Tsukuba, Japan – Amino acids are the basic building blocks of living organisms and typically occur in a configuration known as the L-form. However, there are a few exceptional examples of the structural mirror image of the L-form (known as the D-form) being present in animals. D-serine is a representative D-form amino acid and has crucial roles in mammals, but its role in non-mammals is unclear. Researchers from Japan recently uncovered a functional role of D-serine in a marine invertebrate, which may provide insight into the evolution of D-amino acid function in organisms.
Credit: University of Tsukuba
Tsukuba, Japan – Amino acids are the basic building blocks of living organisms and typically occur in a configuration known as the L-form. However, there are a few exceptional examples of the structural mirror image of the L-form (known as the D-form) being present in animals. D-serine is a representative D-form amino acid and has crucial roles in mammals, but its role in non-mammals is unclear. Researchers from Japan recently uncovered a functional role of D-serine in a marine invertebrate, which may provide insight into the evolution of D-amino acid function in organisms.
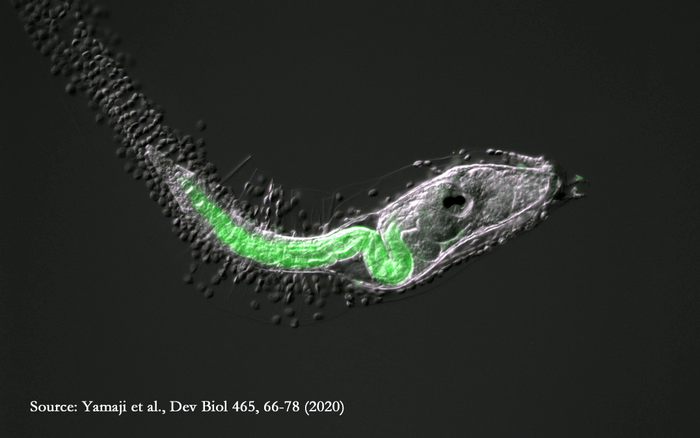
In a study published this month in Science Advances, a team led by the University of Tsukuba found that D-serine serves as a chemical signal that allows tissue migration in marine sea squirts when they lose their tails on transforming from tadpoles into their mature form. Their findings offer a broader understanding of the chemical signals that occur during the organism’s transformation.
In mammals, D-serine binds to an ion channel found in neurons called the N-methyl-D-aspartate type glutamate receptor (NMDAR) to regulate the transmission of messages in the brain. D-serine also plays a functional role in mammalian skin tissue. However, its role in non-mammals is less understood, something the researchers at the University of Tsukuba aimed to address.
“D-serine has been detected in organisms such as insects, nematodes, and molluscs,” says lead author of the study, Professor Yasunori Sasakura. “Its global presence in metazoans is reflective of the conserved presence of a protein that converts L-serine to its D-form, called a serine racemase.”
The team’s previous results implicated a serine racemase in the tail regression of tadpoles of the marine sea squirt Ciona. In this study, they sought to clarify the role of D-serine in this process and found that D-serine is responsible for forming a pocket in the Ciona epidermis that allows the tail to regress into the main body. This pocket was formed by D-serine binding to NMDAR in the epidermis, causing the release of fluid-filled vesicles.
“The results were striking,” explains Professor Sasakura. “We found that the epidermal vesicle release in Ciona is quite similar to a process occurring in mammalian skin, involving a flux of cations mediated through NMDARs.”
To evaluate what happened when D-serine was absent during Ciona tail regression, the research team created a mutation that omitted the protein responsible for making D-serine from L-serine. Ciona organisms lacking this protein failed to complete tail regression, whereas regular Ciona organisms were able to successfully complete the process.
“Our findings provide insight into how epidermal homeostasis is maintained in animals, contributing toward further evolutionary perspectives of D-amino acid function among metazoans,” says Sasakura.
###
This study was supported by grants from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science to HM (18K06888), TH (19H03204), and YS (16H04815, 19H03262), and the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science postdoctoral fellowship to GK (PE19712).
The article, “D-serine controls epidermal vesicle release via NMDA receptor allowing tissue migration during the metamorphosis of the chordate Ciona,” was published in Science Advances at DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abn3264
Journal
Science Advances
DOI
10.1126/sciadv.abn3264
Article Title
D-serine controls epidermal vesicle release via NMDA receptor allowing tissue migration during the metamorphosis of the chordate Ciona
Article Publication Date
11-Mar-2022




