Researchers at Wihuri Research Institute and University of Helsinki, Finland, in collaboration with scientists from Vanderbilt and Groningen Universities used recombinant gene transfer technologies to discover a fine-tuning mechanism that can be used to increase the density of blood vessels in adipose tissue. This prevented or even reversed the progression towards type 2 diabetes in animal models. The study was published by Cell Metabolism.
There are almost 400 million people suffering from type 2 diabetes across the globe and this number is expected to increase sharply over the next decades. As obesity is the major contributor to this growing problem, white adipose tissue is the first line of defense against the development of type 2 diabetes. A healthy white adipose tissue can store fat and thus prevent the detrimental effects of excessive fat accumulation in other key metabolic organs such as liver and skeletal muscle. This causes systemic inflammation and failure of insulin function to promote glucose uptake from blood to tissues.
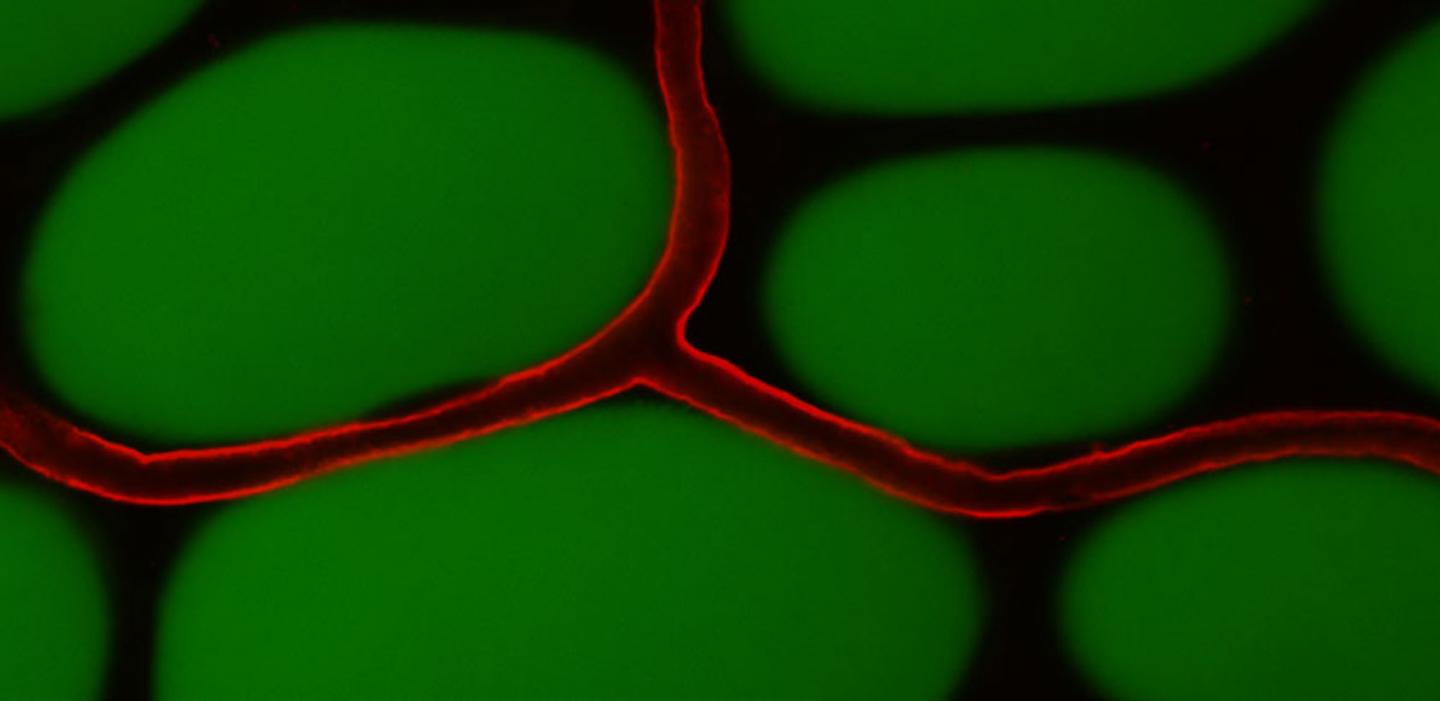
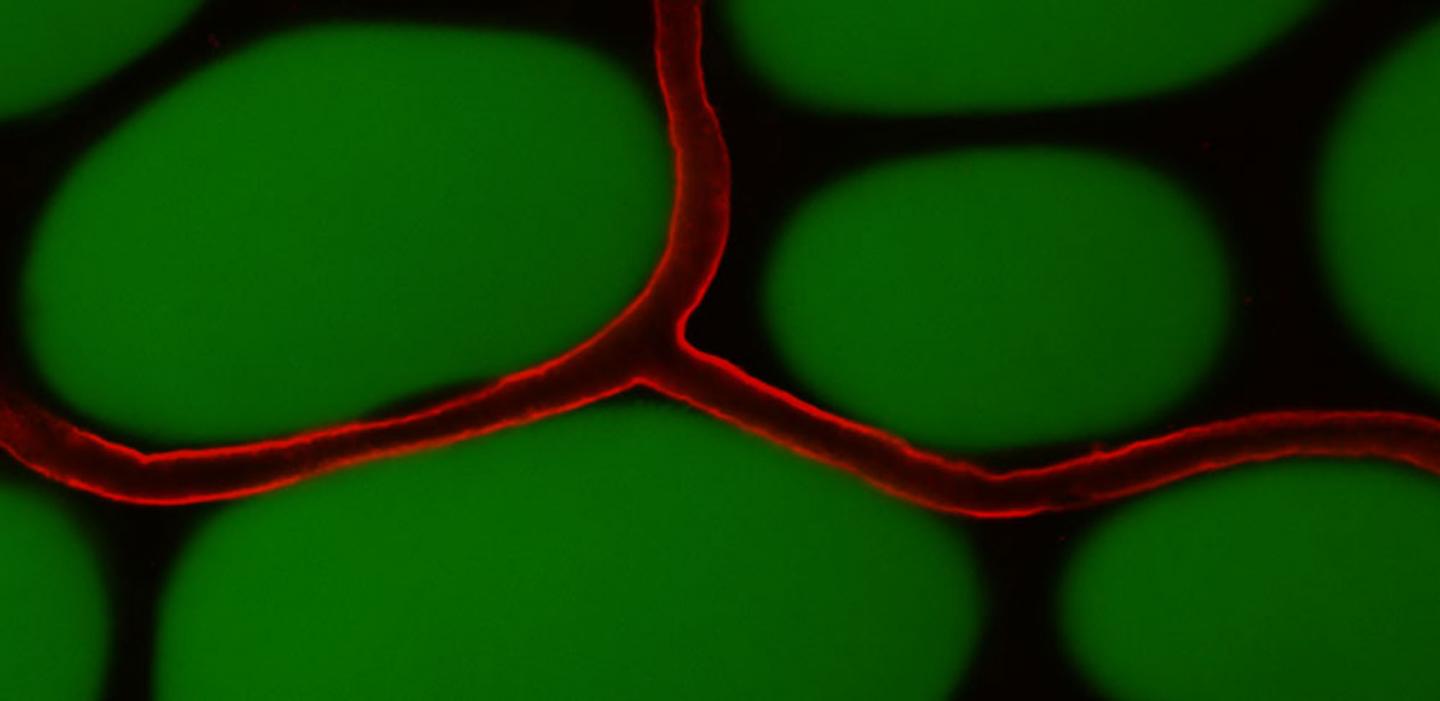
A Finnish group discovered that vascular endothelial growth factor B (VEGFB), can increase the density of adipose tissue vasculature in animal models. This resulted in a reduction of inflammation and improved insulin function in obese mice.
