The prevalence of pathogenic E. coli has meant the frequent misidentification of a similar bacterium of the Escherichia genus. E. albertii is an emerging zoonotic foodborne pathogen, first isolated in Bangladesh in 1991. Large-scale outbreaks of food poisoning caused by E. albertii have since been reported especially in Japan, causing severe symptoms in both children and adults.
Credit: Osaka Metropolitan University
The prevalence of pathogenic E. coli has meant the frequent misidentification of a similar bacterium of the Escherichia genus. E. albertii is an emerging zoonotic foodborne pathogen, first isolated in Bangladesh in 1991. Large-scale outbreaks of food poisoning caused by E. albertii have since been reported especially in Japan, causing severe symptoms in both children and adults.
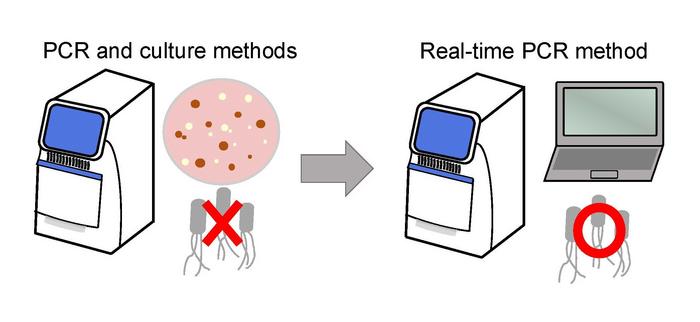
In the hopes of establishing a diagnostic method, a joint research group led by Professor Shinji Yamasaki and Dr. Sharda Prasad Awasthi, a specially appointed associate professor, from the Graduate School of Veterinary Science at Osaka Metropolitan University, have developed a way to detect E. albertii more accurately using a quantitative real-time PCR method.
Specimen examination using this technique showed that E. albertii survived in the human intestinal tract for approximately four weeks and continued to be found in feces. The identical genotype of the bacterial DNA of E. albertii that infected siblings also suggested that intrafamilial transmission may have occurred.
“These results and a novel real-time PCR developed in this study are expected to contribute not only to the selection of appropriate treatment for E. albertii gastroenteritis, but also to the elucidation of the source and route of infection,” Professor Yamasaki declared.
The findings were published in Heliyon.
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
Journal
Heliyon
DOI
10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30042
Method of Research
Experimental study
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
Detection of prolong excretion of Escherichia albertii in stool specimens of a 7-year-old child by a newly developed Eacdt gene-based quantitative real-time PCR method and molecular characterization of the isolates
Article Publication Date
27-Apr-2024
COI Statement
Shinji Yamasaki reports financial support was provided by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science. Shinji Yamasaki reports a relationship with Sakura Cooperation that includes: consulting or advisory. Shinji Yamasaki has patent pending for the Detection of Escherichia albertii. Other authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.




