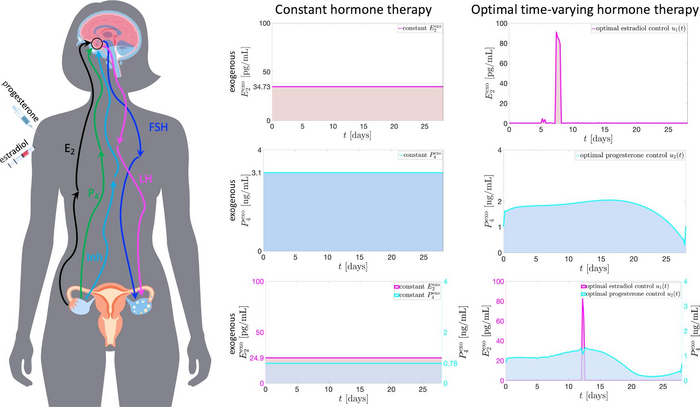
The dosage of hormones in common contraceptives could be reduced by as much as 92% and still effectively suppress ovulation, according to a computational model described this week in PLOS Computational Biology by Brenda Lyn A. Gavina, PhD student at the University of the Philippines Diliman, and her collaborators.
Credit: Gavina et al., 2023, PLOS Computational Biology, CC-BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/)
The dosage of hormones in common contraceptives could be reduced by as much as 92% and still effectively suppress ovulation, according to a computational model described this week in PLOS Computational Biology by Brenda Lyn A. Gavina, PhD student at the University of the Philippines Diliman, and her collaborators.
A normal menstrual cycle involves multiple phases which are regulated by the endocrine system and influenced by levels of various hormones. The most contraceptive approaches, including pills, injectables and implants, involve the administration of exogenous estrogen and/or progesterone to block ovulation— the phase of the cycle in which an egg is released into the uterus.
In the new study, researchers used data on hormone levels in 23 women aged 20 to 34 with normal menstrual cycles. The team developed computational models depicting the interactions between various hormone levels as well as the impacts of exogenous hormones.
The model provided evidence that it is possible to reduce the total dose by 92% in estrogen-only contraceptives, or the total dose by 43% in progesterone-only contraceptives, and still prevent ovulation. By combining estrogen and progesterone, the doses of each hormone could be reduced even further. In addition, the model showed the importance of timing the hormones during the cycle, pointing toward ways that exogenous estrogen and progesterone could be given during only certain phases of the menstrual cycle rather than at steady constant doses.
“These results may give clinicians insights into optimal dosing formulations and schedule of therapy that can suppress ovulation,” the authors say.
############
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS Computational Biology: https://journals.plos.org/ploscompbiol/article?id=10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010073
Citation: Gavina BLA, de los Reyes V AA, Olufsen MS, Lenhart S, Ottesen JT (2023) Toward an optimal contraception dosing strategy. PLoS Comput Biol 19(4): e1010073. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010073
Author Countries: Denmark, Philippines, Republic of Korea, USA
Funding: BLAG was supported by University of the Philippines Office of International Linkages, a Continuous Operational and Outcomes-based Partnership for Excellence in Research and Academic Training Enhancement (UP-OIL-COOPERATE) grant, and a Commission on Higher Education Faculty Development Program – II (CHED-FDP-II) scholarship. ADLRV acknowledges the support of the Institute of Mathematics, University of the Philippines Diliman and the Institute for Basic Science (IBS-R029-C3). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Journal
PLoS Computational Biology
DOI
10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010073
Method of Research
Computational simulation/modeling
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Toward an optimal contraception dosing strategy
COI Statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.