But VEGFB alone had only moderate effect on obesity and did not solve the problem of excessive fat accumulation in the body. Further investigations helped the researchers to decipher the molecular mechanisms behind these observations and to reveal a solution for this problem.
The research team showed that eliminating or blocking of the receptor, VEGFR1, which binds VEGFB, can provide additional benefit to the treatment of obesity and type 2 diabetes. The combined treatment had a more pronounced effect on the growth of adipose tissue vasculature, prevented the development of obesity, and restored metabolic balance in mice. This was achieved by activating the catabolic (breakdown) process in the adipose tissue.
This was a profound effect as white adipose tissue is an anabolic (buildup) tissue that typically serves as the primary long-term nutrient storage depot. The blood vessel growth stimulated by targeting the VEGFB/VEGFR1 molecular pathway induced the capacity of adipose tissue to convert nutrients, primarily glucose and fatty acids, into heat.
It is not known how blood vessels trigger this process but it is a promising therapeutic approach to increase basal metabolism and combat the global epidemic of obesity.
These discoveries have revealed a therapeutic potential of VEGFB/VEGFR1 pathway in the treatment of obesity and type 2 diabetes. Further research may lead to clinical trials for these conditions of immense significance to public health.
###
Media Contact
Dr. Marius Robciuc
[email protected]
358-294-125-525
@helsinkiuni
http://www.helsinki.fi/university/