Research Innovation Center at Stanford (METRICs) at Stanford University, US, and colleagues, publishes November 21st in the open access journal PLOS Biology.
Credit: Anne-Lise Paris, (www.in-graphidi.com), PLOS, CC-BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
An analysis of 5.8 million authors across all scientific disciplines shows that the gender gap is closing, but there is still a long distance to go. The new research by John Ioannidis of the Meta-Research Innovation Center at Stanford (METRICs) at Stanford University, US, and colleagues, publishes November 21st in the open access journal PLOS Biology.
There is a strong gender gap in science which manifests itself in many ways. One of the most prominent ones is the relative representation of men and women among the scientists whose work receive the most attention in the scientific literature.
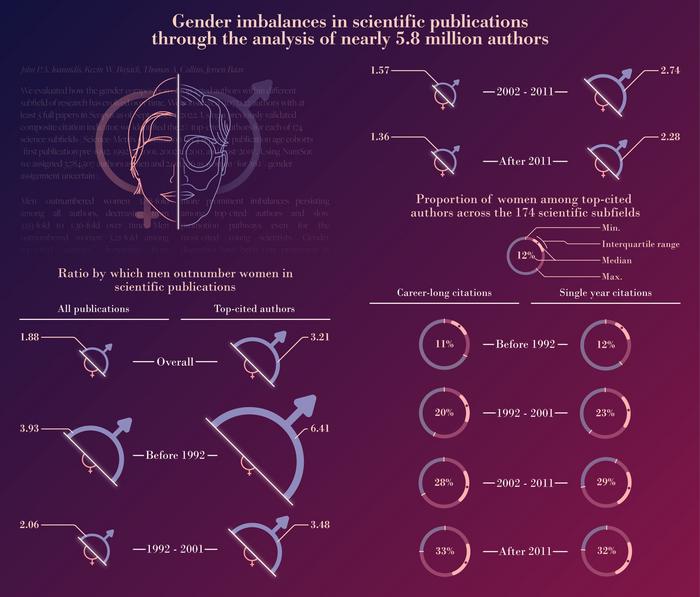
In the new study, the researchers evaluated the entire Scopus database, a database that includes papers across all scientific fields. The database included 5.8 million authors who could have their gender identity assigned with high certainty. Of those, 3.8 million were men and 2.0 million were women.
The researchers found that men outnumbered women 3.93 times among those authors who started publishing before 1992, but only 1.36 times among those authors who started publishing after 2011. However, when limited to the authors who had the highest impact (namely, those who were in the top 2% of their discipline based on a citation indicator), men outnumbered women 3.21 times among top-cited authors, decreasing from 6.41 times in the senior groups to 2.28 times in the youngest group who started publishing after 2011. In the youngest group, 32 of the 174 fields of science (18%) had at least as many women as men, or even more women than men, within the category of top-cited authors.
Gender imbalances in author numbers decreased sharply over time in both high-income countries (including the USA) and other countries, but the latter had little improvement in gender imbalances for top-cited authors. In random samples of 100 women and 100 men from the youngest group, in-depth assessment showed that most were working in academic environments as of 2023, but promotion to full professor was very rare. The authors argue that both gender imbalances and slow promotion pathways for the most gifted scientists, regardless of gender, need to be improved.
Ioannidis adds, “Our work documents substantial shrinkage over time of the inequalities between men and women in the top echelons of scientific citation impact, but there is substantial room for further improvements in most scientific fields.”
#####
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Biology: http://journals.plos.org/plosbiology/article?id=10.1371/journal.pbio.3002385
Citation: Ioannidis JPA, Boyack KW, Collins TA, Baas J (2023) Gender imbalances among top-cited scientists across scientific disciplines over time through the analysis of nearly 5.8 million authors. PLoS Biol 21(11): e3002385. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3002385
Author Countries: United States, the Netherlands
Funding: The work of JPAI is supported by an unrestricted gift from Sue and Bob O’ Donnell to Stanford University. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Journal
PLoS Biology
DOI
10.1371/journal.pbio.3002385
Method of Research
Meta-analysis
Subject of Research
People
COI Statement
Competing interests: METRICS has been funded by grants from the Laura and John Arnold Foundation (Arnold Ventures). TAC and JB are Elsevier employees and Elsevier runs Scopus which is the source of the data.




