Credit: ©Science China Press
Up to now, cancer is still one of the major diseases that threaten the survival of mankind, and it is difficult to cure clinically. In addition to single or combined surgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy, which are commonly used clinically, a number of promising therapeutic strategies have been recently put forward including immunotherapy and gene therapy, photothermal therapy (PTT), photodynamic therapy, and so on. However, these techniques usually rely on chemical and genetic drugs or exotic nanomaterials to actualize treatments, making them quite difficult or debatable for practical clinical applications in near future due to the uncertainties of potential biotoxicity and biohazards, and related genetic and ethical issues; and immunotherapy and gene therapy are complex and expensive. Therefore, the popularization of these techniques in clinical practice is restricted. Consequently, developing simple, green, efficient and cheap treatment method is an urgent need to combat cancer.
Hydrogen, owing to its small molecular size and physiological inertness, resistance to oxidation, and good gas diffusivity in-vivo, is considered as a kind of green and endogenous gas. It performs the eminent physiological/pathological regulation functions, which is widely used for the treatment many diseases, such as, Alzheimer’s disease, arthritis, diabetes and especially cancer. As early as 1975, researchers have applied the antioxidation of H2 to treat skin squamous cell carcinoma, but it requires using diving medical equipment to provide high pressure H2 which is restricted for clinic tumor therapy applications, how to produce H2 non-invasively and sufficiently without using nanomaterials and how to realize H2 releasing on demand in vivo are two huge challenges facing for the H2 therapy of cancers.
Acupuncture is a traditional and unique minimally-invasive method to treat diseases in China. It is quite effective to treat systemic diseases, especially for arthritis, cervical spondylopathy, psoatic strain and so on. But applying it to the treatment of major diseases, such as cancers is still a great challenge.
In a new research article published in the Beijing-based National Science Review, scientists at the State Key Laboratory of Electroanalytical Chemistry, Changchun Institute of Applied Chemistry, Chinese Academy of Sciences, China, and at School of Public Health, Jilin University, Changchun, China present the latest advances a green, efficient and precise hydrogen therapy of cancer based on in-vivo electrochemistry. Co-authors Guo-Hua Qi, Bo Wang, Xiangfu Song, Haijuan Li and Yong-dong Jin report the hydrogen cancer therapy in vivo with electrochemical. They have summarized the development of hydrogen in the treatment of cancer and the key problems limiting its development of clinical application.
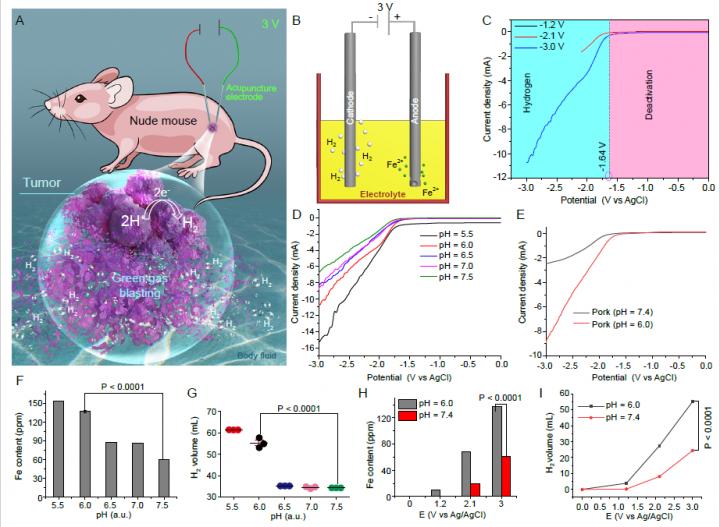
These scientists have developed a simple and precise cancer therapy approach based on selective electrochemical generation of H2 in tumor region, termed in-vivo H2 generation electrochemotherapy (H2-ECT) by innovative combined use of traditional Chinese acupuncture Fe needle (electrode) and in-vivo electrochemistry. The H2-ECT method enables large-scale tumor therapy by applying gas diffusion effect, avoiding the shortcoming of limited effective area for classic electrochemical reactions. Moreover, due to the puncture positioning and acidic tumor microenvironment (compared to normal tissue), the method provides ideal selectivity and targeting to precisely kill tumors with minimal damage to normal tissue, which is very promising for potential clinic applications. The effectiveness of the method has been demonstrated by successful and fast treatment of glioma and breast cancers in mice in this study. The cost of cancer therapy is very low and less than 1 $ for each treatment.
Scientifically, a green and conceptually new in-vivo H2 generation electrochemotherapy (H2-ECT) of tumor has been developed. Prof. Yongdong Jin said that in a broader perspective, the H2-ECT provides a reliable method for the treatment of cancer and solves the heavy economic burden of cancer therapy bring to the family by high cost, so that it is easily popularized in poor country.
###
This research was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the Instrument Developing Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
See the article:
Guohua Qi, Bo Wang, Xiangfu Song, Haijuan Li and Yongdong Jin
A green, efficient and precise hydrogen therapy of cancer based on in-vivo electrochemistry
Natl Sci Rev, doi: 10.1093/nsr/nwz199
https:/
The National Science Review is the first comprehensive scholarly journal released in English in China that is aimed at linking the country’s rapidly advancing community of scientists with the global frontiers of science and technology. The journal also aims to shine a worldwide spotlight on scientific research advances across China.
Media Contact
Yongdong Jin
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




