Credit: NASA Earth Observatory
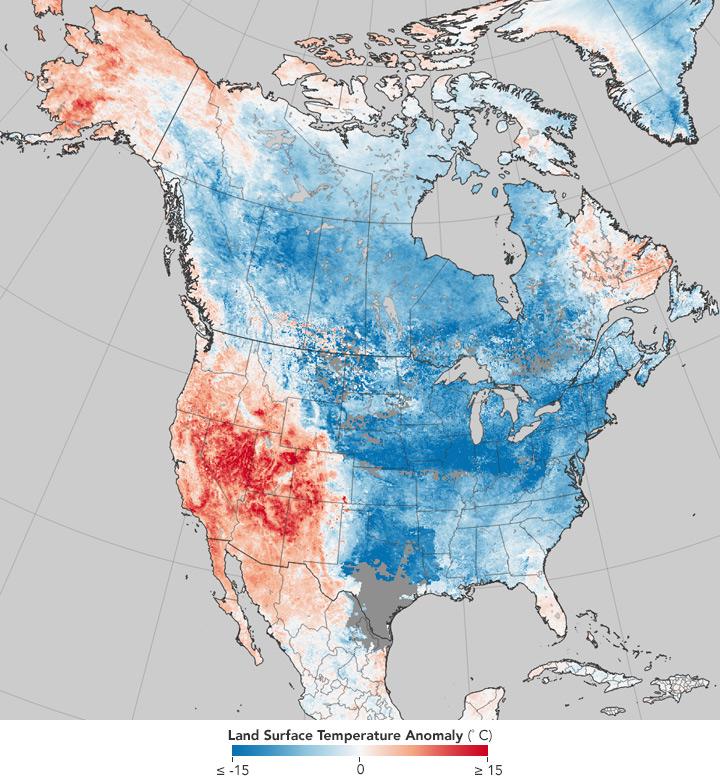
Persistent weather conditions, including dry and wet spells, generally have increased in the United States, perhaps due to rapid Arctic warming, according to a Rutgers-led study.
Persistent weather conditions can lead to weather extremes such as drought, heat waves, prolonged cold and storms that can cost millions of dollars in damage and disrupt societies and ecosystems, the study says.
Scientists at Rutgers University-New Brunswick and the University of Wisconsin-Madison examined daily precipitation data at 17 stations across the U.S., along with large upper-level circulation patterns over the eastern Pacific Ocean and North America.
Overall, dry and wet spells lasting four or more days occurred more frequently in recent decades, according to the study published online today in Geophysical Research Letters. The frequency of persistent large-scale circulation patterns over North America also increased when the Arctic was abnormally warm.
In recent decades, the Arctic has been warming at least twice as fast as the global average temperature, the study notes. The persistence of warm Arctic patterns has also increased, suggesting that long-duration weather conditions will occur more often as rapid Arctic warming continues, said lead author Jennifer Francis, a research professor in Rutgers' Department of Marine and Coastal Sciences.
"While we cannot say for sure that Arctic warming is the cause, we found that large-scale patterns with Arctic warming are becoming more frequent, and the frequency of long-duration weather conditions increases most for those patterns," said Francis, who works in the School of Environmental and Biological Sciences.
The results suggest that as the Arctic continues to warm and melt, it's likely that long-duration events will continue to occur more often, meaning that weather patterns – heat waves, droughts, cold spells and stormy conditions – will likely become more persistent, she said.
"When these conditions last a long time, they can become extreme events, as we've seen so often in recent years," she said. "Knowing which types of events will occur more often in which regions and under what background conditions – such as certain ocean temperature patterns – will help decision-makers plan for the future in terms of infrastructure improvements, agricultural practices, emergency preparedness and managed retreat from hazardous areas."
Future research will expand the analysis to other regions of the Northern Hemisphere, develop new metrics to find causal connections, and analyze projections to assess future risks from extreme weather events linked to persistent patterns, she said.
###
Study co-authors include Natasa Skific, research associate in Rutgers' Department of Marine and Coastal Sciences, and Stephen J. Vavrus at the University of Wisconsin-Madison.
Media Contact
Todd Bates
[email protected]
848-932-0550
@RutgersU
http://www.rutgers.edu
Original Source
https://news.rutgers.edu/more-persistent-weather-patterns-us-linked-arctic-warming/20180919#.W6KL72hKi70 http://dx.doi.org/10.1029/2018GL080252